Applications information – Rainbow Electronics MAX5511 User Manual
Page 15
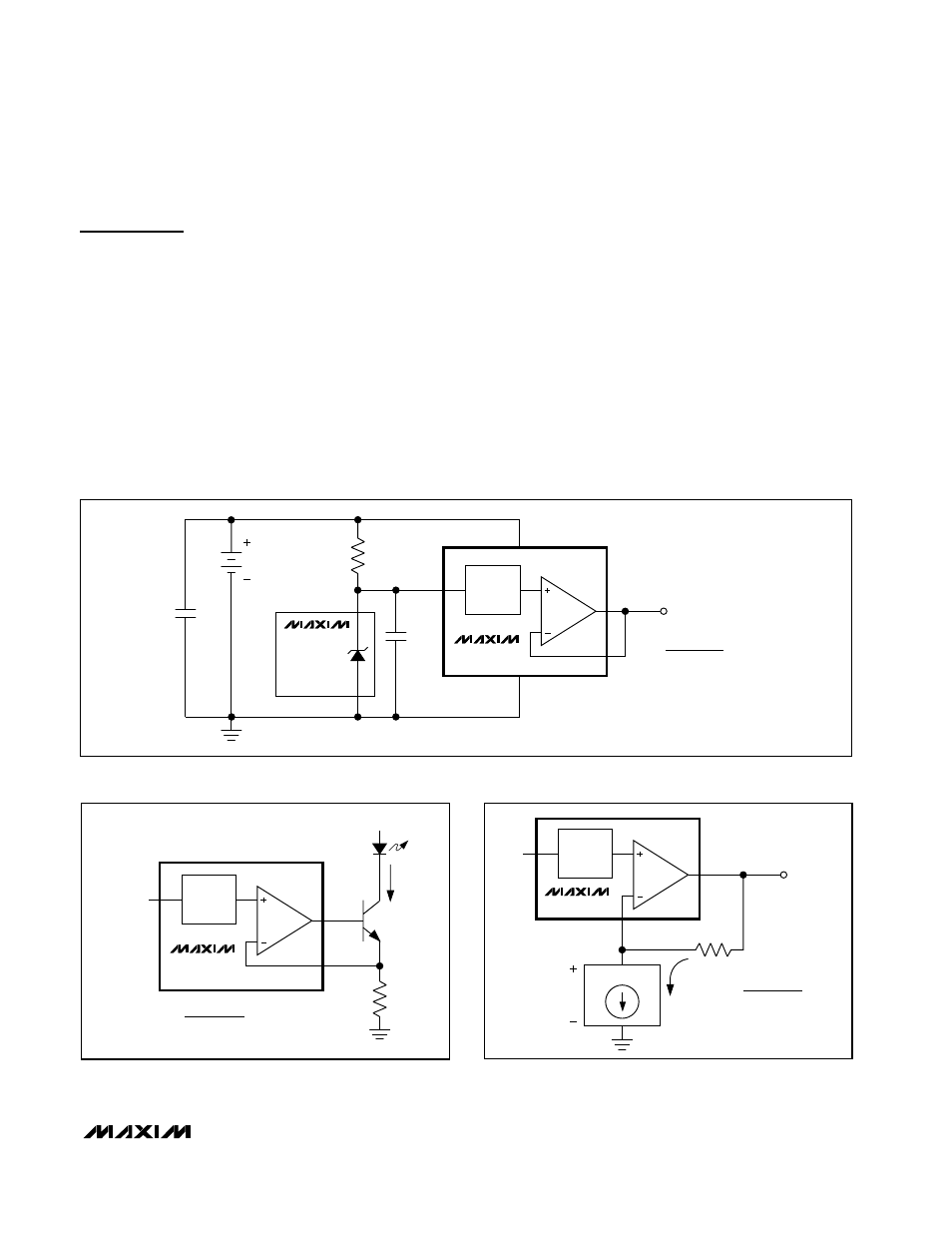
Applications Information
1-Cell and 2-Cell Circuit
See Figure 3 for an illustration of how to power the
MAX5510/MAX5511 with either one lithium-ion battery
or two alkaline batteries. The low current consumption
of the devices makes the MAX5510/MAX5511 ideal for
battery-powered applications.
Programmable Current Source
See the circuit in Figure 4 for an illustration of how to
configure the MAX5510 as a programmable current
source for driving an LED. The MAX5510 drives a stan-
dard NPN transistor to program the current source. The
current source (I
LED
) is defined in the equation in
Figure 4.
Voltage Biasing a Current-Output
Transducer
See the circuit in Figure 5 for an illustration of how to con-
figure the MAX5510 to bias a current-output transducer.
In Figure 5, the output voltage of the MAX5510 is a func-
tion of the voltage drop across the transducer added to
the voltage drop across the feedback resistor R.
Self-Biased Two-Electrode
Potentiostat Application
See the circuit in Figure 6 for an illustration of how to
use the MAX5511 to bias a two-electrode potentiostat
on the input of an ADC.
MAX5510/MAX5511
+1.8V to +5.5V, Ultra-Low-Power, 8-Bit,
Voltage-Output DACs
______________________________________________________________________________________
15
REFIN
MAX5510
MAX6006
(1µA, 1.25V
SHUNT
REFERENCE)
GND
+1.25V
0.01µF
536kΩ
V
DD
DAC
VOUT
N
DAC
IS THE NUMERIC VALUE
OF THE DAC INPUT CODE.
V
OUT
(4.88mV / LSB)
1.8V ≤ V
ALKALINE
≤ 3.3V
2.2V ≤ V
LITHIUM
≤ 3.3V
V
OUT
=
V
REFIN
× N
DAC
256
0.1µF
Figure 3. Portable Application Using Two Alkaline Cells or One Lithium Coin Cell
R
2N3904
N
DAC
IS THE NUMERIC VALUE OF THE DAC INPUT CODE.
I
LED
REFIN
LED
MAX5510
V+
DAC
VOUT
I
LED
=
V
REFIN
× N
DAC
256 × R
FB
Figure 4. Programmable Current Source Driving an LED
R
FB
N
DAC
IS THE NUMERIC VALUE
OF THE DAC INPUT CODE.
I
T
REFIN
MAX5510
DAC
VOUT
V
OUT
= V
BIAS
+ (I
T
× R)
V
OUT
V
BIAS
TRANSDUCER
V
BIAS
=
V
REFIN
× N
DAC
256
Figure 5. Transimpedance Configuration for a Voltage-Biased
Current-Output Transducer
