Product description, Recommended processes and equipment, Welding capability – Lincoln Electric POWER MIG SVM157-A User Manual
Page 15: Limitations, Description of controls, Wire drive roll, Wire size conversion parts, Operation
OPERATION
B-3
B-3
POWER MIG 200
PRODUCT DESCRIPTION
The POWER MIG™ 200 is a complete semiautomatic
DC voltage arc welding machine built to meet NEMA
specifications. It combines a tapped transformer volt-
age power source with a constant speed wire feeder to
form a reliable robust performance welding system. A
simple control scheme, consisting of continuous full
range wire feed speed control, and 7 output voltage tap
selections provides versatility with ease of use and
accuracy.
Other features include a 2" (51 mm) O.D. wire reel
spindle with adjustable brake, an integral gas cylinder
mounting undercarriage, an adjustable Argon blend
flow regulator with cylinder pressure gauge and inlet
hose, a 12 ft. (3.6 m) Magnum 250L GMAW gun and
cable with fixed (flush) nozzle, a 7 ft. (2.1 m) power
cable with plug, and a 10 ft. (3.0 m) work cable with
clamp.
Optional Spool Gun and Adapter kit, Dual Cylinder
Mounting kit and Aluminum Feeding Kit for push feed-
ing with standard built in feeder are also available.
RECOMMENDED PROCESSES AND
EQUIPMENT
The POWER MIG 200 is recommended for GMA weld-
ing processes using 10 to 44 lb (4.5 to 20 kg) 2" (51
mm) I.D. spools or Readi-Reel® coils (with optional
adapter) of .025" through .045" (0.6 – 1.2 mm) solid
steel, .035" (0.9 mm) stainless, 3/64" (1.2 mm) alu-
minum and .045" (1.2 mm) Outershield®; as well as
.035" (0.9 mm) and .045" (1.2 mm) Innershield® self-
shielding electrodes.
The POWER MIG is factory equipped to feed .035"
(0.9 mm) electrodes. It also includes a 200A, 60% duty
cycle (or 250A, 40% duty cycle) rated, 12 ft. (3.6 m)
GMAW gun and cable assembly equipped for these
wire sizes. Use of GMAW processes requires a supply
of shielding gas.
WELDING CAPABILITY
