Setup page, Bass management – TC Electronic Studio Konnekt 48 User Manual
Page 12
10 Speaker sets
The speaker sets can be labeled individually. Simply
click in the text field and enter a name of your choice.
Assigning an output to a speaker set
With no bass management an output is assigned
directly to a speaker set by checking the ASSIGN
check box for the output.
However, when bass management is used you must
set main speakers to “main” and sub to “sub”.
Example: Example:
Without Bass Management
With Bass Management
11 Trim
Range: -20 dB to 0 dB
Individual trim levels for each channel.
12 DLY
Range: 0 to 30 ms
Perfect listening conditions and placement of
speakers according to an ITU 775 circle are not
always possible. This delay parameter allows for
individual alignment of speakers.
13 Output label
The physical outputs have fixed names according to
the labels on the rear panel. However, you can also
add an additional personal label to these channel
outputs.
Bass management
The bass management system is designed to subtract the
bass contents of all main channels and reproduce this by
the use of a subwoofer and is easily set up with the
Studio Konnekt 48.
Let us take at look at the components and how to set up
bass management using the Studio Konnekt 48.
The Subwoofer
A subwoofer is a monitor that reproduces low frequencies.
The purpose is to take over from the main monitor(s) as
frequencies approach the lower end of the monitors
frequency range. Depending on the performance and size
of the main monitors the used threshold frequency
between main monitors an sub, may vary from 80 to 120 Hz.
From psycho-acoustics we know that there is no
directional information in audio signals below
approximately 120 Hz. Hence the advantage of placing
the subwoofer in a position where the best distribution is
achieved.
The LFE Channel
LFE is short for Low Frequency Enhancement or Low
Frequency Effects, the first being the original name but
the second being the most correct with regards to its
application.
It is also referred to as the “.1”-channel, which indicates
that the frequency range of this channel is only a fraction
of the other channels in a multi-channel setup. The
actual frequency range is 20 Hz to 120 Hz.
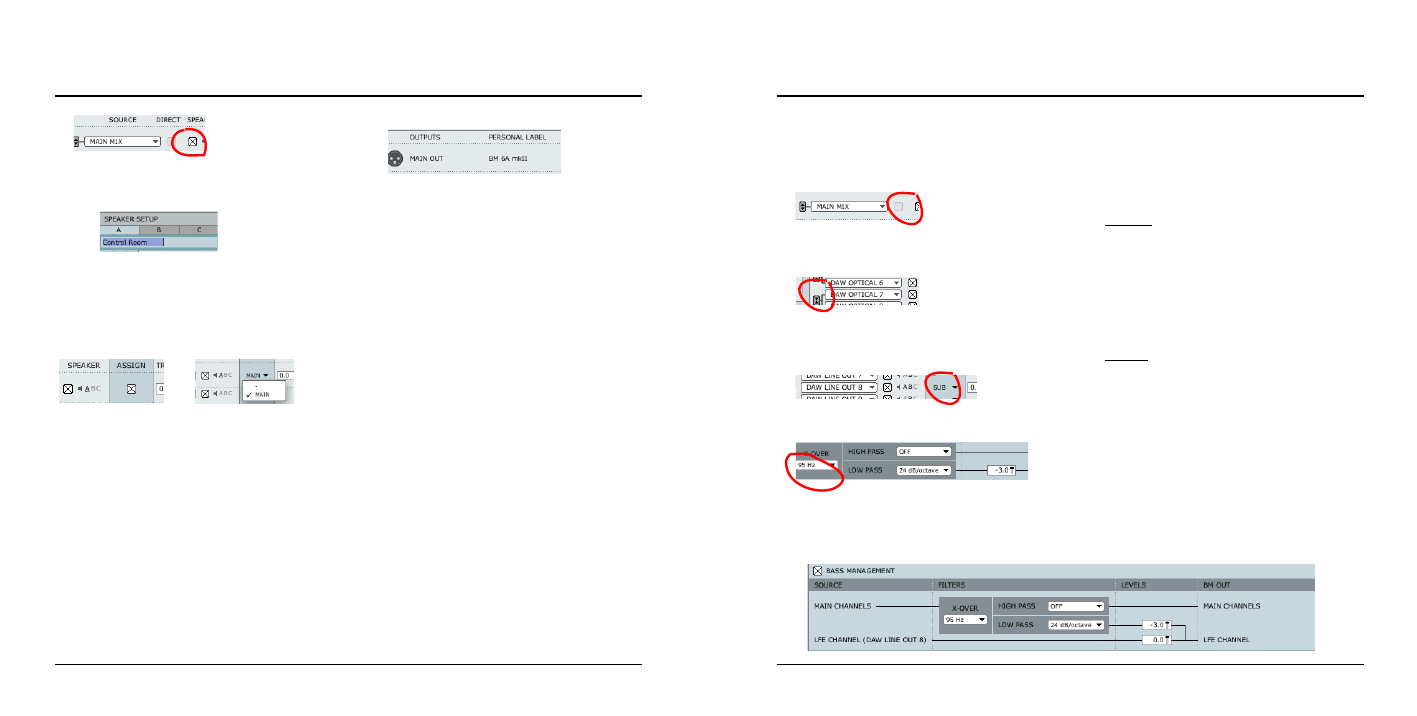
16 + 17 High Pass & Low Pass
The high/low pass filters filtrate the signal before
distribution to main and sub-channels. The high-pass
filter is typically used when relatively small main
monitors are used. The performance of such small
main monitors will improve significantly, when they
don’t have to reproduce very low frequency signals.
High-Pass
The high-pass filter filters the low-end frequencies
from the main channels above the x-over frequency
and according to the high-pass options.
-
“off” - no high-pass filter
-
“12 dB/octave” for a 12 dB slope above the X-
over point
-
“24 dB/octave” for a 12 dB slope above the X-
over point
Low-Pass
The low-pass filter filtrates the high-end frequencies
from the signal below the x-over frequency according
to the low-pass options.
-
“12 dB/octave” for a 12 dB slope below the X-
over point
-
“24 dB/octave” for a 24 dB slope below the X-
over point
18 Levels
Individual level adjustment for the LFE channel and
the extracted signal below the X-over frequency.
14 Bass Management
For bass management to be active a few conditions must
be setup:
-
main channels must be assigned:
-
for bass management of the main channels to be
active, mark the bass management-box
-
a subwoofer is connected to “line out 8” and thus any
LFE channel should be routed to this output by
setting Assign to “Sub”.
15 X-OVER
Sets the X-over frequency for the main channels to
determine the frequency where the main channel
signal is split. Frequencies below this point is routed
to the sub channel (line out 8).
SETUP PAGE
SETUP PAGE
21
20
