Gas piping – Rinnai RL75E User Manual
Page 20
20
VB Series Outdoor LS Manual
Pipe Sizing Procedure - Example
Pipe Size (inches)
3/4
1
1 1/4
1 1/2
10
273 514 1060
1580
20
188 353 726 1090
30
151 284 583 873
40
129 243 499 747
50
114 215 442 662
60
104 195 400 600
70
95 179 368 552
80
89 167 343 514
90
83 157 322 482
100
79 148 304 455
125
70 131 269 403
150
63 119 244 366
175
58 109 224 336
200
54 102 209 313
Length
Length
Pipe Size (inches)
1/2 3/4 1 1
1/4
10
291 608 1150
2350
20
200 418 787 1620
30
160 336 632 1300
40
137 287 541 1110
50
122 255 480 985
60
110 231 434 892
80
101 212 400 821
100
94 197 372 763
125
89 185 349 716
150
84 175 330 677
175
74 155 292 600
200
67 140 265 543
Gas Piping
The gas supply must be capable of handling the entire gas load at the location. Gas line sizing is based on gas
type, the pressure drop in the system, the gas pressure supplied, and gas line type. For gas pipe sizing in the
United States, refer to the National Fuel Gas Code, NFPA 54. For Canadian gas pipe sizing, refer to the Natural
Gas and Propane Installation Code CAN/CSA B149.1. The below information is provided as an example. The
appropriate table from the applicable code must be used.
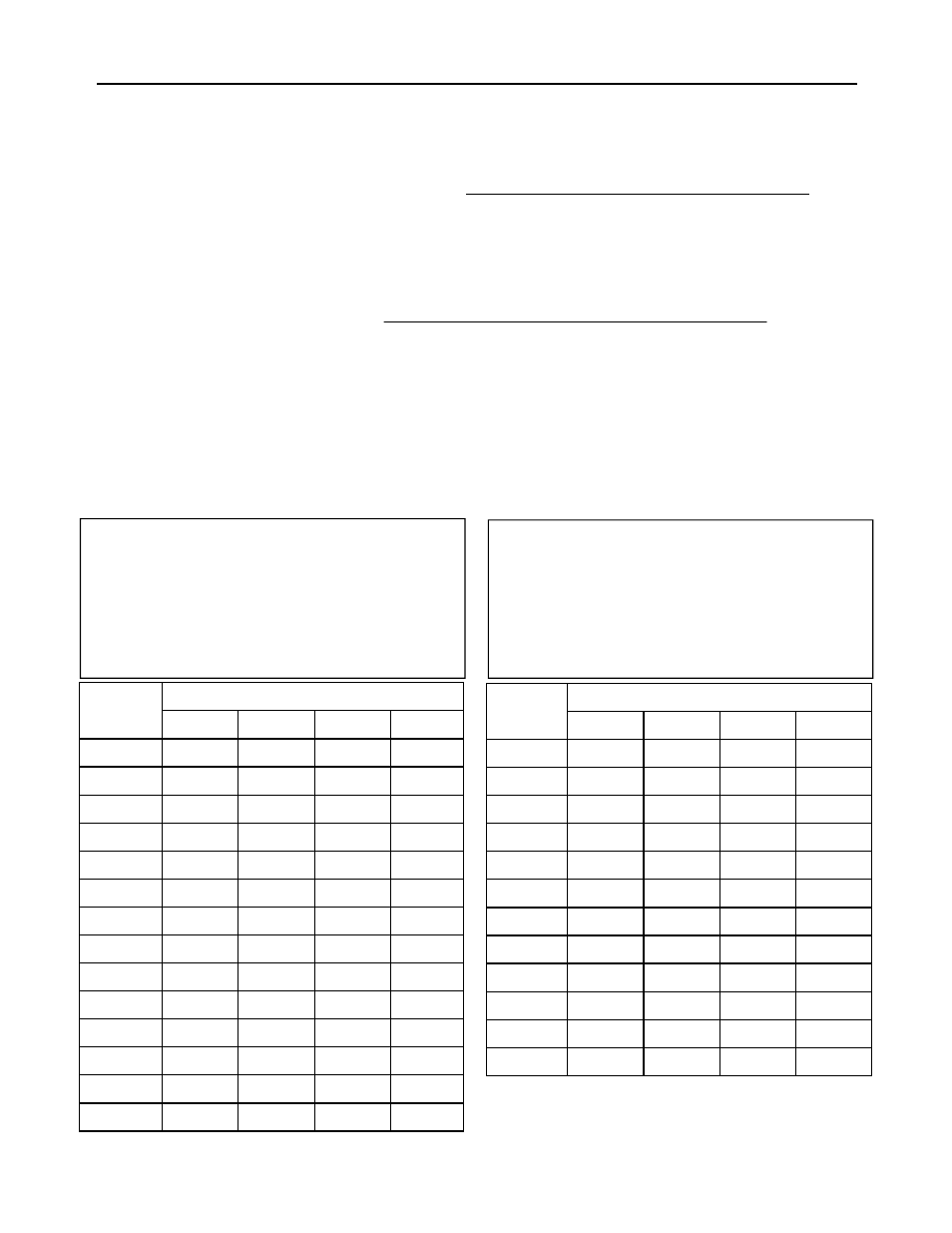
Pipe Sizing Table - Natural Gas
Pipe Sizing Table - Propane Gas
Inlet Pressure: less than 2 psi (55 inches W.C.)
Pressure Drop: 0.3 inches W.C.
Specific Gravity: 0.60
Inlet Pressure: 11.0 inches W.C.
Pressure Drop: 0.5 inches W.C.
Specific Gravity: 1.50
Schedule 40 Metallic Pipe
cubic feet per hour
Schedule 40 Metallic Pipe
Capacity in Thousands of BTU per Hour
1.For some tables, you will need to determine the cubic feet per hour of gas required by dividing the gas input by
the heating value of the gas (available from the local gas company). The gas input needs to include all gas
products at the location and the maximum BTU usage at full load when all gas products are in use.
Gas
Input
of
all
gas
products
(BTU
/
HR)
Cubic Feet per Hour (CFH) =
Heating
Value
of
Gas
(BTU
/
FT
3
)
2.Use the table for your gas type and pipe type to find the pipe size required. The pipe size must be able to
provide the required cubic feet per hour of gas or the required BTU/hour.
Example: The gas input of the RL94e is 199,000 BTU/HR using propane. Additional appliances at the location
require 75,000 BTU/hr. Therefore the maximum BTU usage will be 274,000 BTU/hr.
If using propane gas with Schedule 40 metallic pipe, 100 ft in length, then the 1 inch pipe size will be
capable of supplying 372,000 BTU/hr of propane gas..
