GE Healthcare Comprehensive solution for liver embolization User Manual
Page 2
Liver neuroendocrine tumor embolization
Drs. T. De Baère and F. Deschamps, IGR – Villejuif, France.
PATIENT HISTORY
This is the case of a 33 year-old-patient with a history of multiple
neuroendocrine tumors.
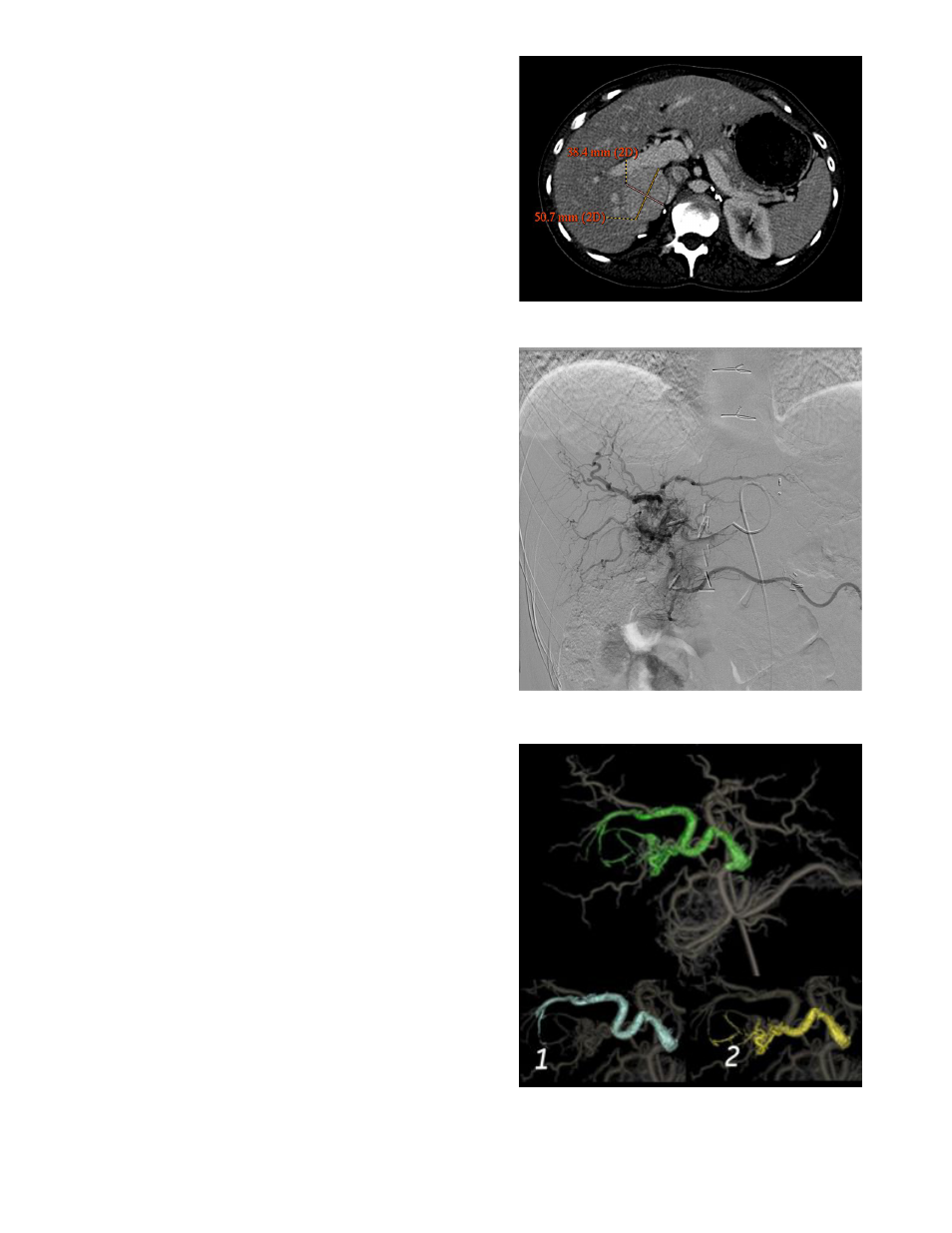
A pre-procedural CT is presenting a 51 x 39 mm nodule on Segment V.
The patient has been referred for a TACE.
PROCEDURE
An initial DSA acquisition shows the complex vasculature of the
tumor (Fig. 1) followed by an Innova 3D acquisition at 40°/s. The 3D
volume is automatically reconstructed on the Advantage Workstation
(AW) and displayed in the operating room. FlightPlan for Liver is then
launched to analyze the liver vasculature and automatically highlight
the vessels traveling to the hypervascular lesion. The physician
identifies two main feeders and two injection points to treat the
patient (Fig. 2).
The two feeders are transferred to the Innova Vision software
running on the AW. Innova Vision is used to help guide the micro-
catheter to the injection point by superimposing FlightPlan for Liver
3D roadmap on the live fluoroscopic image. Note that there is an
automatic synchronization between the gantry motion and the 3D
model to reach the injection points. 100-300 μm of embolic agent and
doxorubicin are then injected to treat the tumor through each of the
feeders (Fig. 3 and Fig.4).
At the end of the procedure an Innova 3D at 40°/s is acquired to
assess the embolization material uptake. Integrated Registration, GE’s
multi-modality image fusion solution and allows comparing fixation
of the embolic material and tumor location as seen on the initial, pre-
procedural Innova 3D. (Fig. 5). Integrated Registration enhances the
value of multiple imaging modalities, especially for complex vascular
anatomies, by allowing direct comparison with pretreatment images.
OUTCOME
A one-month CT scan shows the necrosis area, note the correlation
with Innova 3D just after the embolization (Fig. 6 c. and d.). Integrated
Registration allows comparing tumor location, fixation of the embolic
material and necrosis area.
CONCLUSION
Sub segmental feeder vessel analysis assists selective embolization to
limit deleterious effects to nearby structures.
The integration of 3D images to guide complex procedures such as
TACE brings more confidence during the interventions.
FlightPlan for Liver helps improve the overall procedure workflow and
potentially reduces the amount of injected contrast media compared
to multiple oblique DSA runs. Post-procedural assessment helps
measure effectiveness, potential need for additional intervention and
presence of an adverse result. Integrated Registration increases the
benefits of multiple imaging modalities during a clinical procedure.
Pre-treatment CT showing the 51x39mm tumor location
Fig.1 DSA - Complex vascularization of the tumor.
Fig. 2 FlightPlan for Liver output: The vessels in the vicinity of the
hypervascular lesion are colored green; two identi-fied feeders are
colored blue and yellow.
