Applications information – Rainbow Electronics MAX9714 User Manual
Page 9
or power-up, the input amplifiers are muted and an
internal loop sets the modulator bias voltages to the
correct levels, preventing clicks and pops when the H-
bridge is subsequently enabled. Following startup, a
soft-start function gradually un-mutes the input ampli-
fiers. The value of the soft-start capacitor has an impact
on the click/pop levels. For optimum performance, C
SS
should be at least 180nF.
Applications Information
Filterless Operation
Traditional class D amplifiers require an output filter to
recover the audio signal from the amplifier’s PWM out-
put. The filters add cost, increase the solution size of
the amplifier, and can decrease efficiency. The tradi-
tional PWM scheme uses large differential output
swings (2
✕
V
DD
peak-to-peak) and causes large ripple
currents. Any parasitic resistance in the filter compo-
nents results in a loss of power, lowering the efficiency.
The MAX9713/MAX9714 do not require an output filter.
The devices rely on the inherent inductance of the
speaker coil and the natural filtering of both the speak-
er and the human ear to recover the audio component
of the square-wave output. Eliminating the output filter
results in a smaller, less costly, more efficient solution.
Because the frequency of the MAX9713/MAX9714 out-
put is well beyond the bandwidth of most speakers,
voice coil movement due to the square-wave frequency
is very small. Although this movement is small, a speak-
er not designed to handle the additional power can be
damaged. For optimum results, use a speaker with a
series inductance > 30µH. Typical 8
Ω speakers exhibit
series inductances in the range of 30µH to 100µH.
Optimum efficiency is achieved with speaker induc-
tances > 60µH.
Gain Selection
Table 2
shows the suggested gain settings to attain a
maximum output power from a given peak input voltage
and given load.
Output Offset
Unlike a class AB amplifier, the output offset voltage of
class D amplifiers does not noticeably increase quies-
cent current draw when a load is applied. This is due to
the power conversion of the class D amplifier. For
example, an 8mV DC offset across an 8
Ω load results
in 1mA extra current consumption in a class AB device.
MAX9713/MAX9714
6W, Filterless, Spread-Spectrum
Mono/Stereo Class D Amplifiers
_______________________________________________________________________________________
9
Figure 3. MAX9714 Efficiency vs. Class AB Efficiency
0
30
20
10
40
50
60
70
80
90
100
0
2
4
6
EFFICIENCY vs. OUTPUT POWER
OUTPUT POWER (W)
EFFICIENCY (%)
MAX9714
V
DD
= 15V
f = 1kHz
R
L
= 16
Ω
CLASS AB
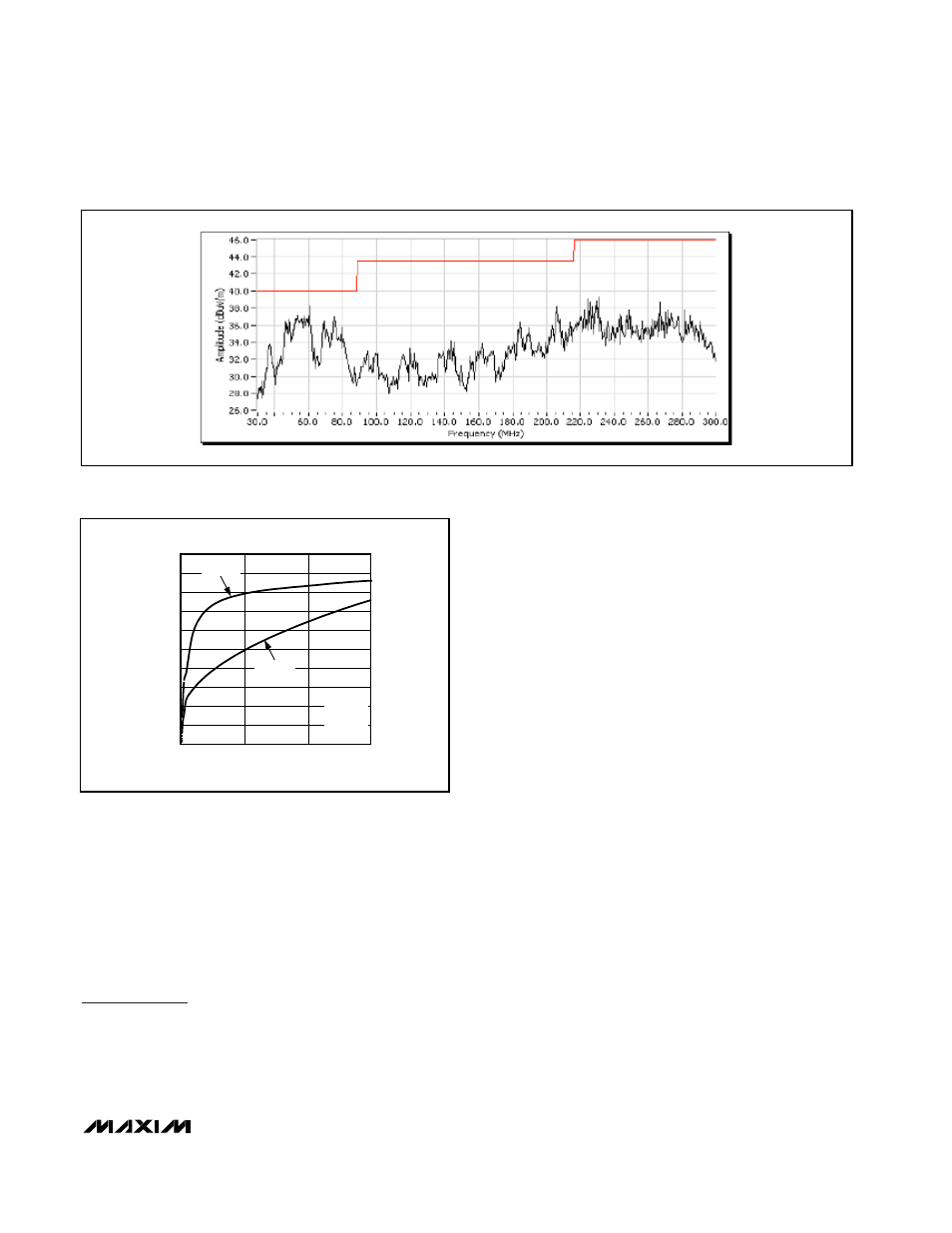
Figure 2. SSM Radiated Emissions