The POWER MIG 200 is rated at 200 amps @ 22 volts,
at a 30% duty cycle based on a ten minute cycle time.
It is capable of higher duty cycles at lower output cur-
rents. The tapped transformer design makes it well
suited for use with most portable or in-plant generating
systems.
LIMITATIONS
The output voltage/current of the POWER MIG 200 is
subject to vary if the input power to the machine varies,
due to its tapped transformer power topology. In some
cases an adjustment of WFS preset and/or voltage tap
selection may be required to accommodate a signifi-
cant drift in input power.
DESCRIPTION OF CONTROLS
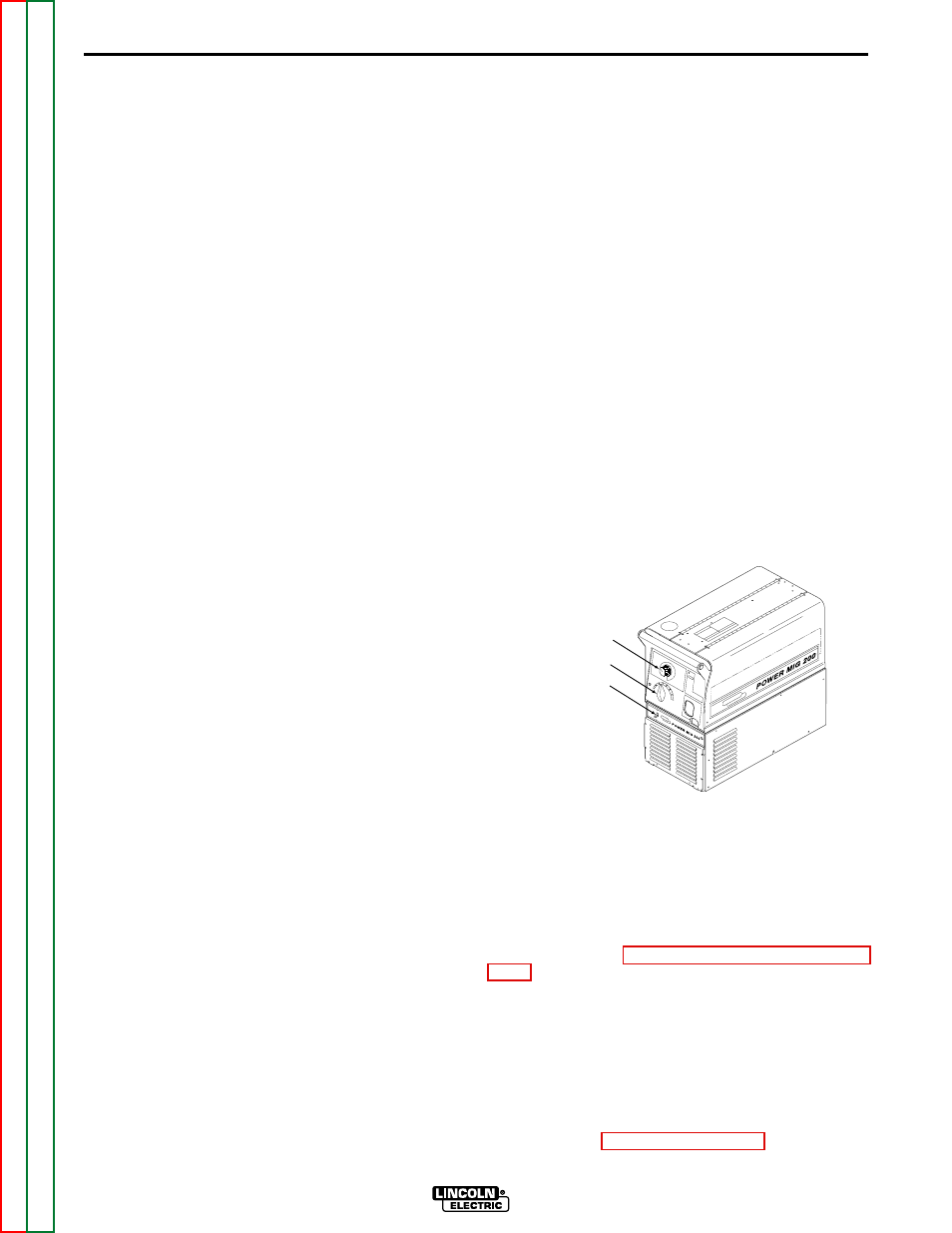
Power ON/OFF Switch — Place the lever in the "ON"
position to energize the POWER MIG 200. See Figure
B.1.
Voltage Control — Seven voltage tap selections are
provided Labeled "A" (minimum voltage) through "G"
(maximum voltage). It should only be adjusted when
not welding. The control selection can be preset to the
setting specified on the Procedure Decal on the inside
of the wire compartment door. See Figure B.?.
Wire Speed Control — This controls the wire feed
speed from 50 – 700 inches per minute (1.2 – 17.8
m/min). Wire speed is not affected when changes are
made in the voltage control. See Figure B.1.
WIRE DRIVE ROLL
The drive rolls installed with the POWER MIG each
have two grooves, both for .030-.035" (0.8-0.9 mm)
solid steel electrode. Drive roll size is indicated by the
stenciling on the exposed side of the drive roll. If feed-
ing problems occur, then the drive roll may be reversed
or changed. See "Procedure for Changing Drive
Roll" in this section.
WIRE SIZE CONVERSION PARTS
The POWER MIG 200 is rated to feed .025 through
.045" (0.6-1.2 mm) solid or cored electrode sizes.
The drive roll kits and Magnum 250L gun and cable
parts are available to feed different sizes and types of
electrodes. See Accessories section.
O
FF
O
N
WIRE FEED SPEED
VOLTAGE
ON/OFF SWITCH
Figure B.1. Control Locations
