Rainbow Electronics MAX2038 User Manual
Page 21
MAX2038
Ultrasound VGA Integrated
with CW Octal Mixer
______________________________________________________________________________________
21
CW Mixer Output Summation
The maximum differential current output is typically
3mA
P-P
and the mixer output compliance voltage
ranges from 4.75V to 12V per mixer channel. The mixer
common-mode current in each of the differential mixer
outputs is typically 3.25mA. The total summed current
would equal N x 3.25mA in each of the 115
Ω load
resistors (where N = number of channels). In this case,
the quiescent output voltage at +V
SUM
and -V
SUM
out-
puts would be 11V - (N x 3.25mA x 115) = 11V - (8 x
3.25mA x 115) = 8.05V. The voltage swing at each out-
put, with one channel driven at max output current (dif-
ferential 3mA
P-P
) while the other channels are not
driven, would be 1.5mA
P-P
x 115
Ω or 174mV
P-P
and
the differential voltage would be 348mV
P-P
. The voltage
compliance range is defined as the valid range for
+V
SUM
and -V
SUM
in this example.
External Compensation
External compensation is required for bypassing inter-
nal biasing circuitry. Connect as close as possible a
4.7µF capacitor from EXT_C1, EXT_C2, and EXT_C3
(pins 13, 14, 15) to ground.
External Bias Resistor
An external resistor at EXT_RES is required to set the
bias for the internal biasing circuitry. Connect, as close
as possible, a 7.5k
Ω (0.1%) resistor from EXT_RES (pin
38) to ground.
Analog Input and Output Coupling
In typical applications, the MAX2038 is being driven from
a low-noise amplifier (such as the MAX2034) and the
VGA is typically driving a discrete differential anti-alias fil-
ter into an ADC (such as the MAX1436 octal ADC). The
differential input impedance of the MAX2038 is typically
240
Ω. The differential outputs of the VGA are capable of
driving a differential load capacitance to GND at each of
the VGA differential outputs of 60pF, and differential
capacitance across the VGA outputs is 10pF, R
L
=
1k
Ω. The differential outputs have a common-mode
bias of approximately 3.75V. AC-couple these differen-
tial outputs if the next stage has a different common-
mode input range.
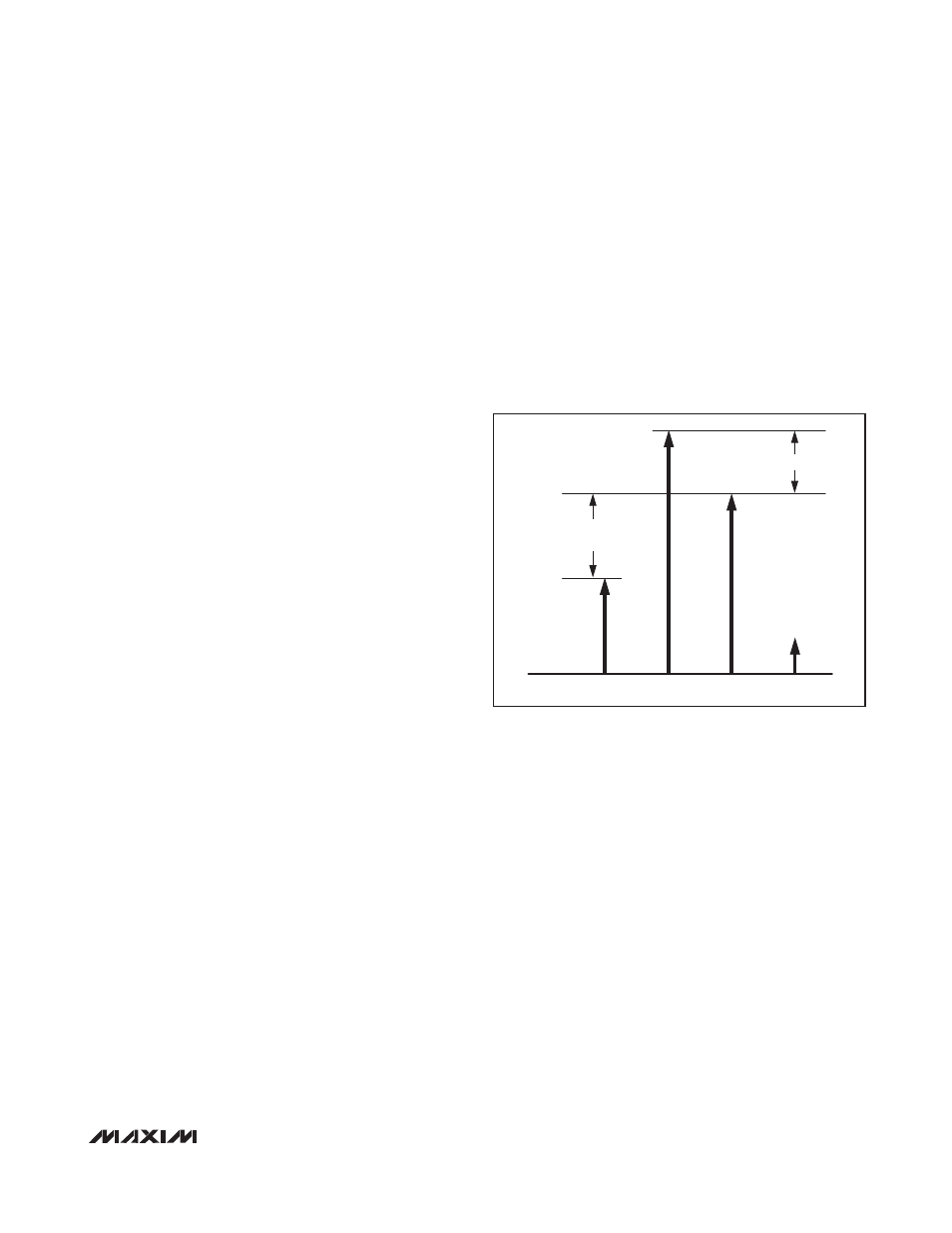
Ultrasound-Specific IMD3 Specification
Unlike typical communications specifications, the two
input tones are not equal in magnitude for the ultra-
sound-specific IMD3 two-tone specification. In this
measurement, f
1
represents reflections from tissue and
f
2
represents reflections from blood. The latter reflec-
tions are typically 25dB lower in magnitude, and hence
the measurement is defined with one input tone 25dB
lower than the other. The IMD3 product of interest (f
1
-
(f
2
- f
1
)) presents itself as an undesired Doppler error
signal in ultrasound applications. See Figure 6.
Board Layout
The pin configuration of the MAX2038 is optimized to
facilitate a very compact physical layout of the device
and its associated discrete components. A typical
application for this device might incorporate several
devices in close proximity to handle multiple channels
of signal processing.
The exposed pad (EP) of the MAX2038’s TQFP-EP
package provides a low thermal-resistance path to the
die. It is important that the PCB on which the MAX2038
is mounted be designed to conduct heat from the EP.
In addition, provide the EP with a low-inductance path
to electrical ground. The EP MUST be soldered to a
ground plane on the PCB, either directly or through an
array of plated via holes.
-25dB
ULTRASOUND
IMD3
f
1
- (f
2
- f
1
)
f
2
+ (f
2
- f
1
)
f
1
f
2
Figure 6. Ultrasound IMD3 Measurement Technique
