3B Scientific Air Cushion Plate User Manual
Page 20
Physical Experiments on the Air-Cushion Table
20
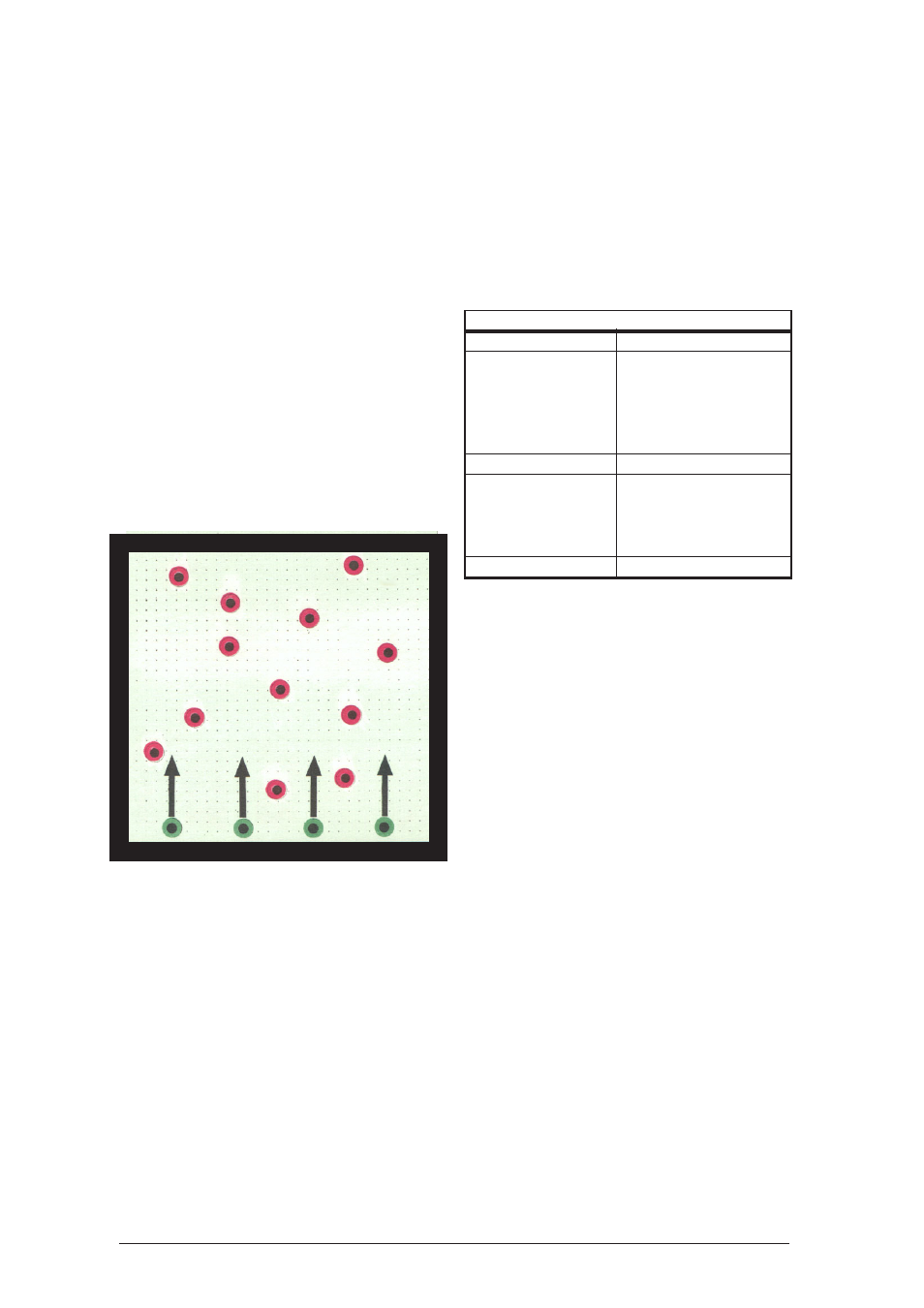
attach the magnetic barriers and spread the red
hover discs evenly on the experiment surface.
Provide an airflow just ensuring that all hover
discs lift off. This keeps the mean velocity of the
red discs low. Shortly afterwards, make the 4
green hover discs shoot between the red ones at
the highest possible speed. This can be done in
quick succession from one corner, using the
pointer to hold each hover disc directly in the
corner and then quickly releasing it.
It is also possible to press all 4 hover discs against
a barrier at the same time, holding them with the
fingers and then releasing them so that they hit
the red hover discs at high speed.
Result:
The green hover discs shooting in at high speed
cause a noticeable increase of the mean velocity
of the red hover discs.
Interpretation:
When supplying energy to a gas, its temperature
will rise. The energy supply can be interpreted as
shooting in of particles with high velocity, mixing
with a gas of higher temperature or heating.
Note:
Energy can also be supplied by repeatedly open-
ing the impulse valve for a short time. To ensure
that the hover discs will float safely even when
the valve is opened, a stronger airflow will be
necessary.
To repeat the experiment, slowly reduce the air-
flow until the motions stop and then return to the
original setting.
2.1.10
Form and Volume Properties of Gases
Components:
Air-cushion table with fan
Overhead projector
Magnetic barrier, long
2 Pieces
Magnetic barrier, short
2 Pieces
Magnetic piston
l Piece
Hover disc, green
12 Pieces
Model simulation
Real Object
Model
Vessel containing
Experiment surface of
the gas
the air-cushion table
surrounded by the
magnetic barriers and
the magnetic piston
Walls of the vessel
Magnetic barriers
Piston to change the
Magnetic piston
form and volume of
the area available
for the gas
Gas molecules
Hover disc
How to proceed:
Align the air-cushion table horizontally and at-
tach the magnetic barriers. Attach the magnetic
piston to divide the experiment surface in two
halves. Closely arrange the hover discs in one
half so that the spaces between them are not much
more than 1 cm.
The fan is turned up to a setting in which all hover
discs are sure to lift off. The area available for
the hover discs is increased by quickly removing
the piston.
The piston is placed back onto the experiment
surface near a barrier and its rod is moved back
and forth to the right and left so that the shape of
the experiment surface available for the hover
discs changes.
Observe the reaction of the hover discs to the
change in area in both cases.
Result:
In both experiments, the hover discs completely
fill out the available area. They are quickly dis-
persed across the entire area.
