Application hints – Rainbow Electronics ADC12138 User Manual
Page 32
Application Hints
(Continued)
3 0 REFERENCE VOLTAGE
The difference in the voltages applied to the V
REF
a
and
V
REF
b
defines the analog input span (the difference be-
tween the voltage applied between two multiplexer inputs or
the voltage applied to one of the multiplexer inputs and ana-
log ground) over which 4095 positive and 4096 negative
codes exist The voltage sources driving V
REF
a
or V
REF
b
must have very low output impedance and noise The circuit
in
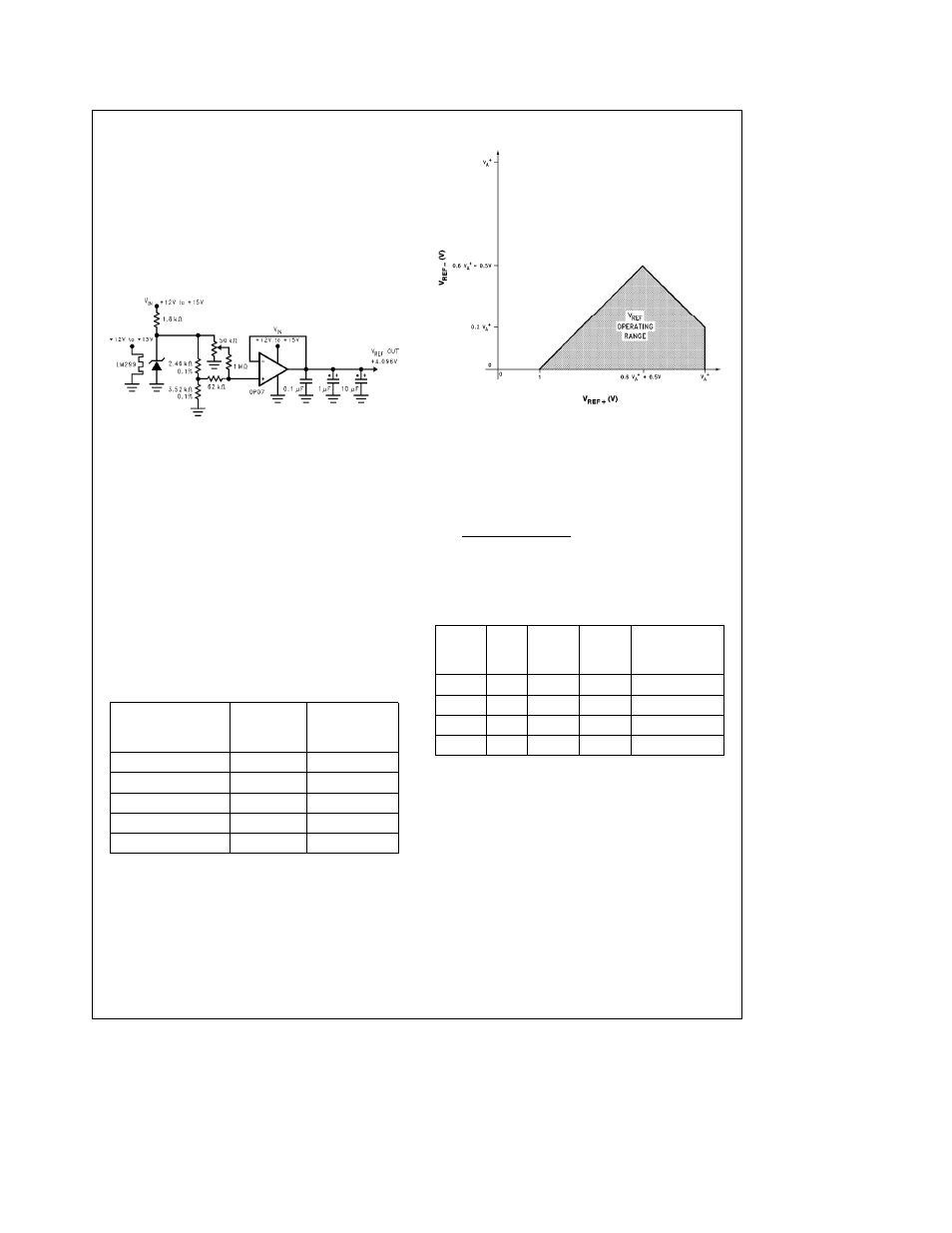
Figure 14
is an example of a very stable reference appro-
priate for use with the device
Tantalum
TL H 12079 – 43
FIGURE 14 Low Drift Extremely
Stable Reference Circuit
The ADC12130 2 8 can be used in either ratiometric or ab-
solute reference applications In ratiometric systems the
analog input voltage is proportional to the voltage used for
the ADC’s reference voltage When this voltage is the sys-
tem power supply the V
REF
a
pin is connected to V
A
a
and
V
REF
b
is connected to ground This technique relaxes the
system reference stability requirements because the analog
input voltage and the ADC reference voltage move togeth-
er This maintains the same output code for given input con-
ditions For absolute accuracy where the analog input volt-
age varies between very specific voltage limits a time and
temperature stable voltage source can be connected to the
reference inputs Typically the reference voltage’s magni-
tude will require an initial adjustment to null reference volt-
age induced full-scale errors
Below are recommended references along with some key
specifications
Output
Temperature
Part Number
Voltage
Coefficient
Tolerance
LM4041CI-Adj
g
0 5%
g
100ppm C
LM4040AI-4 1
g
0 1%
g
100ppm C
LM9140BYZ-4 1
g
0 5%
g
25ppm C
LM368Y-5 0
g
0 1%
g
20ppm C
Circuit of
Figure 14
Adjustable
