Task file registers – Maxtor DIAMONDMAX 91536H2 User Manual
Page 35
HOST SOFTWARE INTERFACE
6 – 1
SECTION 6
Host Software Interface
The host communicates with the drive through a set of controller registers accessed via the host’s I/O ports.
These registers divide into two groups: the Task File, used for passing commands and command parameters and
the Control/Diagnostic registers.
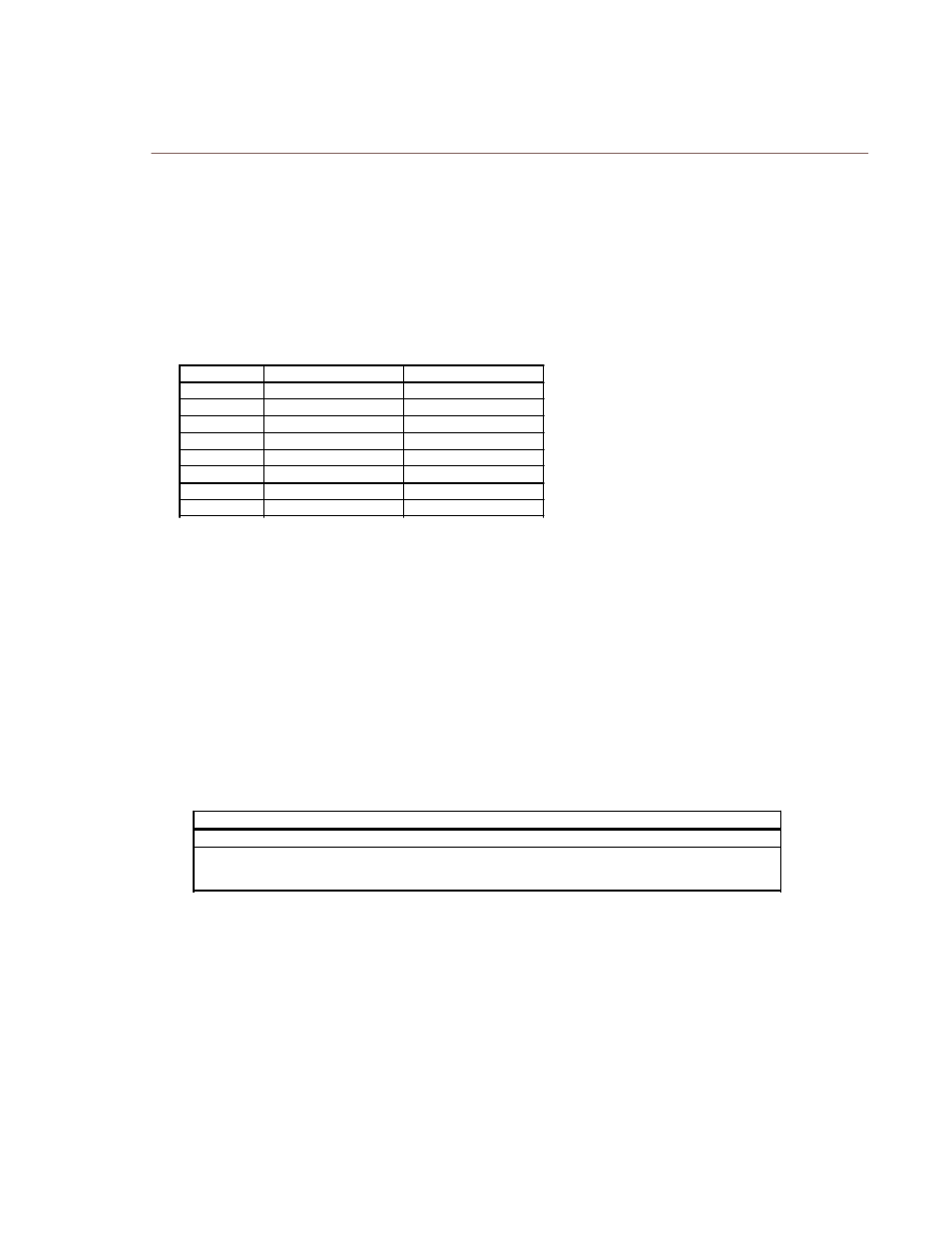
Task File Registers
The Task File consists of eight registers used to control fixed disk operations. The host accesses each register
by the I/O port address shown in this Task File register map:
I/O PORT
R E A D
WRITE
1 F 0 h
Data Register
Data Register
1 F 1 h
Error Register
Features Register
1 F 2 h
Sector Count
Sector Count
1 F 3 h
Sector Number
Sector Number
1 F 4 h
Cylinder Low
Cylinder Low
1 F 5 h
Cylinder High
Cylinder High
1 F 6 h
Drive/Head (SDH)
Drive/Head (SDH)
1 F 7 h
Status Register
Command Register
Data Register
Provides access to the drive’s sector buffer for read and write operations. With the exception of ECC byte
transfers (which, during Read long and Write long commands, are 8 bits wide), data transfers through the
Data register are all 16 bits wide.
Error Register
A read-only register containing specific information regarding the previous command. Data interpretation
differs depending on whether the controller is in operational or diagnostic mode. A power up, reset,
software reset, or receipt of a diagnostic command sets the controller into diagnostic mode. This mode
invalidates contents of the Status register. The contents of the Error register reflect a completion code.
Issuing any command (apart from a Diagnostic command) places the controller into operational mode.
In operational mode, the Error register is valid only when the Error bit in the Status register is set. The bit
definitions for operational mode follow:
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
0
E C C
0
IDNF
0
ABRT
TK0
AMNF
Interface
C R C
Data
E C C E r r o r
Not
Used
ID
Not Found
Not
Used
Aborted
Command
Track 0
Error
Address
Mark Not
Found
Interface CRC – An interface CRC error occurred during an Ultra DMA transfer.
Data ECC Error – An non-correctable ECC error occurred during a Read Sector command.
Firmware Problem – Indicates a firmware problem was detected, (e.g., invalid interrupt, divide overflow).
ID Not Found – Either a matching ID field not found, or a CRC error occurred.
Aborted Command – Invalid commands, write fault, no seek complete, or drive not ready.
Track 0 Error – Track 0 was not found during execution of a Restore command.
Address Mark Not Found – The Address Mark could not be found after an ID match.
Features Register
Enables or disables features through the Set Features command.
