Grundig Digital Radio User Manual
Page 53
DIGITAL RADIO GUIDE
TERRESTRIAL TRANSMISSION SYSTEMS - HD RADIO
53
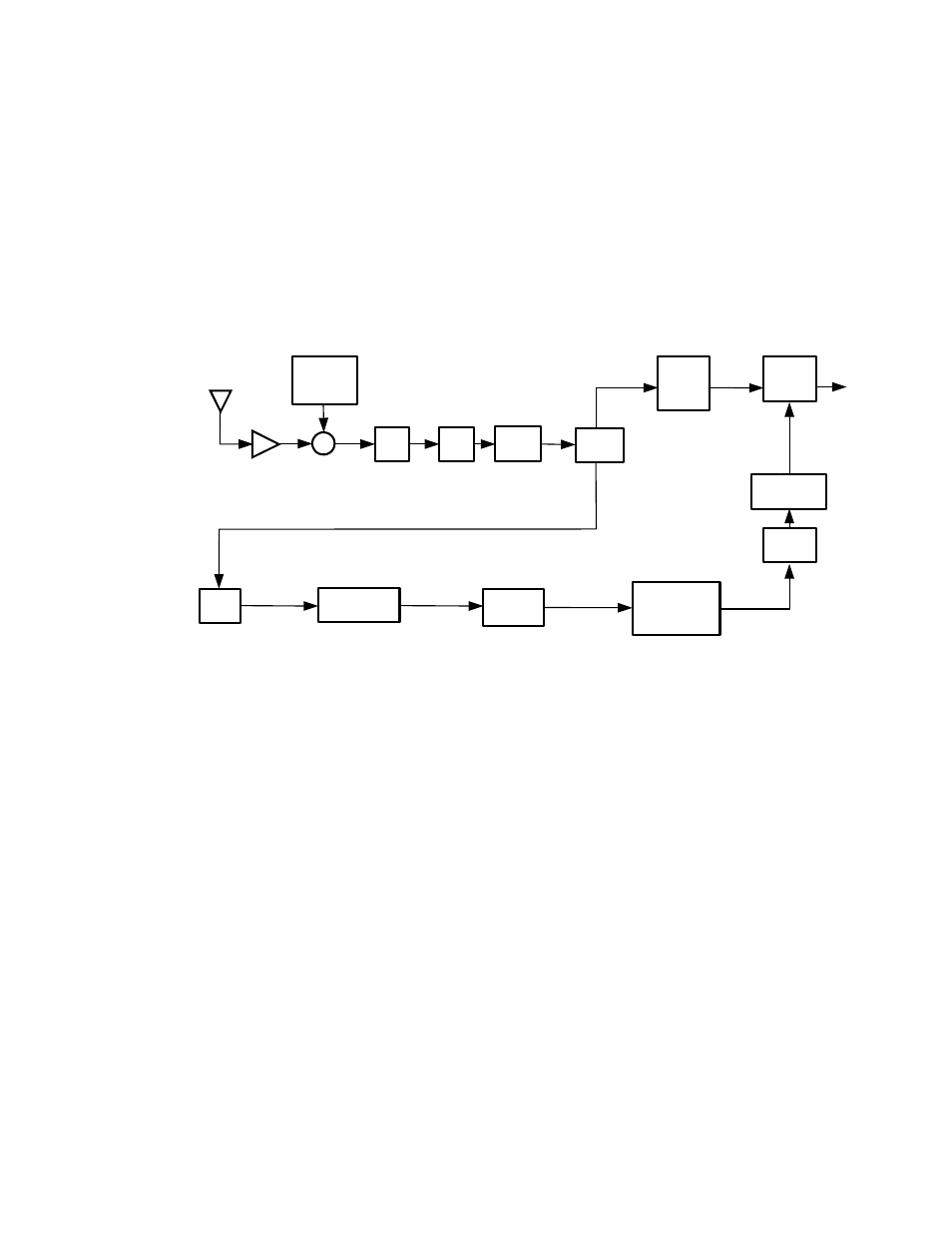
stereo signal is digitally demodulated and demultiplexed by the FM receiver to produce a
sampled, stereo audio signal.
The base band digital signal is first sent to the modem, where it is processed by the First
Adjacent Cancellation system to suppress interference from potential first-adjacent
analogue FM signals. The signal is then OFDM demodulated, deframed, and passed to
the FEC decoding and deinterleaving function. The resulting bit stream is processed by
the codec function to decompress the source-encoded digital audio signal. This digital
stereo audio signal is then passed to the blend function.
Figure 4.15: FM hybrid IBOC receiver functional block
FM
Isolation
FAC
QPSK/OFDM
Demodulator
Deframe
FM+DAB
sa m p le d a n a lo g u e FM
Audio
Decoder
X
BPF
A/D
DDC
FM
Stereo
Det
Tunable
LO
RF Front End
10.7 MHz IF
Audio
Diversity
Delay
Audio
Blend
FM
Stereo
DSB
Stereo
FEC Decode
and
De-interleave
4.4.7
Features Common to North American Digital Radio Systems
(1)
Sound Quality
Sound quality of digital radio systems has improved dramatically in recent years
with progressively lower bitrates being shown in various applications as achieving
near CD quality. Rates well below 96 kbps are routinely utilized in digital radio
systems in operation in North America and meeting with wide customer acceptance.
(2)
Multipath Resistance
OFDM based systems are made to be resistant to multipath within a guard interval.
In the case of the Eureka system, the guard interval is set to 62 ?s (18.6 km at the
speed of light). This means that any echoes coming from up to 18.6 km will be
considered as constructive to the signal. This allows the use of on-channel
repeaters (that are treated as active echoes).
Note also that some systems, such as the Eureka system, also use unequal error
protection and error concealment techniques. This allows for a graceful
degradation of the digital signal quality when fading occurs and allows for S/N
requirement reductions for the receiver. The Eureka system is especially noted for
achieving multipath free reception, but narrower bandwidth systems such as the