g
2ppm C
The reference voltage inputs are not fully differential The
ADC12130 2 8 will not generate correct conversions or
comparisons if V
REF
a
is taken below V
REF
b
Correct con-
versions result when V
REF
a
and V
REF
b
differ by 1V and
remain at all times between ground and V
A
a
The V
REF
common mode range (V
REF
a
a
V
REF
b
) 2 is restricted to
(0 1
c
V
A
a
) to (0 6
c
V
A
a
) Therefore with V
A
a
e
5V
the center of the reference ladder should not go below 0 5V
or above 3 0V
Figure 15
is a graphic representation of the
voltage restrictions on V
REF
a
and V
REF
b
TL H 12079 – 44
FIGURE 15 V
REF
Operating Range
4 0 ANALOG INPUT VOLTAGE RANGE
The ADC12130 2 8’s fully differential ADC generate a
two’s complement output that is found by using the equation
shown below
for (12-bit) resolution the Output Code e
(V
IN
a
b
V
IN
b
) (4096)
(V
REF
a
b
V
REF
b
)
Round off to the nearest integer value between b4096 to
4095 if the result of the above equation is not a whole num-
ber
Examples are shown in the table below
Digital
V
REF
a
V
REF
b
V
IN
a
V
IN
b
Output
Code
a
2 5V
a
1V
a
1 5V
0V
0 1111 1111 1111
a
4 096V
0V
a
3V
0V
0 1011 1011 1000
a
4 096V
0V
a
2 499V a2 500V 1 1111 1111 1111
a
4 096V
0V
0V
a
4 096V 1 0000 0000 0000
5 0 INPUT CURRENT
At the start of the acquisition window (t
A
) a charging current
flows into or out of the analog input pins (A DIN1 and
A DIN2) depending on the input voltage polarity The ana-
log input pins are CH0 – CH7 and COM when A DIN1 is tied
to MUXOUT1 and A DIN2 is tied to MUXOUT2 The peak
value of this input current will depend on the actual input
voltage applied the source impedance and the internal mul-
tiplexer switch on resistance
With MUXOUT1 tied to
A DIN1 and MUXOUT2 tied to A DIN2 the internal multi-
plexer switch on resistance is typically 1 6 kX The A DIN1
and A DIN2 mux on resistance is typically 750X
32
