SMA WB 3000-US User Manual
Page 6
SMA America, LLC
Turbine operation
Addendum operating requirements
DBWB30-40US-UUS113610
6/12
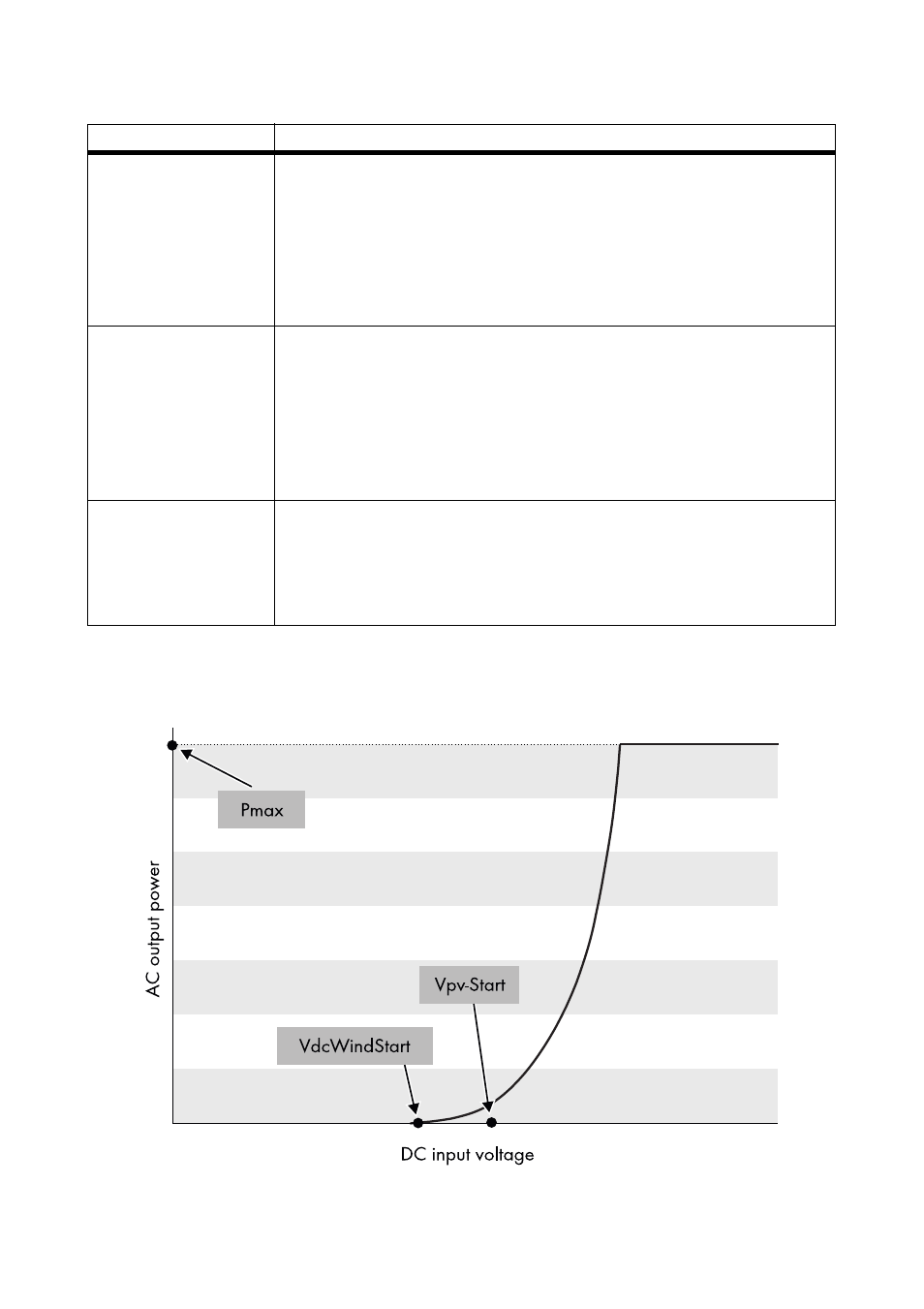
The inverter regulates its output power according to the generator voltage. The following illustration
shows the function of a typical polynomial characteristic curve. Here, the fed-in AC power is shown
according to the DC input voltage of the inverter.
KI-Wind-Ramp
This value defines the control speed of the power characteristic curve. The
inverter reacts to changes in the DC input voltage by adjusting its output
power using the power characteristic curve. The higher this parameter is
set, the quicker the inverter regulates the output difference in response to
changes in DC input voltage. Values that are too high lead to vacillations
and instability in the system. Values that are too low delay the optimal load
of the turbine and thereby reduce the optimal yield.
T-Stop
This value defines the time in which the inverter remains connected to the
grid despite low input voltage. When the DC input voltage exceeds the
minimum DC voltage, the inverter remains on the grid for the time "T-Stop"
, but does not feed in any power. During this time, it receives its own power
from the AC grid. When the DC input voltage exceeds the minimum DC
input voltage in that time, the inverter feeds the power directly into the grid.
No grid synchronization is required.
T-Start
This value defines the waiting time of the inverter, before it connects to the
grid. When the tests are successfully completed and the DC input voltage
rises above the configured time "Vpv-Start", the inverter connects to the
grid. This value is prescribed by country-specific standards and may only
be changed with the permission of SMA Solar Technology.
Parameter
Description
