Assigning and editing vector variable data, Vector calculation examples, E-42 – Casio fx-115ES PLUS User Manual
Page 43
E-42
Assigning and Editing Vector Variable Data
Important: The following operations are not supported by the Vector Editor:
m, 1m(M–), 1t(STO). Pol, Rec, ÷R, and multi-statements also
cannot be input with the Vector Editor.
To assign new data to a vector variable:
1. Press
15(VECTOR)1(Dim), and then, on the menu that appears,
select the vector variable to which you want to assign data.
2. On the next menu that appears, select dimension (
m
).
3. Use the Vector Editor that appears to input the elements of the vector.
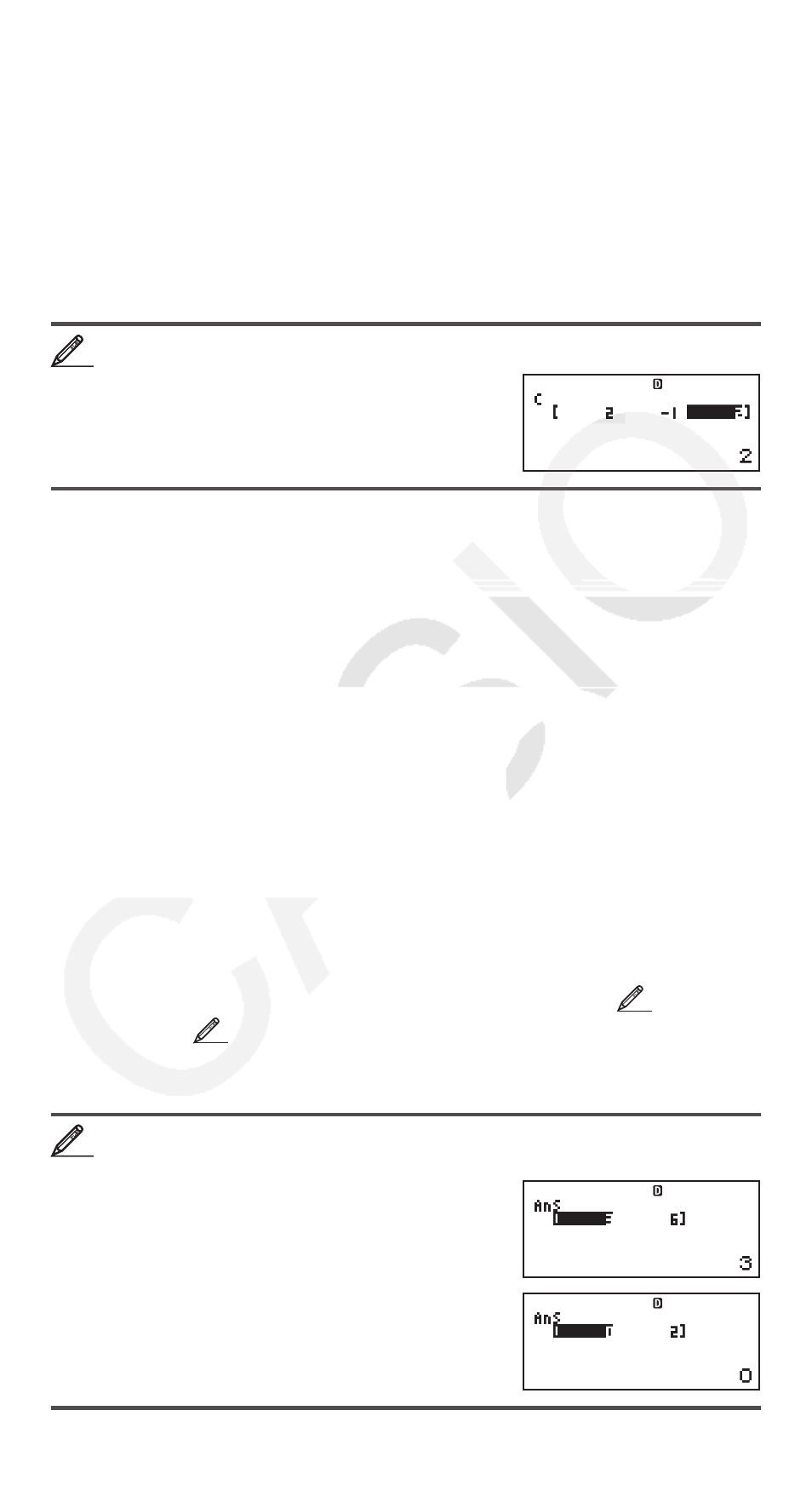
To assign (2, –1, 2) to VctC
15(VECTOR)1(Dim)3(VctC)1(3)
2
=- 1 = 2 =
To edit the elements of a vector variable:
1. Press
15(VECTOR)2(Data), and then, on the menu that appears,
select the vector variable you want to edit.
2. Use the Vector Editor that appears to edit the elements of the vector.
• Move the cursor to the cell that contains the element you want to change,
input the new value, and then press
=.
To copy vector variable (or VctAns) contents:
1. Use the Vector Editor to display the vector you want to copy.
• If you want to copy VctA, for example, perform the following key operation:
15(VECTOR)2(Data)1(VctA).
• If you want to copy VctAns contents, perform the following to display the
VctAns screen:
A15(VECTOR)6(VctAns)=.
2. Press
1t(STO), and then perform one of the following key operations
to specify the copy destination:
-(VctA), $(VctB), or w(VctC).
• This will display the Vector Editor with the contents of the copy
destination.
Vector Calculation Examples
The following examples use VctA = (1, 2) and VctB = (3, 4) from
1
, and VctC =
(2, –1, 2) from
2
. You can input a vector variable into a key operation by
pressing
15(VECTOR) and then pressing one of the following number
keys:
3(VctA), 4(VctB), 5(VctC).
3 × VctA (Vector scalar multiplication), 3 × VctA – VctB (Calculation
example using VctAns)
A 3 *VctA=
-VctB=
2
2
VCT
VCT
3
3
VCT
VCT
VCT
VCT
