Engaged applicatio, Engaged application, Operation – SAF-HOLLAND XL-AR363-02 EDL/ARF Feature User Manual
Page 9
XL-AR363-02 Rev. D
9
OPERATION
continued
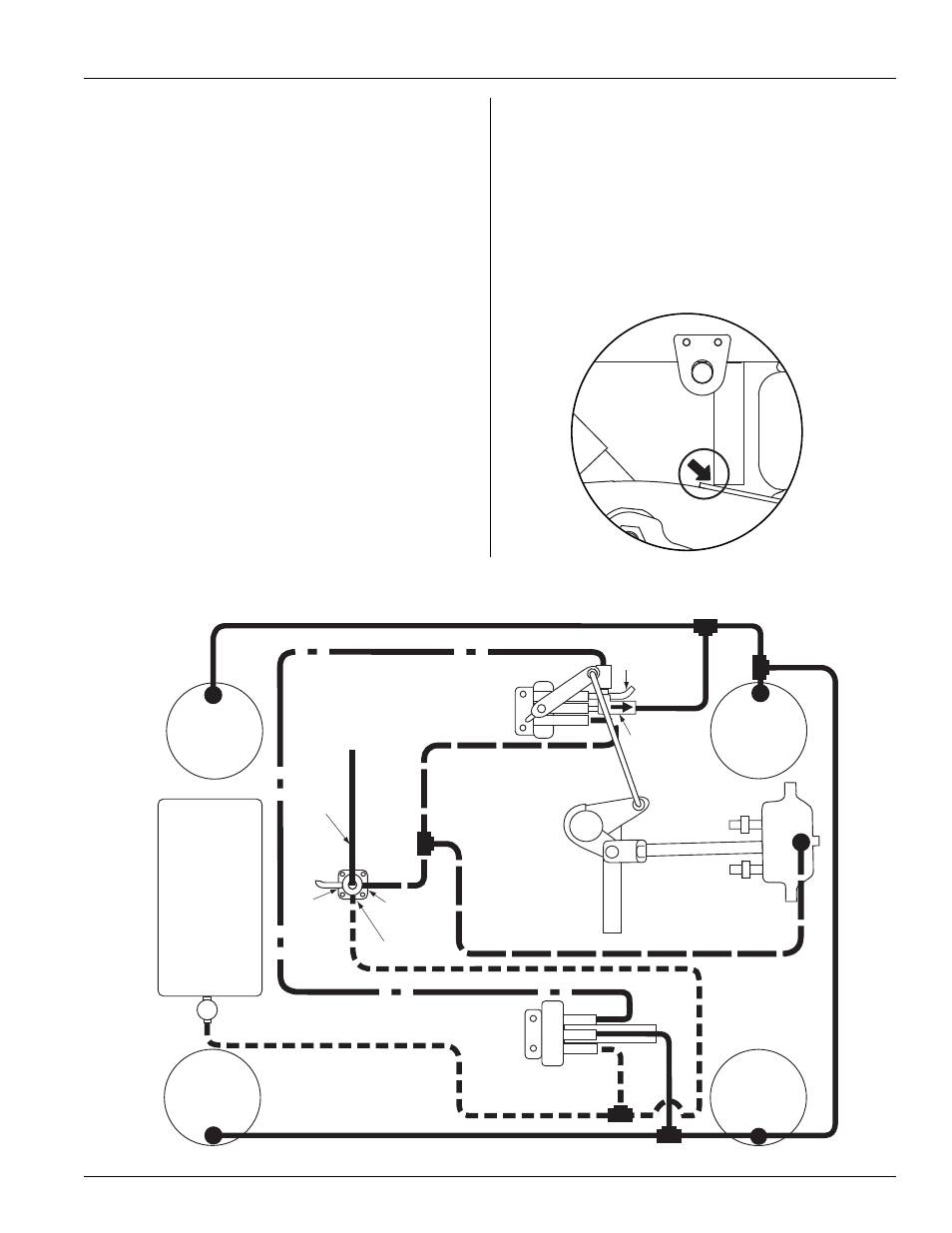
FIGURE 17
Trapped
Flipper Plate
Trapped
Flipper
Plate
N.C. Port
Cylinder
Port
N.O.
Port
Exhaust To
Atmosphere
Pilot (Top)
Port to
Emergency
Brake Line
Exhaust
Air Spring
Air
Reservoir
Air Spring
Pressure Protection Valve
Minimum of 75 psig (5.2 bars) to allow
Air to Flow through Valve
Primary
Height
Control
Valve
Auto
Reset
(Sensor)
Valve
Air Spring
Air Spring
One-Way
Check
Valve
EDL
Flipper
Plate
Engaged
(Down) Position
Pilot
Valve
EDL
Actuator
FIGURE 18
EDL/ARF Piping Diagram with Flipper Plates Engaged (down position)
ARF Description when Releasing
Trapped Flipper Plates
Trapped flipper plates in the down (engaged)
position (
FIGURE 17
)
1. With parking brakes disengaged, the air reservoir begins to fill with
air. When air reservoir pressure reaches 85 psig (5.9 bars), the
pressure protection valve opens, supplying air to the
suspension system.
2. System pressure is supplied directly to the height control valve
(HCV) and to the normally closed (N.C.) port of the pilot valve.
3. As brake system pressure increases, pressure increases to the top
port or “pilot port” of the pilot valve.
4. Increased pressure to the “pilot port” opens the N.C. port of the
pilot valve, applying system pressure through the cylinder port to the
sensor valve and the EDL actuator chamber.
5. System pressure to the EDL actuator chamber in turn pushes the
actuator push rod—which is fastened to the EDL rod assembly by a
clevis and pin—attempting to rotate the
flipper plates up (out of the way).
6. At the same time system pressure is applied to the EDL actuator
chamber, air also flows through the sensor valve and one-way check
valve. Air flowing through the check valve into the air springs
temporarily raises the slider box. With the slider box raised—freeing
the “trapped” flipper plates—the actuator push rod rotates the
flipper plates up.
7. After quickly releasing the flipper plates, the HCV returns the
suspension to its normal ride height. To return to the normal ride
height, increased air pressure from the air springs exhausts through
the HCV and out through the sensor valve top port.
