Applications information – Rainbow Electronics MAX944 User Manual
Page 8
MAX941/MAX942/MAX944
Output Stage Circuitry
The MAX941/MAX942/MAX944 contain a current-driven
output stage as shown in Figure 4. During an output
transition, I
SOURCE
or I
SINK
is pushed or pulled to the
output pin. The output source or sink current is high
during the transition, creating a rapid slew rate. Once
the output voltage reaches V
OH
or V
OL
, the source or
sink current decreases to a small value, capable of
maintaining the V
OH
or V
OL
static condition. This signifi-
cant decrease in current conserves power after an out-
put transition has occurred.
One consequence of a current-driven output stage is a
linear dependence between the slew rate and the load
capacitance. A heavy capacitive load will slow down a
voltage output transition. This can be useful in noise-
sensitive applications where fast edges may cause
interference.
__________Applications Information
Circuit Layout and Bypassing
The high gain bandwidth of the MAX941/MAX942/
MAX944 requires design precautions to realize the
comparators’ full high-speed capability. The recom-
mended precautions are:
1) Use a printed circuit board with a good, unbro-
ken, low-inductance ground plane.
2) Place a decoupling capacitor (a 0.1µF ceramic
capacitor is a good choice) as close to V+ as
possible.
3) Pay close attention to the decoupling capacitor’s
bandwidth, keeping leads short.
4) On the inputs and outputs, keep lead lengths
short to avoid unwanted parasitic feedback
around the comparators.
5) Solder the device directly to the printed circuit
board instead of using a socket.
High-Speed, Low-Power, 3V/5V, Rail-to-Rail,
Single-Supply Comparators
8
_______________________________________________________________________________________
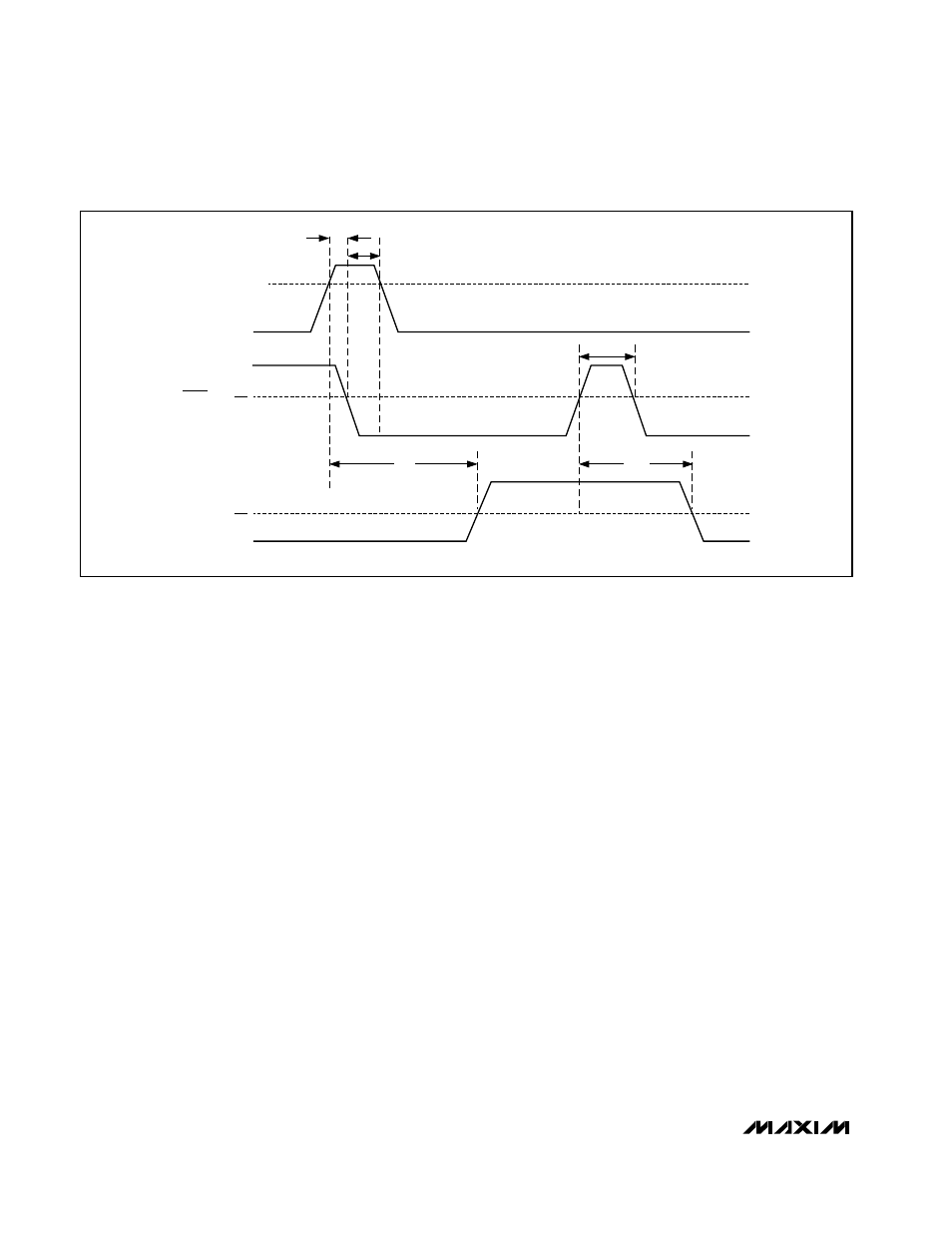
V
OH
t
LPW
OUT
t
LPD
t
PD
V+
0
V+
0
V+
2
V+
2
V
OL
LATCH
DIFFERENTIAL
INPUT
VOLTAGE
V
OS
t
H
t
S
Figure 2. MAX941 Timing Diagram with Latch Operator
