Xygen, Ensor – HONDA Insight User Manual
Page 87
87
L
EAN
-B
URN
O
XYGEN
S
ENSOR
A normal zirconia oxygen sensor is only capable of measuring the oxygen content of the exhaust in a
narrow air-fuel mixture range, right around stoichiometric (14.7:1). This is fine for normal operating
conditions. But, when the car is running in the lean burn mode, the oxygen content of the exhaust is higher
than a normal oxygen sensor is capable of measuring.
The Insight uses a LAF (Linear Air-Fuel) sensor for the primary oxygen sensor that is capable of
measuring air-fuel ratios as lean as 23:1. This allows the ECM to maintain precise control over the mixture
during both normal and lean burn conditions.
The engine's LAF Sensor is designed to detect air-fuel ratios as lean as 25:1. The fuel-injection
Electronic Control Module uses this data, along with engine rpm, crankshaft angle, throttle angle, car mass,
coolant temperature and valve position, to maintain a lean air-fuel ratio below 2500-3200 rpm (depending
on throttle position and engine load).
The VTEC-E engine can burn such a lean mixture partly because of a strong air-fuel swirl created in
the combustion chamber, created by the mixture's entry through only one of two intake valves during low-
rpm operation. Although the overall air-fuel mixture is lean, optimized injection timing, along with the
vortex, creates a "stratified" charge - the air-fuel ratio is richer near the spark plug and leaner toward the
combustion chamber periphery. The richer mixture ignites more readily and creates a fast-burning, stable
flame that promotes more complete combustion.
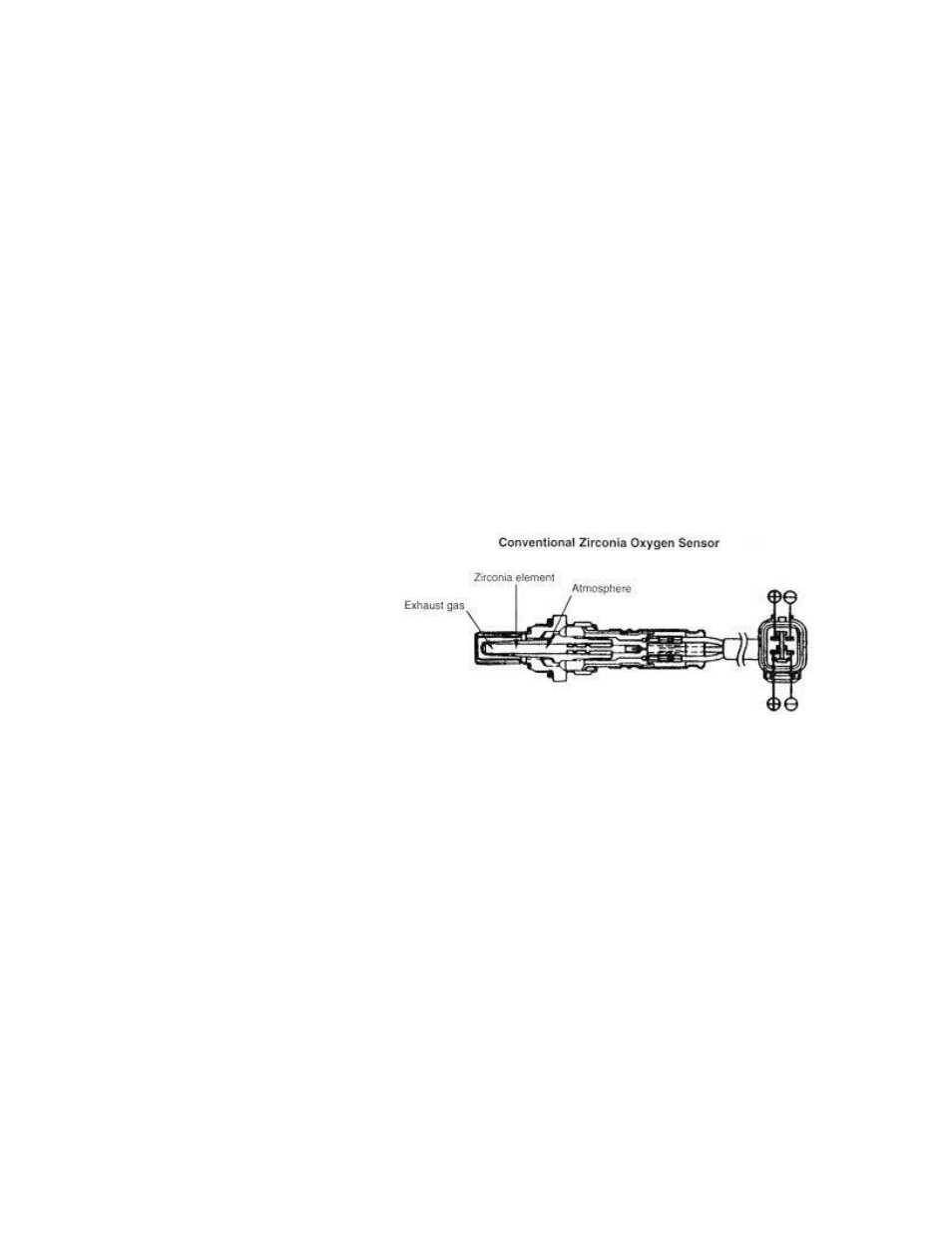
A standard zirconia oxygen sensor
uses a thimble shaped zirconia element
that is exposed to the atmosphere on
one side, and to the exhaust stream on
the other side. If the amount of oxygen
on the two sides is different, it generates
a voltage. Since the amount of oxygen
on the atmospheric side is fixed, the
generated voltage represents the amount
of oxygen in the exhaust. With the
engine not running there is atmospheric
pressure in the exhaust, and the voltage
is zero since the same amount of
oxygen exists on both side of the element. When the engine is running there is less oxygen in the exhaust,
so voltage is generated up to a maximum of one volt.
The LAF sensor has two zirconia elements that share a diffusion chamber. There are a total of three
chambers:
• Exhaust flow chamber
• Diffusion chamber
• Atmosphere reference chamber
The zirconia element that is in contact with the exhaust is the sensor element. The diffusion chamber is
the space between the two zirconia elements. By applying varying voltage to the control element, the ECM
can control the amount of oxygen in the diffusion chamber. Since the diffusion chamber is the reference
chamber for the sensor element, this action changes the output of the sensor element.
The ECM monitors the output of the sensor element as the oxygen content of the exhaust changes, and
it applies voltage to the element to try to maintain the sensor output at .450 volts. It then monitors the
control voltage to determine the actual air-fuel ratio.
