Figure 41, Example of an rf 50 line, Table 39 – Sierra Wireless WISMO218 User Manual
Page 81: Antenna specifications
WA_DEV_W218_PTS_002
Rev 005
Page 81 of 109
Product Technical Specification &
Customer Design Guidelines
Table 39. Antenna Specifications
Characteristic
WISMO218
E-GSM 900
DCS 1800
TX Frequency
880 to 915 MHz
1710 to 1785 MHz
RX Frequency
925 to 960 MHz
1805 to 1880 MHz
Impedance
50
VSWR
Rx max
1.5 :1
Tx max
1.5 :1
Typical radiated gain
0dBi in one direction at least
Caution: Sierra Wireless strongly recommends working with an antenna manufacturer either to develop an
antenna adapted to the application or to adapt an existing solution to the application. Both the
mechanical and electrical antenna adaptations are one of the key issues in the design of the GSM
terminal.
The RF antenna connection uses one of the castellation pins of the WISMO218, with grounded
castellation pins at both sides.
This castellation pin must be connected to an RF 50 line, in order to protect the antenna line from
the noise coming from base-band signals.
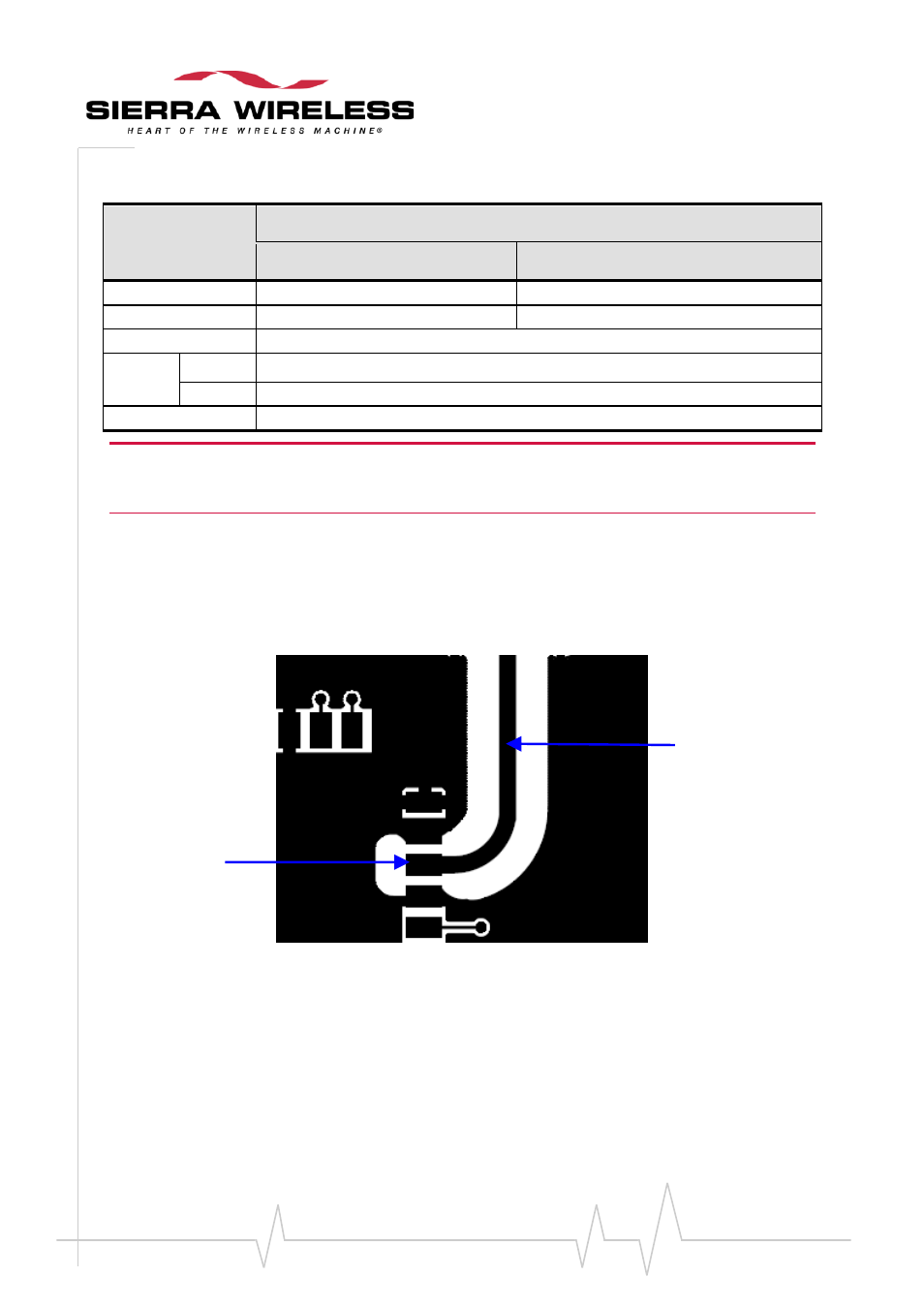
Figure 41. Example of an RF 50
line
This 50 line is surrounded by two ground planes in order to protect this antenna line from noise.
The length of the line shouldn’t be too long (more than a few centimeters) because of RF insertion
loss. The width of the line must be calculated in order to ensure a 50 characteristic impedance.
For this same reason, the RF embedded line should likewise be kept about 1cm away from any (noisy)
baseband signal in order to ensure a good RX sensitivity level.
The other end of the RF 50 line can be connected to an RF connector or a soldering pad in order to
connect an antenna.
Castellation pin for ANT
50
RF line
