Mitosis – 3B Scientific Cell Division I Chart, Mitosis User Manual
Page 3
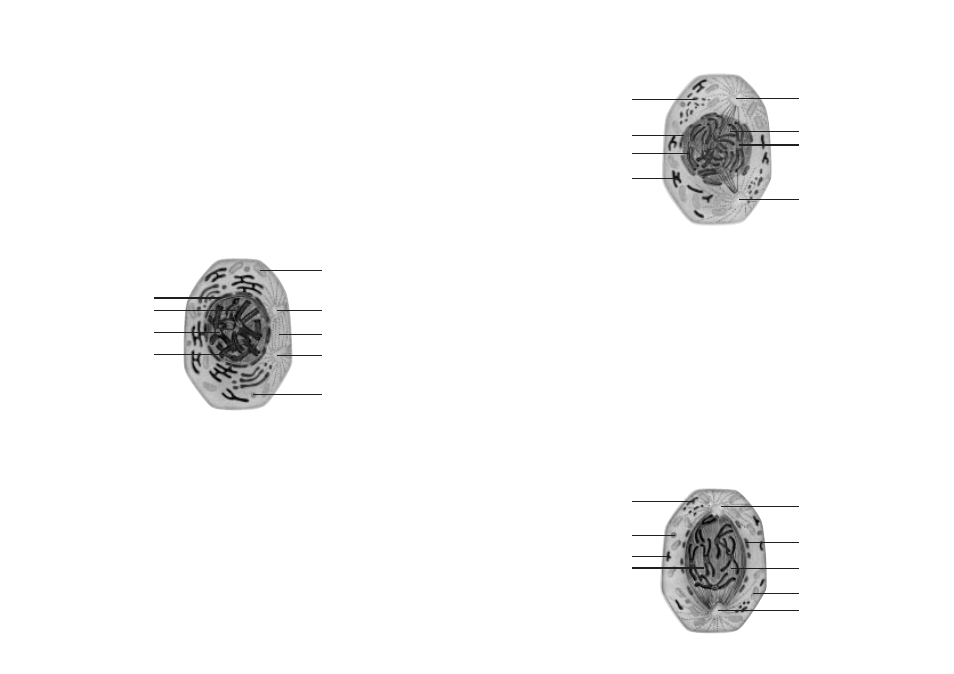
2. Prophase
The cell prepares for division and abandons its functions. The cytoplasm becomes less glutinous as the
stabilizing microtubules are broken down. The permeability of the cell surface is increased in order to
allow the intake of liquid from the surroundings. The microtubular complex, the basis of the cytoskeleton,
dissolves.
The nuclear membrane (1) and the nucleolus (2) also begin to dissolve. In the nucleus, the DNA begins to
condense and form precisely defined chromosomes. Each chromosome has been replicated in the prece-
ding S phase and now consists of two sister chromatids (3). Each of these sister chromatids contains a spe-
cific DNA sequence, the so-called centromere (4), which is in charge of the separation of the daughter
cells.
The pairs of centrioles (5), which were duplicated in the interphase, begin to move away from one ano-
ther in the direction of the two cell poles. They form the so-called central spindle (6) between themselves,
which consists of many microtubules. The mitochondria (7) and lysosomes (8) present in this area are
pushed aside.
3. Early Prometaphase
In the early prometaphase the nucleolus dissolves and the nuclear membrane dissolves into membrane
vesicles (1). The chromosomes (2) inside the nucleus can be clearly seen.
The two centrioles (3) continue on their path towards the poles. The microtubules (4) of the central
spindle, which were so far located outside the nucleus, can now penetrate into the area of the nucleus
and attach to the kinetochores (5) located in the middle of each duplicated chromosome. The kine-
tochores are protein complexes, which have formed for this purpose at the centromeres.
The endoplasmic reticulum (6) and the Golgi complex (7) begin to dissolve.
English
Mitosis
4. Later Prometaphase
Now the nuclear membrane (1) has dissolved almost completely and the centriole pairs (2) have reached
the two poles of the cell opposite each other. The microtubules (3) of the central spindle begin to align
the chromosomes (4) which are connected to them.
The mitochondria (5) and lysosomes (6) that were pushed aside line up evenly within the cytoplasm
again.
The endoplasmic reticulum (7) and the Golgi complex (8) are almost completely dissolved now.
Mitosis
English
1
2
3
5
6
5
8
7
4
1
2
6
7
3
4
5
3
8
2
1
3
5
2
6
7
4
