Detailed description, Table 1. operating modes – Rainbow Electronics MAX9714 User Manual
Page 8
MAX9713/MAX9714
Detailed Description
The MAX9713/MAX9714 filterless, class D audio power
amplifiers feature several improvements to switch-
mode amplifier technology. The MAX9713 is a mono
amplifier, the MAX9714 is a stereo amplifier. These
devices offer class AB performance with class D effi-
ciency, while occupying minimal board space. A
unique filterless modulation scheme and spread-spec-
trum switching mode create a compact, flexible, low-
noise, efficient audio power amplifier. The differential
input architecture reduces common-mode noise pick-
up, and can be used without input-coupling capacitors.
The devices can also be configured as a single-ended
input amplifier.
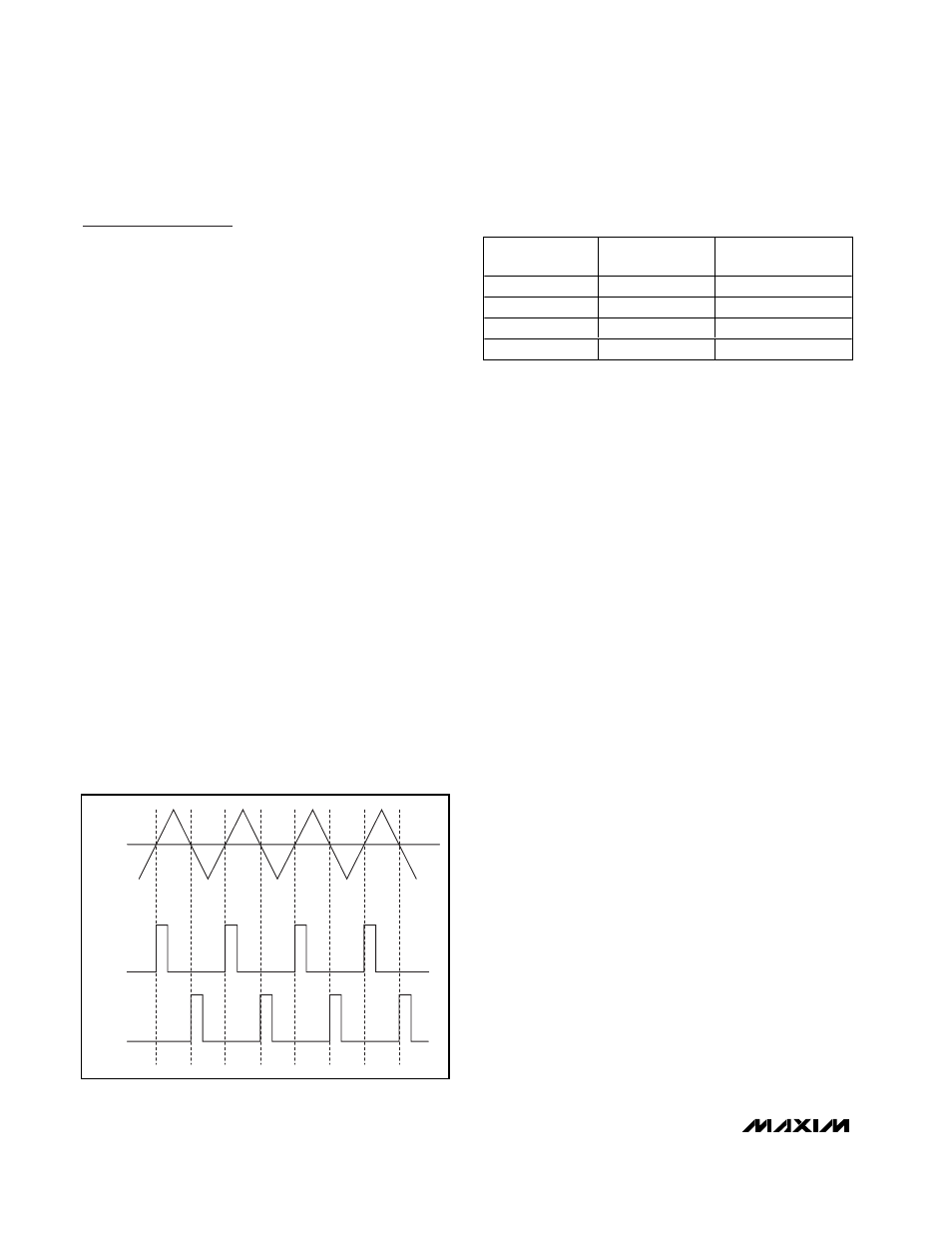
Comparators monitor the device inputs and compare
the complementary input voltages to the triangle wave-
form. The comparators trip when the input magnitude of
the triangle exceeds their corresponding input voltage.
Operating Modes
Fixed-Frequency Modulation (FFM) Mode
The MAX9713/MAX9714 feature three FFM modes with
different switching frequencies (
Table 1
). In FFM mode,
the frequency spectrum of the class D output consists
of the fundamental switching frequency and its associ-
ated harmonics (see the Wideband FFT graph in the
Typical Operating Characteristics). The MAX9713/
MAX9714 allow the switching frequency to be changed
by
±35%, should the frequency of one or more of the
harmonics fall in a sensitive band. This can be done at
any time and not affect audio reproduction.
Spread-Spectrum Modulation (SSM) Mode
The MAX9713/MAX9714 feature a unique, patented
spread-spectrum mode that flattens the wideband
spectral components, improving EMI emissions that
may be radiated by the speaker and cables. This mode
is enabled by setting FS1 = FS2 = H. In SSM mode, the
switching frequency varies randomly by
±1.7%kHz
around the center frequency (335kHz). The modulation
scheme remains the same, but the period of the trian-
gle waveform changes from cycle to cycle. Instead of a
large amount of spectral energy present at multiples of
the switching frequency, the energy is now spread over
a bandwidth that increases with frequency. Above a
few megahertz, the wideband spectrum looks like white
noise for EMI purposes (
Figure 2
).
Efficiency
Efficiency of a class D amplifier is attributed to the
region of operation of the output stage transistors. In a
class D amplifier, the output transistors act as current-
steering switches and consume negligible additional
power. Any power loss associated with the class D out-
put stage is mostly due to the I*R loss of the MOSFET
on-resistance, and quiescent current overhead.
The theoretical best efficiency of a linear amplifier is
78%, however that efficiency is only exhibited at peak
output powers. Under normal operating levels (typical
music reproduction levels), efficiency falls below 30%,
whereas the MAX9714 still exhibits >80% efficiencies
under the same conditions (
Figure 3
).
Shutdown
The MAX9713/MAX9714 have a shutdown mode that
reduces power consumption and extends battery life.
Driving SHDN low places the device in low-power
(0.2µA) shutdown mode. Connect SHDN to a logic high
for normal operation.
Click-and-Pop Suppression
The MAX9713/MAX9714 feature comprehensive click-
and-pop suppression that eliminates audible transients
on startup and shutdown. While in shutdown, the H-
bridge is pulled to GND through 300k
Ω. During startup,
6W, Filterless, Spread-Spectrum
Mono/Stereo Class D Amplifiers
8
_______________________________________________________________________________________
Table 1. Operating Modes
FS1
FS2
SWITCHING MODE
(kHz)
L
L
335
L
H
460
H
L
236
H
H
335
±7%
Figure 1. MAX9714 Outputs with No Input Signal Applied
V
IN
= 0V
OUT-
OUT+
