Chapter 2 basic calculations, 4) coordinate conversion – Casio fx-7400G PLUS Basic Operation User Manual
Page 20
32
Chapter 2
Basic Calculations
Example
Operation
Display
What is the absolute value of
the common logarithm of
3
?
4
|
log
3
|
= 0.1249387366
K[1(NUM)
4
1(Abs)l(3/4)w
0.1249387366
What is the integer part of
K[1(NUM)
2(Int)(7800/96)w
81
What is the decimal part of
K[1(NUM)
3(Frac)(7800/96)w
0.25
200
÷ 6 =
200/6w
33.33333333
× 3 =
*3w
100
Round the value used
200/6w
33.33333333
for internal calculations
K[1(NUM)4(Rnd)w
33.33333333
to 11 digits*
*3w
99.99999999
What is the nearest integer
K[1(NUM)[1(Intg)
not exceeding – 3.5?
-3.5w
– 4
* When a Fix (number of decimal places) or Sci (number of significant digits) is in effect, Rnd
rounds the value used for internal calculations in accordance with the current Fix or Sci
specification. In effect, this makes the internal value match the displayed value.
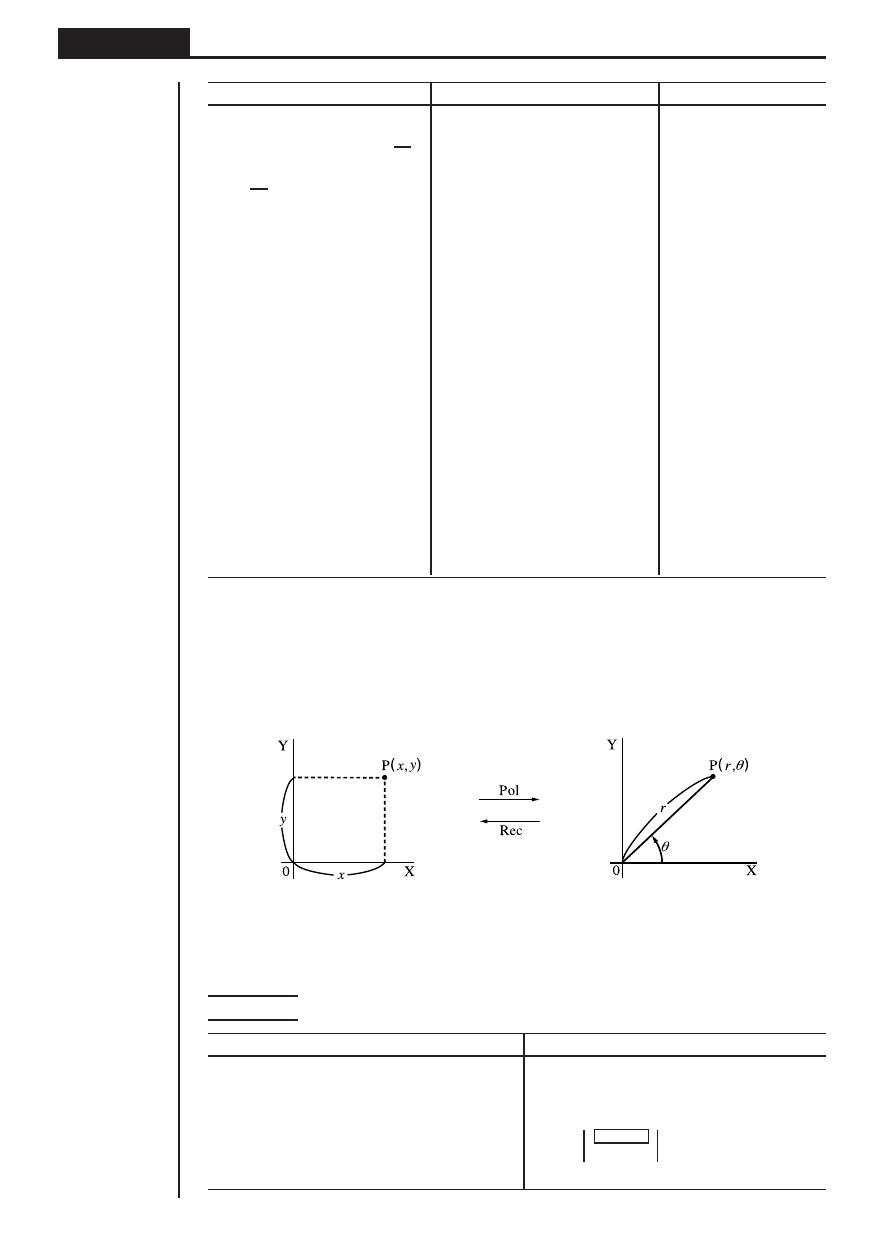
(4) Coordinate Conversion
u
uu
u
u Rectangular Coordinates
u
uu
u
u Polar Coordinates
• With polar coordinates,
θ
can be calculated and displayed within a range of
–180
°<
θ
< 180
° (radians and grads have same range).
Example
To calculate r and
θ
°
when x = 14 and y = 20.7
Operation
Display
!Zcc1(Deg)Q
K[2(ANGL)[[
1(Pol()14,20.7)w
Ans
1 –24.989–
→ 24.98979792 (r)
2 – 55.928 – → 55.92839019 (
θ
)
7800
––––– ?
96
7800
––––– ?
96
