Table 2. output voltage adjustment settings, Table 3. lg pin adjustment settings – Rainbow Electronics MAX1638 User Manual
Page 13
MAX1638
High-Speed Step-Down Controller with
Synchronous Rectification for CPU Power
______________________________________________________________________________________
13
Specifying the Inductor
Three key inductor parameters must be specified:
inductance value (L), peak current (I
PEAK
), and DC
resistance (R
DC
). The following equation includes a
constant LIR, which is the ratio of inductor peak-to-
peak AC current to DC load current. Typically LIR can
be between 0.1 to 0.5. A higher LIR value allows for
smaller inductors and better transient response, but
results in higher losses and output ripple. A good com-
promise between size and loss is a 30% ripple current
to load current ratio (LIR = 0.30), which corresponds to
a peak inductor current 1.15 times higher than the DC
load current.
where f is the switching frequency, between 300kHz and
1MHz; I
OUT
is the maximum DC load current; and LIR is
the ratio of AC to DC inductor current (typically 0.3). The
exact inductor value is not critical and can be adjusted to
make trade-offs among size, transient response, cost,
and efficiency. Although lower inductor values minimize
size and cost, they also reduce efficiency due to higher
peak currents. In general, higher inductor values
increase efficiency, but at some point resistive losses
due to extra turns of wire exceed the benefit gained from
lower AC current levels. Load-transient response can be
adversely affected by high inductor values, especially at
low (V
IN
- V
OUT
) differentials.
