Bipolar junction transistors (bjts) – Velleman DCA55 User Manual
Page 11
Atlas DCA User Guide
October 2007 – Rev 7
Page 11
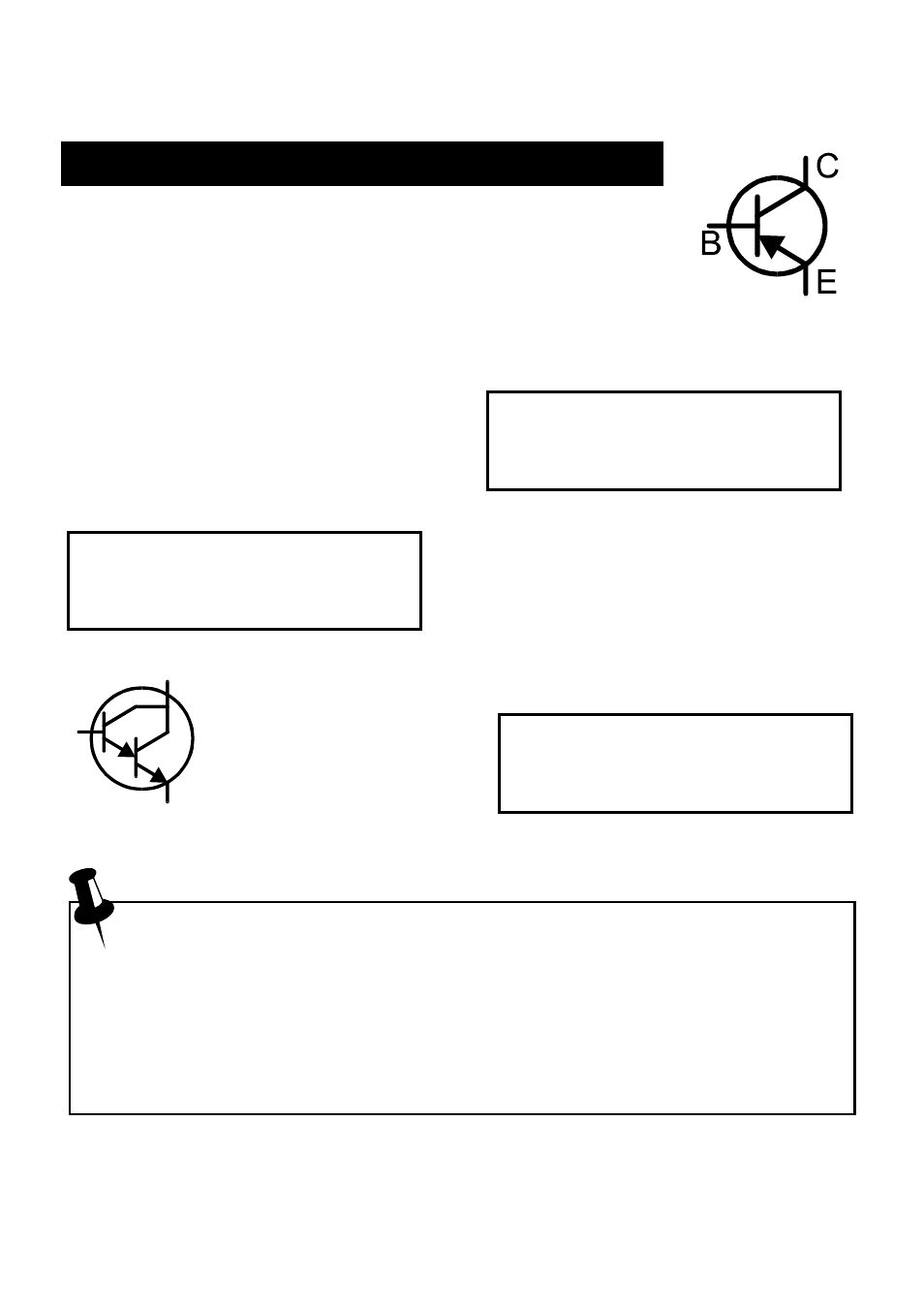
Bipolar Junction Transistors (BJTs)
Bipolar Junction Transistors are simply “conventional”
transistors, although variants of these do exist such as
Darlingtons, diode protected, resistor shunted types and
combinations of these types. All of these variations are
automatically identified by the Atlas DCA.
Bipolar
Junction
Transistors
are
available in two main types, NPN and
PNP. In this example, the unit has
detected a Silicon PNP transistor.
The unit will determine that the
transistor is Germanium only if the base-
emitter voltage drop is less than 0.4V
and is also PNP.
If the device is a Darlington transistor (two BJTs connected
together), the unit will
display
a
similar
message to this:
Note that the Atlas DCA will determine that the transistor under test is
a Darlington type if the base-emitter voltage drop is greater than
1.00V for devices with a base-emitter shunt resistance of greater than
60kΩ or if the base-emitter voltage drop is greater than 0.80V for
devices with a base-emitter shunt resistance of less than 60kΩ. The
measured base-emitter voltage drop is displayed as detailed later in
this section.
PNP Silicon
Transistor
PNP Germanium
Transistor
NPN Darlington
Transistor
