Grundig Digital Radio User Manual
Page 74
DIGITAL RADIO GUIDE
SATELLITE TRANSMISSION - SIRIUS / XM
74
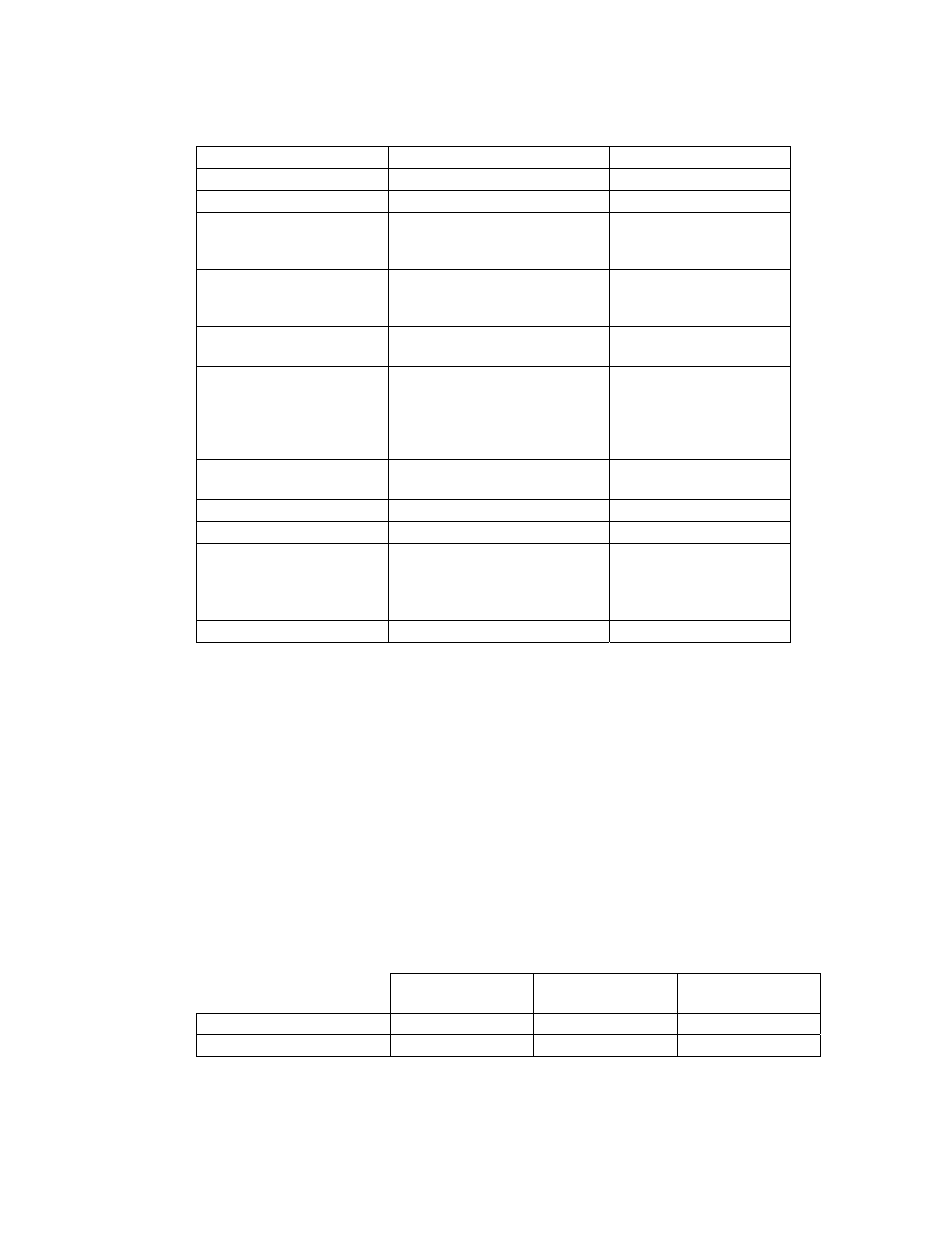
Changes Made For Sirius Inclined Elliptical Orbits
Parameter
Geostationary
Inclined Elliptical
Dry Mass
1300 kg
1575 kg
RF power (operating)
2.5 kW
4 kW
DC power – EOL
Solar Array
Battery
7.5 kW
7.5 kW
8.5 kW
8.8 kW
Control System
3-wheel mom bias
4-wheel mom bias
On-board orbit
propagator
Control Modes
Orbit Normal
Orbit Normal
Yaw Steering
TX Antenna
Fixed Gregorian
Gain 27.8 dBi;
Cross-pol 24 dB
Gregorian; two axis
steering 360º rotating
shaped subreflector
Gain 27.2 dBi; Cross-
pol 28 dB
RX Antenna
Fixed offset fed
Offset fed; two axis
steering
Solar array
2x4 panel HES
2x5 panel HES
Battery
2x32 cell - 149 AH
2x34 cell - 178 AH
TT&C
X, C and S bands
CONUS ground station
Limited motion antennas
C and S bands
2 near equatorial
ground stations Full
motion antennas
Launch Vehicle
Ariane
Proton
The launch of the Sirius Satellite Radio constellation marks the first use of satellites for
Digital Audio Radio Service broadcasting in the United States. The three high power
direct broadcast satellites will provide service for millions of subscribers. The Sirius Radio
system is the world’s first satellite broadcast system using non-geostationary orbits.
The use of inclined elliptical orbits coupled with multiple modes of transmission diversity
provides notable advantages for broadcast service to the mobile market. Pioneering
technology was developed and implemented by Sirius Satellite Radio and Space
Systems/Loral in order to accomplish this unique achievement.
5.2.2
Deployment Status
Current population and transmission status of Sirius and XM satellite radio services is
shown in the following chart.
Continental US
Coverage
Satellites
Ground
Repeaters
Sirius Satellite Radio
100%
3 in HEO
~100
XM Satellite Radio
100%
2 in GSO
~800