The peak inductor current at full load is 1.15 x I
OUT
if the
previous equation is used; otherwise, the peak current
can be calculated using the following equation:
The inductor’s DC resistance is a key parameter for effi-
cient performance, and should be less than the current-
sense resistor value.
Calculating the Current-Sense
Resistor Value
Calculate the current-sense resistor value according to
the worst-case minimum current-limit threshold voltage
(from the
Electrical Characteristics
) and the peak
inductor current required to service the maximum load.
I
I
V
V
V
f
x L x V
PEAK
OUT
OUT
IN MAX
OUT
OSC
IN MAX
(
)
(
)
=
+
−
(
)
2
L
V
V
V
V
x f
x I
x LIR
OUT
IN MAX
OUT
IN MAX
OSC
OUT
(
)
(
)
=
−
(
)
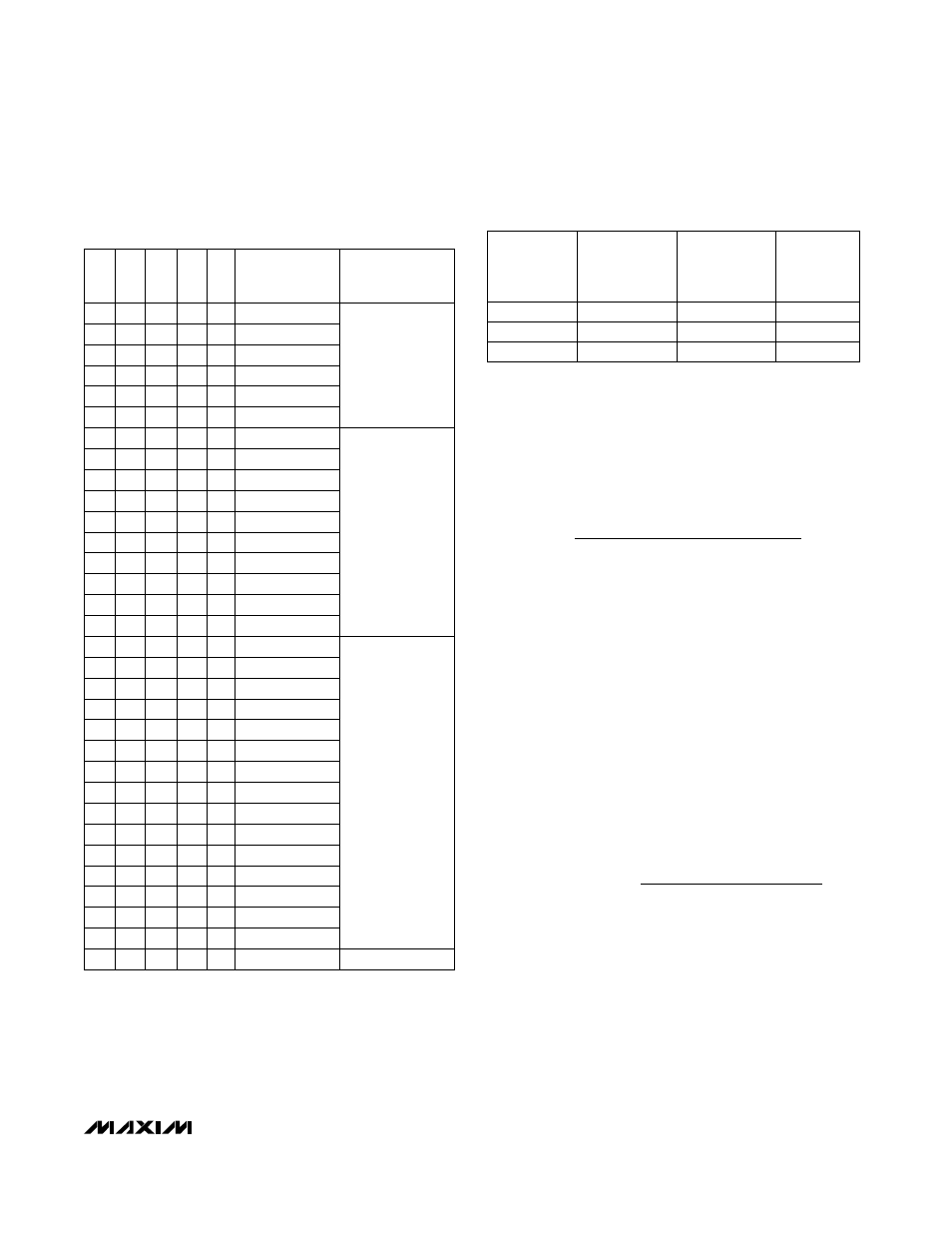
Table 2. Output Voltage Adjustment
Settings
D3
0
D1
0
D2
0
D0
0
OUTPUT
VOLTAGE
(V)
2.050
COMPATIBILITY
0
0
D4
0
1
2.000
0
0
1
0
0
1.950
0
1
0
1
1.900
0
0
0
0
0
1
0
1.850
0
0
1
1
1.800
Intel-compatible
DAC codes
0
0
1
1
0
1.750
0
1
1
1
1.700
0
0
0
1
0
0
0
1.650
1
0
0
1
1.600
0
1
1
0
0
1.550
1
1
0
1
1.500
0
0
0
1
0
1
0
1.450
1
0
1
1
1.400
0
1
1
1
0
1.350
1
1
1
1
1.300
Continuation of
50mV increment
to 1.3V
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
3.500
0
0
0
1
3.400
1
0
1
0
0
3.300
0
1
0
1
3.200
1
1
1
0
0
1
0
3.100
0
0
1
1
3.000
1
0
1
1
0
2.900
0
1
1
1
2.800
1
1
1
1
0
0
0
2.700
1
0
0
1
2.600
1
1
1
0
0
2.500
1
1
0
1
2.400
1
1
1
1
0
1
0
2.300
1
0
1
1
2.200
1
1
1
1
0
2.100
Intel-compatible
DAC codes
1
1
1
1
N/A
Shutdown
1
1
1
AC LOAD-
REGULATION
ERROR
(%)
1
LG
CONNECTED
TO:
DC LOAD-
REGULATION
ERROR
(%)
REF
0.1
GND
0.05
V
CC
0.2
0.5
2
TYPICAL
A
E
(V
GAIN
/
I
GAIN
)
8
2
4
Table 3. LG Pin Adjustment Settings
