1 0 functional description, 2 0 analog considerations – Rainbow Electronics ADC0820 User Manual
Page 11
1 0 Functional Description
(Continued)
TL H 5501 – 20
Note
MS means most significant
LS means least significant
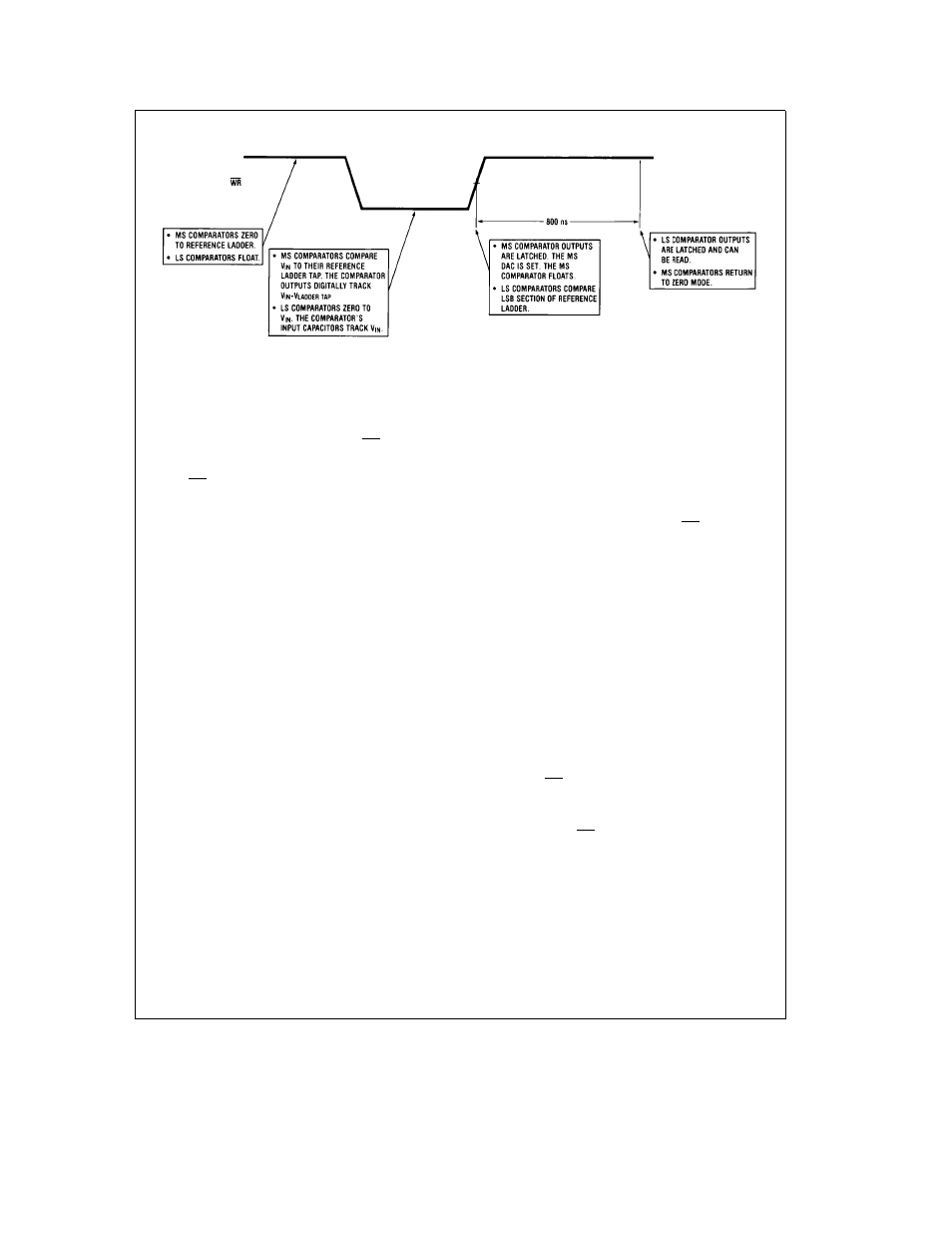
FIGURE 8 Operating Sequence (WR-RD Mode)
OTHER INTERFACE CONSIDERATIONS
In order to maintain conversion accuracy WR has a maxi-
mum width spec of 50 ms When the MS flash ADC’s sam-
pled-data comparators (Section 1 2) are in comparison
mode (WR is low) the input capacitors (C
Figure 6
) must
hold their charge Switch leakage and inverter bias current
can cause errors if the comparator is left in this phase for
too long
Since the MS flash ADC enters its zeroing phase at the end
of a conversion (Section 1 3) a new conversion cannot be
started until this phase is complete The minimum spec for
this time (t
P
Figures 2 3a 3b
and
4
) is 500 ns
2 0 Analog Considerations
2 1 REFERENCE AND INPUT
The two V
REF
inputs of the ADC0820 are fully differential
and define the zero to full-scale input range of the A to D
converter This allows the designer to easily vary the span
of the analog input since this range will be equivalent to the
voltage difference between V
IN
(a) and V
IN
(b) By reducing
V
REF
(V
REF
e
V
REF
(a)bV
REF
(b)) to less than 5V the sen-
sitivity of the converter can be increased (i e if V
REF
e
2V
then 1 LSBe7 8 mV) The input reference arrangement
also facilitates ratiometric operation and in many cases the
chip power supply can be used for transducer power as well
as the V
REF
source
This reference flexibility lets the input span not only be var-
ied but also offset from zero The voltage at V
REF
(b) sets
the input level which produces a digital output of all zeroes
Though V
IN
is not itself differential the reference design
affords nearly differential-input capability for most measure-
ment applications
Figure 9
shows some of the configura-
tions that are possible
2 2 INPUT CURRENT
Due to the unique conversion techniques employed by the
ADC0820 the analog input behaves somewhat differently
than in conventional devices The A D’s sampled-data com-
parators take varying amounts of input current depending
on which cycle the conversion is in
The equivalent input circuit of the ADC0820 is shown in
Figure 10a
When a conversion starts (WR low WR-RD
mode) all input switches close connecting V
IN
to thirty-one
1 pF capacitors Although the two 4-bit flash circuits are not
both in their compare cycle at the same time V
IN
still sees
all input capacitors at once This is because the MS flash
converter is connected to the input during its compare inter-
val and the LS flash is connected to the input during its
zeroing phase (Section 1 3) In other words the LS ADC
uses V
IN
as its zero-phase input
The input capacitors must charge to the input voltage
through the on resistance of the analog switches (about 5
kX to 10 kX) In addition about 12 pF of input stray capaci-
tance must also be charged For large source resistances
the analog input can be modeled as an RC network as
shown in
Figure 10b
As R
S
increases it will take longer for
the input capacitance to charge
In RD mode the input switches are closed for approximately
800 ns at the start of the conversion In WR-RD mode the
time that the switches are closed to allow this charging is
the time that WR is low Since other factors force this time
to be at least 600 ns input time constants of 100 ns can be
accommodated without special consideration Typical total
input capacitance values of 45 pF allow R
S
to be 1 5 kX
without lengthening WR to give V
IN
more time to settle
11
