Grundig Digital Radio User Manual
Page 25
DIGITAL RADIO GUIDE
TERRESTRIAL TRANSMISSION SYSTEMS - DAB
25
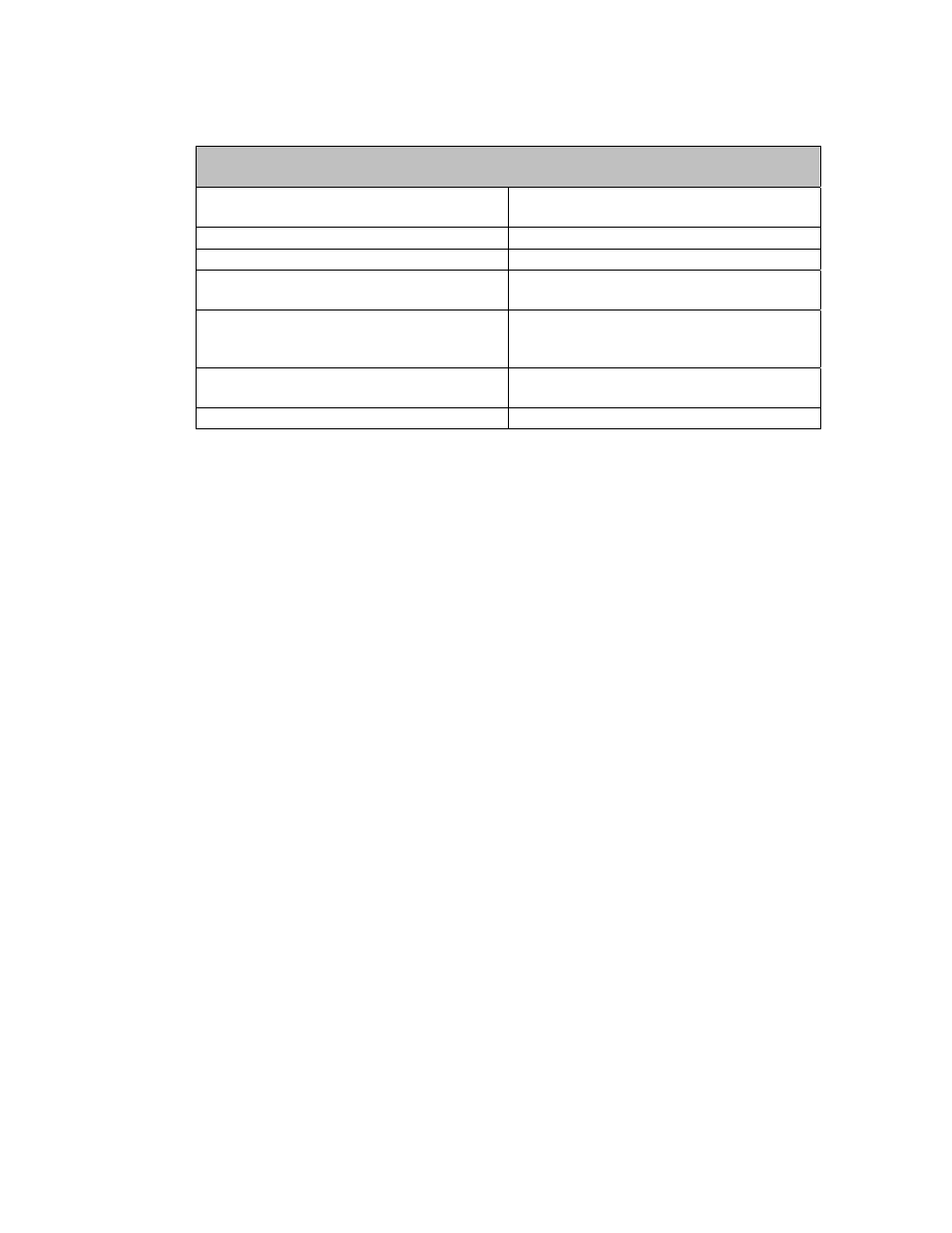
Table 4.1. Eureka 147 Main System Features
EUREKA 147
Main System Features
Single Frequency Network (SFN)
capability
All transmitters working on a single
frequency.
Flexible audio bit rate
Allows reconfiguration of the multiplex.
Data services
Separately defined streams or packets.
Programme Associated Data (PAD)
Embedded in the audio bit stream and
adjustable.
Facilitates Conditional Access
DAB ensemble transports conditional
access information (CAI) and provides
signal scrambling mechanism.
Service Information
Used in the operation and control of
receivers.
Operating frequency range
30 MHz to 3 GHz.
4.2.4
Infrastructure Requirements
Eureka 147 is a wideband technology requiring services to be multiplexed before
transmission. The use of VHF and UHF bands means Eureka 147 services will be
typically transmitted from high sites such as the tops of hills, buildings or towers.
In general, new Eureka 147 services are also likely to be co-located with existing FM
radio or television transmission services given the cost of developing new sites and the
increasing difficulty in getting local council planning approval for new transmission sites.
In Canada, implementation of the Eureka system uses a new band (L-Band), hence new
transmitters, antenna system, exciter and encoders have been required. Stations that
were originally broadcasting more than one FM program from the same site can fully
encapsulate the multiplexed stream of the DAB system in the STL (studio-to-transmitter
link), significantly reducing the costs associated with discrete feeder links.
Canada’s
DAB allotment plan has room for the replacement of all existing AM and FM stations in
the L-Band. The plan also includes many empty allotments for future services. Finally,
since the plan was based on providing only five programming channels in each DAB
multiplex, new audio coding schemes will allow for the possible implementation of two to
three additional services in each ensemble.
4.2.5
Synergies with Other Systems
(1)
DAB and GSM (Global System for Mobile Communications)
DAB is an efficient broadcasting (e.g., one-to-many) system capable of providing
reliably digital services to all users located in a coverage zone in real time. It is
especially suitable for the reception to mobile and portable receivers and in the
areas in which the direct line of sight between the transmitter and the receiver is
not possible.
On the other hand, GSM (Global System for Mobile Communications) and its
successors (GPRS and UMTS) are more suitable to deliver on-demand media
