Opticon LPR5627 User Manual
Page 12
Manual No. 25-ULPNR101-03; Feb, 2003 LPN5627 / LPR5627 Laser Fixed Mount
Scanner
Page 8
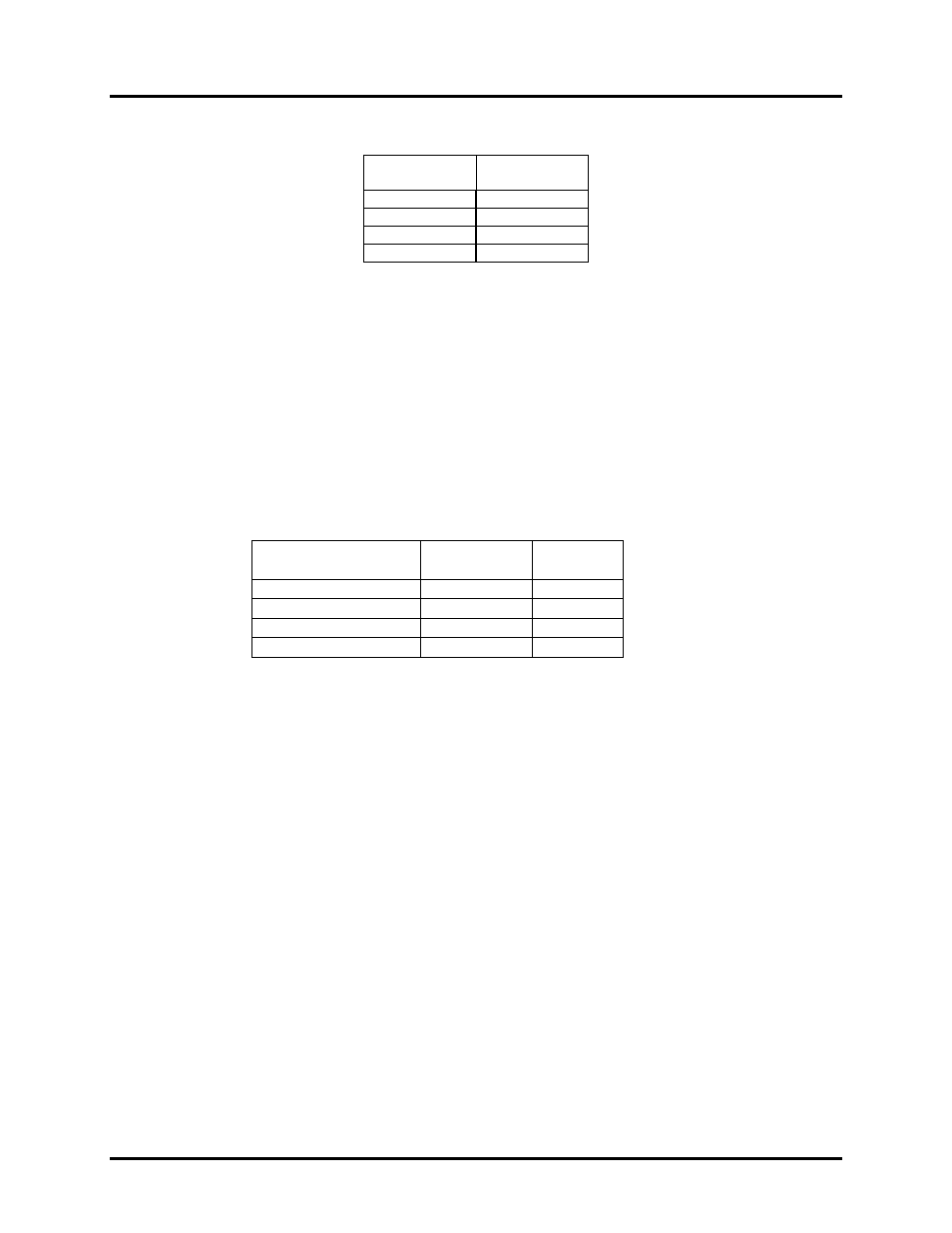
Readable Bar Code Width LPN5627/LPR5627
(Field-of-View Specification Based Upon 40 Degree Sweep)
Distance
from Window
Max.
Width
2.0”
2.0”
4.0”
3.5”
8.0”
6.4”
12.0”
9.3”
The table above shows the field-of-view at various distances from the window. The field-of-view is the
maximum width that the scanner is capable of reading. It is the distance from the left edge of the view
to the right edge. A bar code label positioned anywhere within this field-of-view can be decoded. The
field-of-view is also a measure of the widest bar code label that can be read.
Remember
: The width of
a bar code label includes not only the bars and spaces but also the required white space (quiet zone) on
each end.
Good design policy is to position the barcode at the midpoint of the scanner’s depth-of-field and at the
center of the field-of-view. Do not position it near the extremes of the reading range.
Comparable depth-of-field parameters for the LPR5627 are the following:
Depth-of-Field LPR5627 (Raster - Specification) *
Bar Code Density
Near
Distance
Far
Distance
40 mil (1.00 mm)
2.3”
10.6”
20 mil (0.50 mm)
2.3”
9.1”
10 mil (0.25 mm)
2.3”
6.7”
6 mil (0.15 mm)
3.5”
4.3”
* measured from front edge of scanner
2) Avoiding Specular Reflection
Do not position the scanner at an angle that causes the laser light to be reflected directly back into the
scanner. This is called specular reflection. Too much reflected light can “blind” the scanner preventing a
good decode.
If the bar code label is located on a flat surface, specular reflectivity occurs between 0 to 10 degrees off
perpendicular. (See diagram) If the bar code label is located on a cylindrical surface, such as a test
tube, the angle of specular reflection is measured tangent to the curve. If the curved surface is also
moving, there may be more than one position causing specular reflection. The following diagram
indicates the area to avoid:
