Applications information, Using a potentiometer to adjust the output voltage, Controlling the lcd using pok and llc cd do on n – Rainbow Electronics MAX686 User Manual
Page 13
Feed-Forward Capacitors
Parallel a feed-forward capacitor (C
F
) across R2 to com-
pensate the feedback loop and ensure stability (Figure
4). Use values up to 100pF for most applications.
Choose the lowest capacitor value that ensures stability;
high capacitance values may degrade line regulation.
Applications Information
Using a Potentiometer to Adjust the
Output Voltage
The output can be adjusted with a potentiometer
instead of the DAC (Figure 5). Choose R
POT
= 100k
Ω
and connect it between REF and GND. Connect R3 to
the potentiometer’s wiper instead of to DACOUT. Use
the same design equations for adjusting the output volt-
age with the DAC.
Controlling the LCD Using
POK and
LLC
CD
DO
ON
N
When the voltage at POK is greater than 1.125V (typical),
the open-drain LCDON output pulls low. LCDON can
withstand up to 27.5V to control an external PNP transis-
tor to switch on the MAX686’s positive output (Figures 6
and 7). A PFET can also be used, but a resistor-divider
must be used in conjunction with it, so that the PFET does
not exceed its V
GS
rating. Three useful applications of
this feature are as follows:
•
An off-switch driver to ensure that a positive boosted
output goes to 0V during shutdown.
Connect POK to
SHDN. Without this switch, the positive output falls to
one diode drop below the input voltage (V
IN
) in shut-
down. LCDON is not needed for negative outputs,
which already fall to 0V in shutdown.
•
An input-sensing cutoff for positive outputs
. Connect
POK to a voltage divider to sense the input voltage.
The output switches on only when the input reaches
the set level (Figure 6).
•
An output-sensing cutoff for positive outputs.
Connect
POK to the feedback voltage divider to sense the out-
put voltage. The output switches on only when it
reaches 90% of the set voltage (Figure 7).
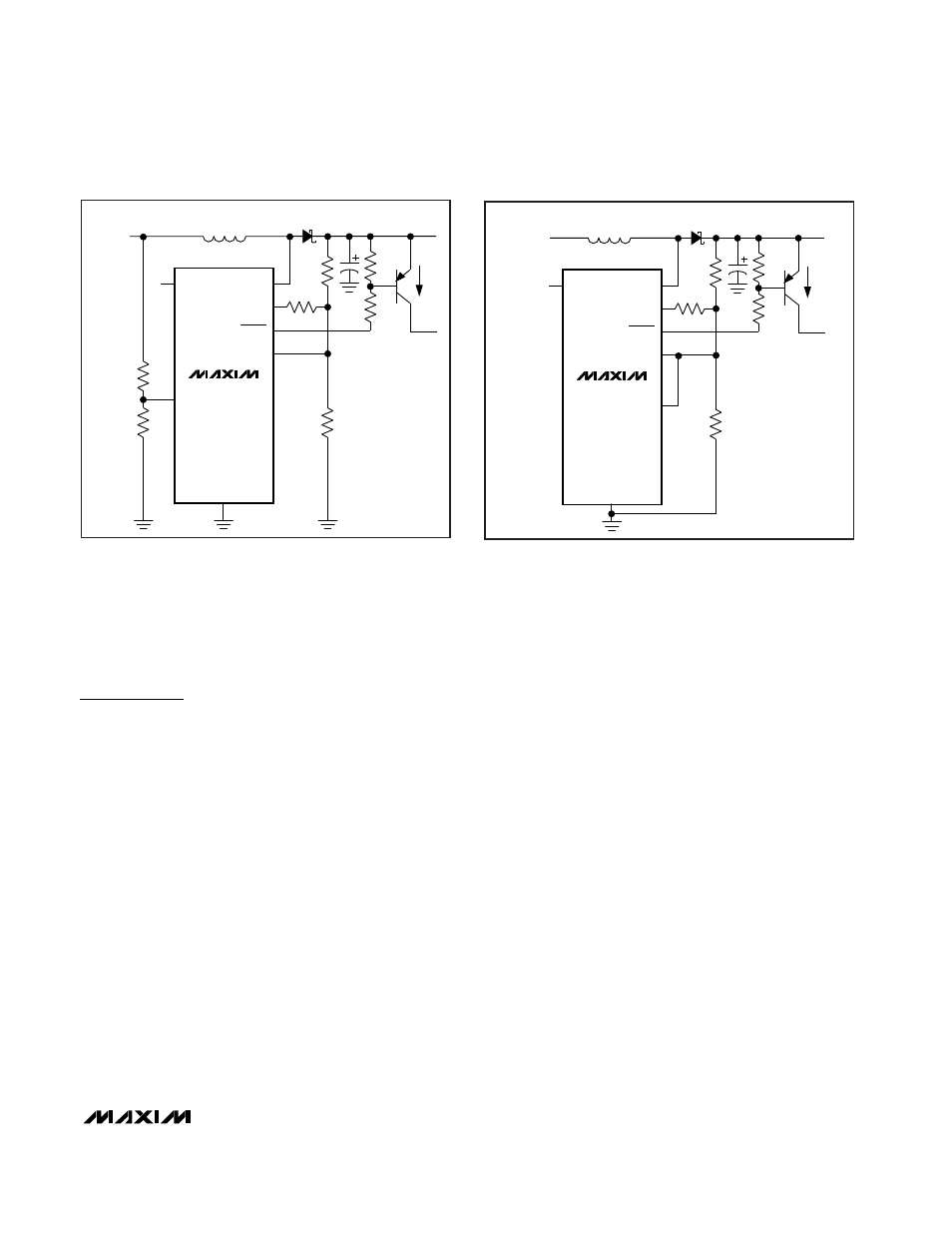
For positive output voltage sensing, connect POK
directly to FB to monitor the output voltage (Figure 7).
The POK threshold is 10% less than the set voltage at
FB. Therefore, when the output voltage drops 10%
below its set value, the POK circuit turns off the external
PNP transistor, disconnecting the load.
For input voltage sensing, a resistor-divider (R4-R5,
Figure 6) from VIN to POK controls the open-drain out-
put LCDON, which pulls low when V
POK
> 1.125V.
Choose R5 = 100k
Ω
. For example, if the minimum bat-
tery voltage is 5.3V, then determine R4 as follows:
R4 = R5 x [(V
IN
/ V
POK
) - 1]
= 100k x [(5.3 / 1.125) -1] = 371k
Ω
LCDON typically drives a low-cost PNP transistor (such
as a 2N2907 or equivalent), switching a positive VOUT to
the LCD. Choose a PNP with low V
CESAT
at the required
load current. R7 limits the base current in the PNP, and
MAX686
DAC-Controlled Boost/Inverter
LCD Bias Supply with Internal Switch
______________________________________________________________________________________
13
MAX686
V
CC
V
OUTSW
V
OUT
I
LCD
POSITIVE
OUTPUT
VOLTAGE
V
IN
= 0.8V
TO 27.5V
POK
GND
R4
R5
LX
DACOUT
LCDON
FB
R6
R2
22
µ
H
R1
R3
MBR0530L
R7
Figure 6. Using the POK for Input Voltage Monitoring
MAX686
V
CC
V
OUTSW
V
OUT
I
LCD
POSITIVE
OUTPUT
VOLTAGE
V
IN
= 0.8V
TO 27.5V
GND
LX
R2
R1
R3
DACOUT
MBR0530L
LCDON
FB
POK
R6
R7
22
µ
H
Figure 7. Using the POK for Output Voltage Monitoring
