Raid 5 – LaCie FIREWIRE 800/400 User Manual
Page 19
LaCie Biggest Quadra
User Manual
page
Understanding RAID
3.3. RAID 5
Independent Data Disks With Distributed Parity Blocks
This is the most versatile RAID level and offers high
I/O transaction rates, which greatly helps applications
that perform large numbers of concurrent requests. If
one drive in a RAID 5 array fails, the lost data can be
rebuilt from data on the remaining, functional disks.
Essentially, RAID level 5 is a striped set with parity,
and requires at least three disks to implement. In this
configuration, data is saved across several hard disks, as
in a RAID 0 array, but parity information is also saved
across the disks. It is this parity information which pro-
vides the fault-tolerance protection; if one hard disk in
the set fails, the data that it contains can be rebuilt by
utilizing the parity information from the other hard
disks. With the parity data being stored across the ar-
ray, this also serves to maximize the amount of storage
capacity available amongst the disks in the array while
still providing data redundancy.
Storage capacity in a RAID level 5 configuration is
the result of a mathematical expression that compares
data from the drives and a calculates another piece of
data called parity. In this situation, then, storage capacity
is calculated by multiplying the number of disks in the
array, minus one, by the capacity of the smallest disk in
the array. So, for instance, if a RAID 5 array is created
with four drives of varying capacities of 40GB, 50GB,
60GB and 70GB, the total capacity of the array would
be 120GB [3 (4 disks – 1 disk) x 40 = 120].
Characteristics and Advantages
■
Highest Read data transaction rate
Medium Write data transaction rate
High efficiency through a low ratio of ECC (Par-
ity) disks to data
Good aggregate transfer rate
❖
❖
❖
❖
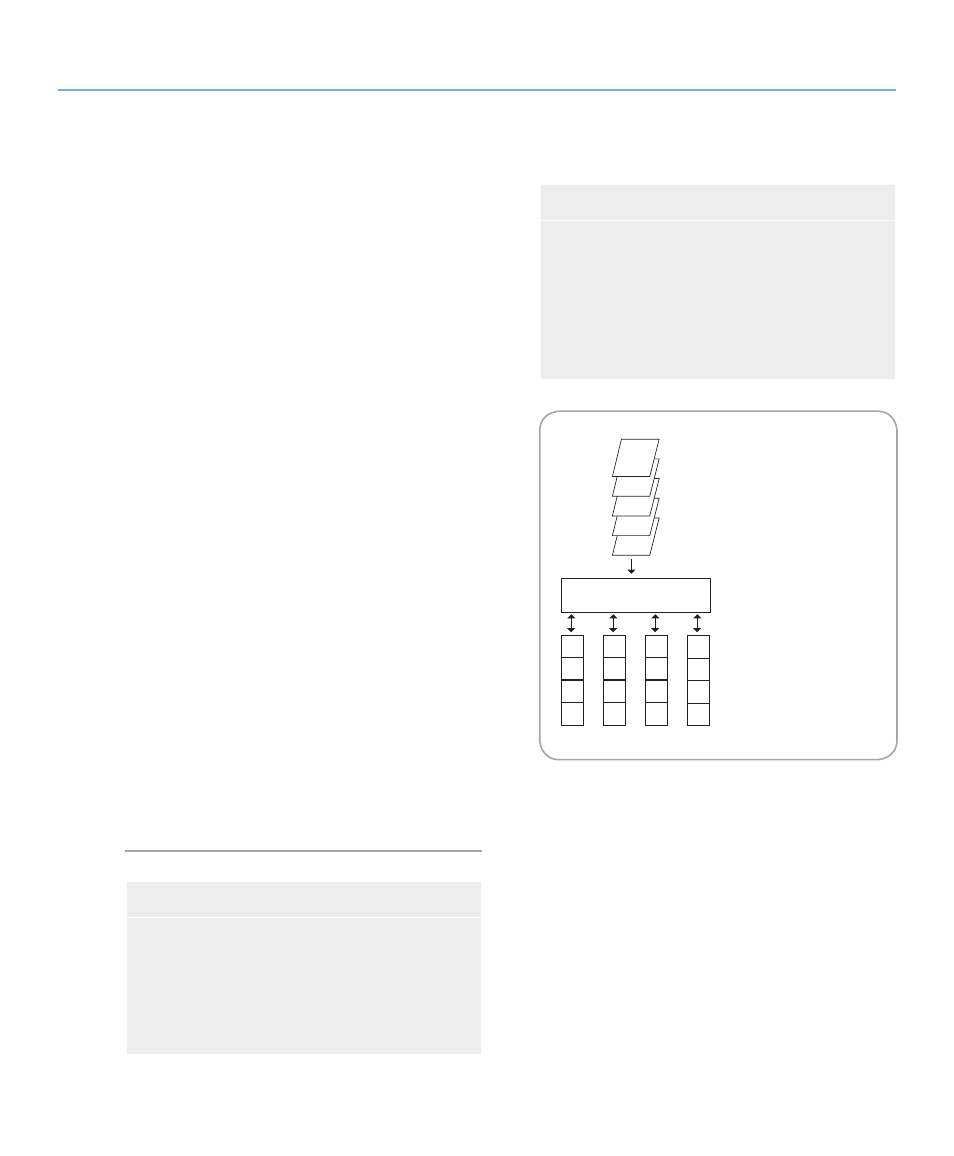
This diagram represents a
RAID 5 array, consisting of
four disks, which are
connected to the Controller.
Parity blocks are represented
by the letter P.
A
D
P
JKL
G
B
E
J
C
H
K
F
I
E
D
C
B
A
CONTROLLER
P
ABC
L
P
GHI
P
DEF
Recommended Uses
■
File and Application Servers
Database Servers
Web, E-mail and News Servers
Intranet Servers
❖
❖
❖
❖
Fig. 3.3.
