Communication requests, Commreq ladder instruction – GE GFK-2193A User Manual
Page 20
GFK-2193A
Chapter 4 Status and Diagnostics
4-3
4
Enable Input
Command Block Pointer
Rack/Slot Location
Task #
Fault Output
COMM_
REQ
IN FT
SYSID
TASK
Communication Requests
The Communications Request uses the parameters of the COMMREQ Ladder Instruction
and an associated Command Block to define the characteristics of the request. An
associated Status Word reports the results of each request.
The Communication Request function (COMMREQ) allows the program to communicate
with a GE Fanuc intelligent module, such as a PROFIBUS slave module.
The COMMREQ function uses a command block that contains the data to be
communicated to the other device, plus information related to the execution of the
COMMREQ. The command block must be placed in the designated memory area using
data move instructions, such as MOVE or BLKMOV (Block Move).
The CPU reports the result of the COMMREQ in the status word, which is a single
location in PLC data memory. The status word address is specified in the command block.
For a list of status codes reported in the status word, see “COMMREQ Status Word” on
page 4-6.
The PROFIBUS slave module supports one COMMREQ, described on page 4-7.
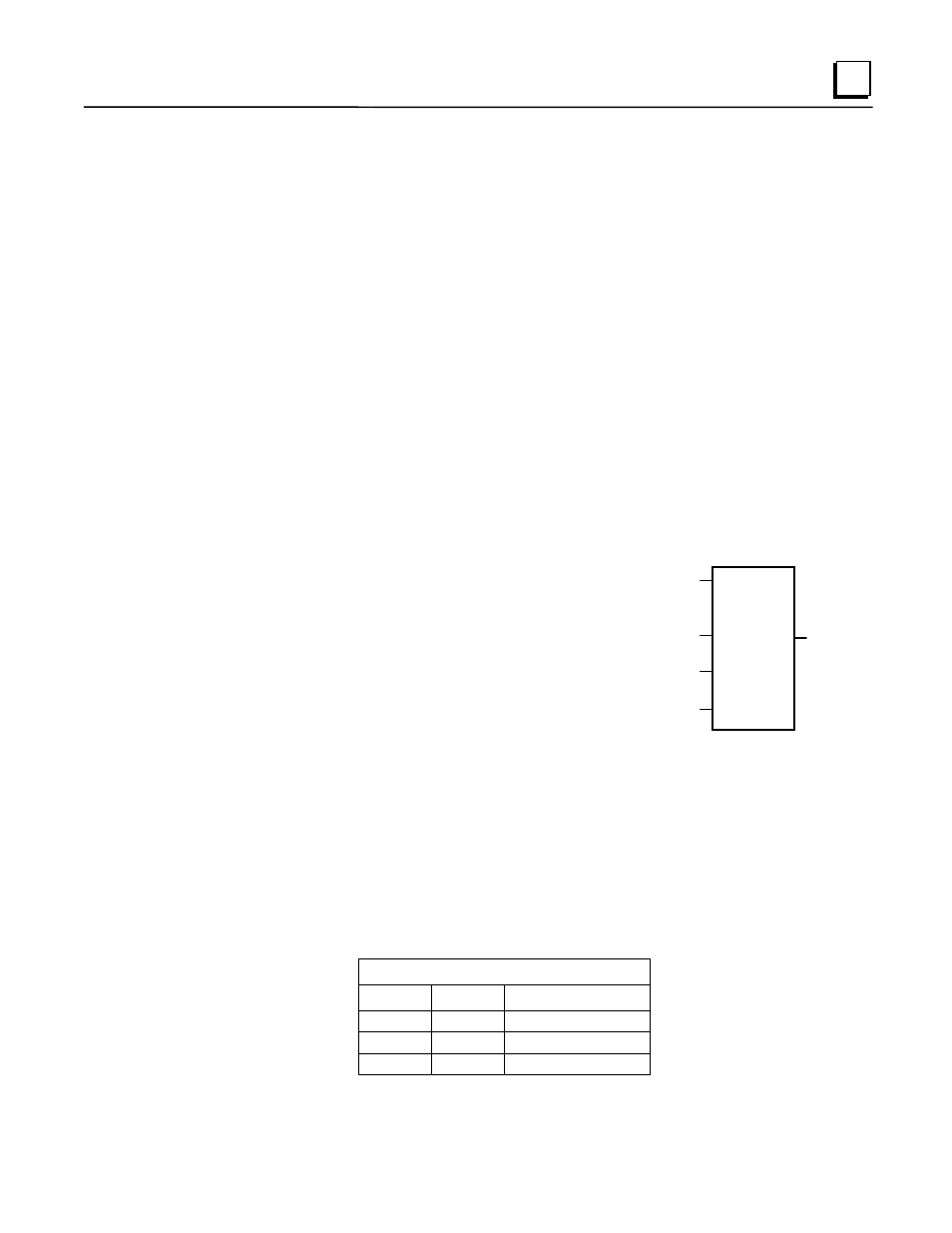
COMMREQ Ladder Instruction
This discussion provides an overview of
the COMMREQ instruction. For details
of the COMMREQ ladder instruction,
refer to the online help provided with the
programming software. The
Communications Request begins when
the COMMREQ Ladder Instruction is
activated. The COMMREQ ladder
instruction has four inputs and one
output:
Figure 4-1. COMMREQ Ladder Instruction
Enable Input: Must be Logic 1 to enable the COMMREQ Instruction. It is recommended that
the enabling logic be a contact from a transition (“one-shot”) coil.
IN: The memory location of the first word of the Command Block. It can be any valid
address in word-type memory (%R, %AI, or %AQ). For example, %R00100 at IN would
indicate that the starting address of the Command Block is %R00100.
SYSID: The rack and slot location of the module that the COMMREQ is targeting. The high
byte contains the rack number, and the low byte contains the slot number. The table
below shows some examples of SYSIDs:
SYSID Examples
Rack Slot Word
Value
0 4
0004
3 4
0304
2 9
0209
TASK: Must be set to 1.
