Quicker diagnosis, Reduced hospital cost – GE Healthcare Discovery CT750 HD User Manual
Page 33
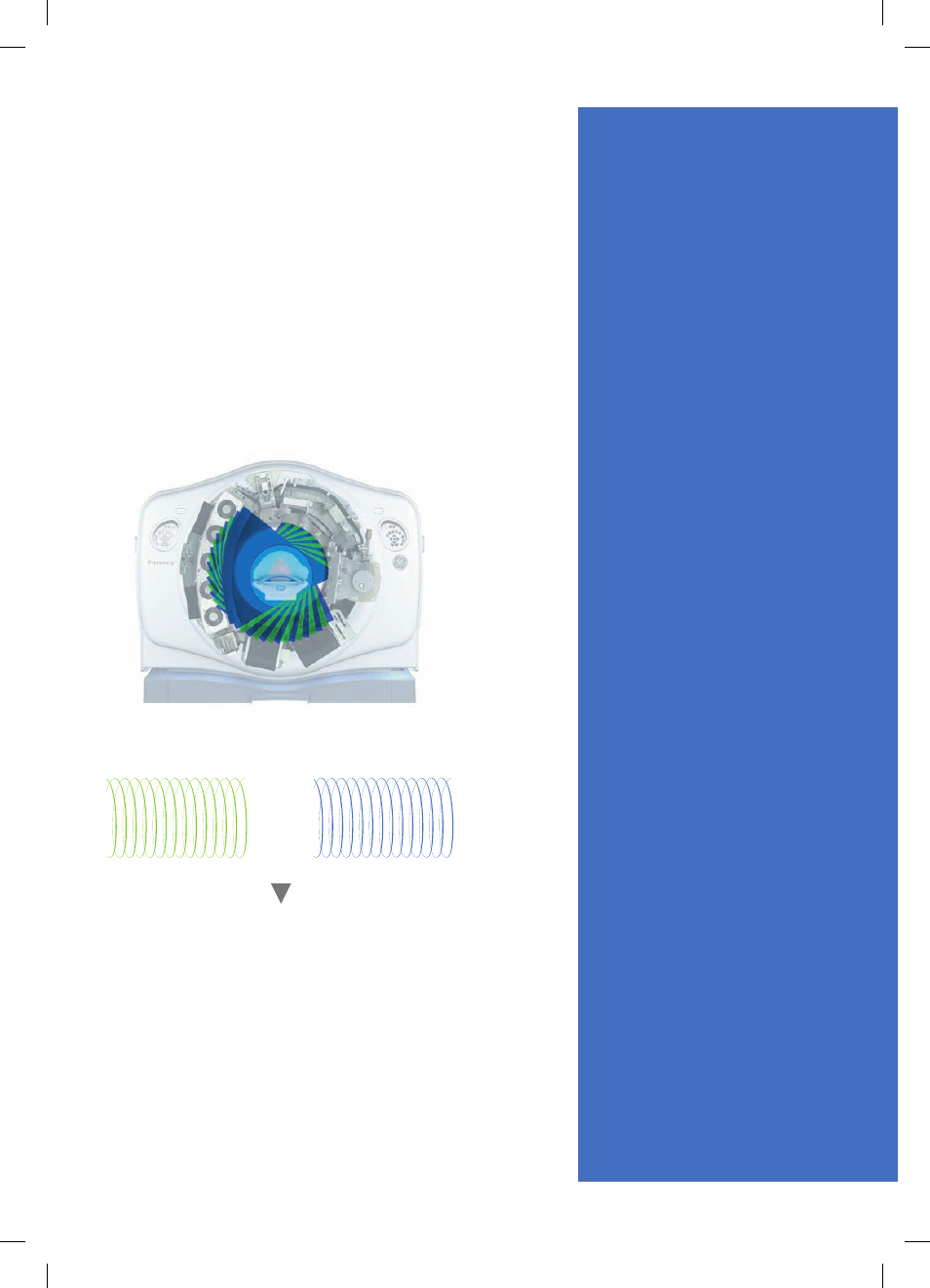
how it works
Central to spectral image acquisition is the Gemstone
detector’s ability to differentiate between two different
energy levels from view to view (as illustrated by the
blue and green data sets below). Both high and low
energy data sets are acquired simultaneously to improve
image registration for material separation throughout
the full 50cm field of view.
Using known attenuation curves, the material specific
difference in attenuation enables an easy classification
of the elementary chemical composition of the scanned
tissue. This creates the ability to generate material
density images.
Spectral images are derived from the material density
images and depict how the object would look if the
X-ray source produced only photons at a single energy.
Quicker
Diagnosis
equals
Reduced
Hospital
Cost
Painful episodes of renal-related
conditions result in more than one
million patient visits to emergency
departments annually.
1
Reducing
the time spent on imaging,
additional testing, and waiting for
results has the potential to
decrease both length of stay and
overall costs to the hospital. This is
critical, as hospitals are paid a fixed
amount per admission regardless
of the number of services provided.
Using GE’s Discovery CT750 HD
with Gemstone Spectral Imaging
(GSI), a single contrast-enhanced
CT may provide information to
evaluate the presence or absence
of a renal lesion. With the same
exam data, GSI can create a “virtual
non-contrast like image” that can
provide information to assess for
kidney stones. GSI also has the
ability to help characterize renal
stones without a urinalysis —
meaning treatment can start
earlier, minimizing in-patient stay
time. GSI can also help physicians
characterize lesions, reducing
the need for additional testing in
patients with symptoms whose
CT results indicate a renal mass.
80 kVp raw data
140 kVp raw data
1,968 views reconstruction
+
1. Brown J. Diagnostic and treatment
patterns for renal colic in US Emergency
Departments. International Urology and
Nephrology 2006; 38: 87-92.
GE Healthcare Discovery CT750 HD 33
