FieldServer FS-8704-12 User Manual
Page 10
FS-8704-12 GE-EGD Driver Manual
Page 10 of 23
FieldServer Technologies 1991 Tarob Court Milpitas, California 95035 USA Web: www.fieldserver.com
Tel: (408) 262 2299 Fax: (408) 262 2269 Toll Free: (888) 509 1970 email: [email protected]
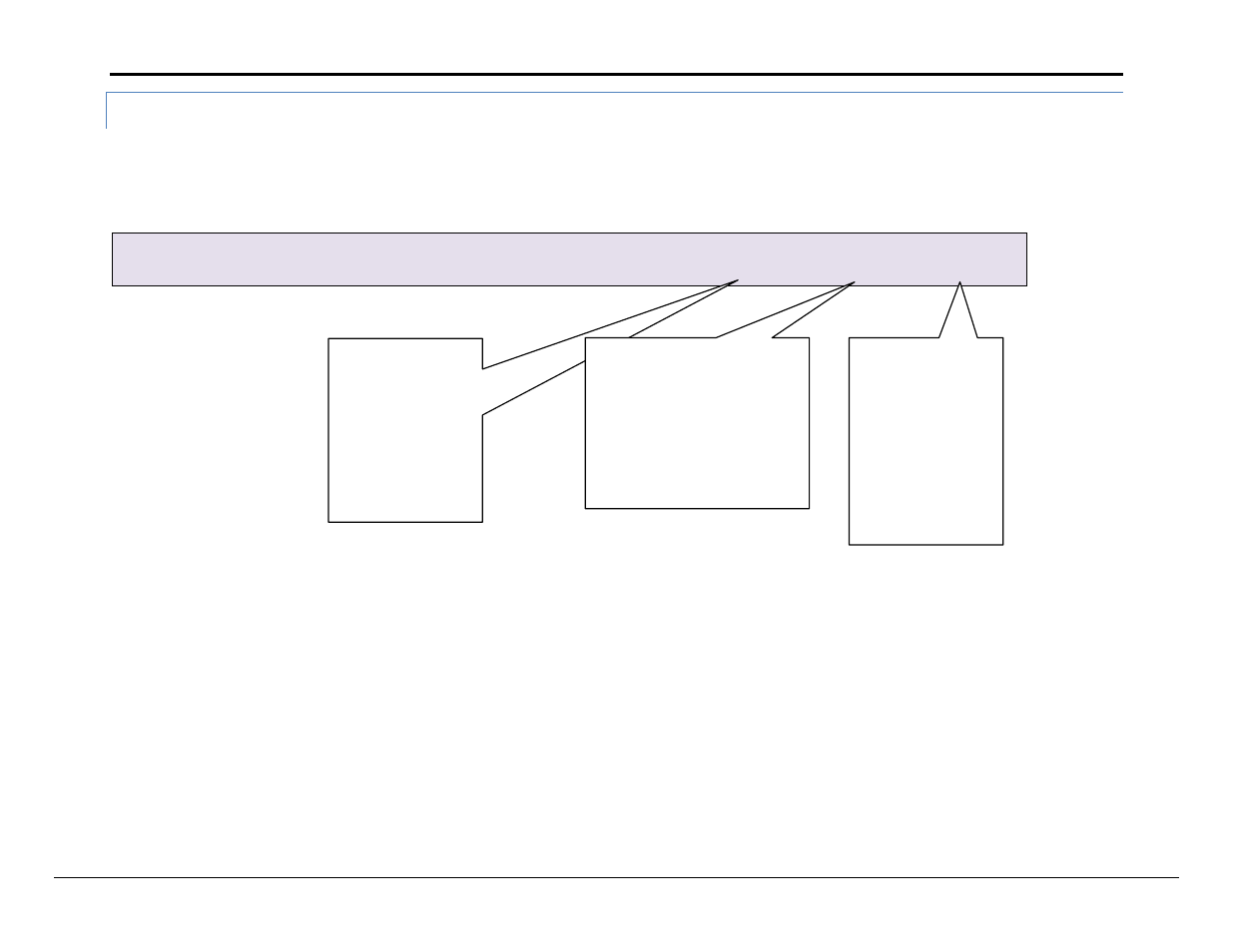
5.3.4 Map Descriptor Example 2: - Mult iple Consumer Map Descriptor
In this example we assume that one produced data packet (produced by 0.0.0.1 and identified as exchange 1) contains different types of data elements making
up the single exchange. This is configured when configuring EGD for the producer. The arrangement of data must correspond exactly with the configuration of
the Map Descriptors used to consume the data. The following two Map Descriptors imply that the exchange contains at least 180 bytes of data and that the
first 40 bytes contain 20 word values and that bytes 100 to 179 contain bit values. We cannot deduce what bytes 40-99 contain.
Map_Descriptor_Name
, Data_Array_Name
, Data_Array_Offset
, Function
Node_Name
Length
Ge_ProducerID
Ge_ExchangeID
Ge_Data_Type
ge_offset
A1
, DA_AI3
, 0
, Passive
Node_A
20
0.0.0.1
1
Int
0
A2
, DA_DI1
, 0
, Passive
Node_A
80
0.0.0.1
1
Bit
100
The producerID and
exchangeID for both
these Map
Descriptors are
identical. Therefore
they will both be
applied to the same
incoming data
packet.
The 2nd Map
Descriptor will
process data bytes
starting at byte 100.
As the first byte is
identified as byte
zero, byte 100 is
actually the 101st
byte in the data part
of the message.
The data types are different.
The first Map Descriptor will be
used to interpret incoming
data as integers and the
second will interpret data as
bits. These data types must
correspond to the way the
producer is configured.
