Nat dns mapping configuration example – H3C Technologies H3C SecBlade FW Cards User Manual
Page 31
24
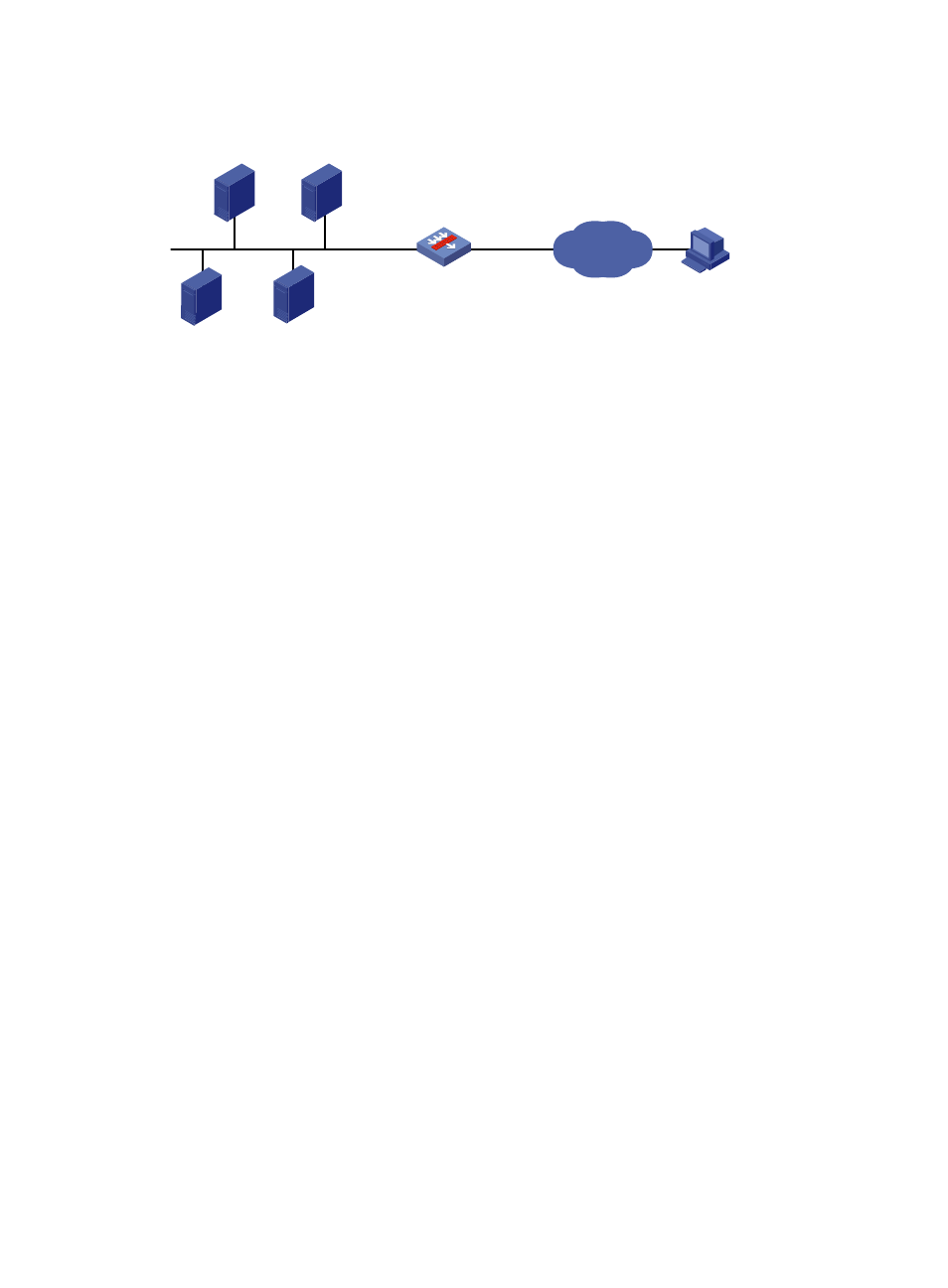
Figure 17 Network diagram for common internal server configuration
2.
Configuration procedure
# As shown in
, configure the IP addresses for the interfaces (omitted).
# Enter interface GigabitEthernet 0/2 view.
[Secpath] interface gigabitethernet 0/2
# Configure the internal FTP server.
[Secpath-GigabitEthernet0/2] nat server protocol tcp global 202.38.1.1 21 inside
10.110.10.3 ftp
# Configure the internal web server 1.
[Secpath-GigabitEthernet0/2] nat server protocol tcp global 202.38.1.1 80 inside
10.110.10.1 www
# Configure the internal web server 2.
[Secpath-GigabitEthernet0/2] nat server protocol tcp global 202.38.1.1 8080 inside
10.110.10.2 www
# Configure the internal SMTP server.
[Secpath-GigabitEthernet0/2] nat server protocol tcp global 202.38.1.1 smtp inside
10.110.10.4 smtp
[Secpath-GigabitEthernet0/2] quit
NAT DNS mapping configuration example
1.
Network requirements
As shown in
, a company provides Web and FTP services to external users, and uses internal IP
network segment 10.110.0.0/16. The IP addresses of the Web and FTP servers are 10.110.10.1/16 and
10.110.10.2/16 respectively. The company has three public addresses 202.38.1.1/24 through
202.38.1.3/24. The DNS server is at 202.38.1.4/24.
•
The public IP address 202.38.1.2 is used to provide services to external users.
•
External users can use the public address or domain name of internal servers to access them.
•
Internal users can access the internal servers by using their domain names.
FTP server
10.110.10.3/16
Web server 1
10.110.10.1/16
Web server 2
10.110.10.2/16
SMTP server
10.110.10.4/16
Host
Internet
GE0/1
10.110.10.10/16
GE0/2
202.38.1.1/24
SecPath
