Napt – H3C Technologies H3C SecBlade FW Cards User Manual
Page 10
3
A NAT gateway can also hold multiple public IP addresses to support concurrent access requests.
Whenever a new external network access request comes from the internal network, NAT chooses an
available public IP address (if any) to replace the source IP address, forwards the packet, and records the
mapping between the two addresses. In this way, multiple internal hosts can access external networks
simultaneously. This is called many-to-many NAT.
NOTE:
The number of public IP addresses that a NAT gateway needs is usually far less than the number of internal
hosts because not all internal hosts will access external networks at the same time. The number of public IP
addresses is related to the number of internal hosts that might access external networks simultaneously
during peak hours.
In practice, an enterprise may need to allow some internal hosts to access external networks while
prohibiting others. This can be achieved through the NAT control mechanism. If a source IP address is
among addresses denied, the NAT gateway will not translate the address.
Many-to-many NAT can be implemented by using an address pool, which is a collection of consecutive
public IP addresses. The NAT gateway selects addresses from the address pool for packets. The number
of addresses in the pool is determined according to the number of available public IP addresses, the
number of internal hosts, and network requirements.
NAT control can be achieved through ACLs. Only packets matching the ACL rules are served by NAT.
NAPT
Network Address Port Translation (NAPT) is a variation of NAT. It allows multiple internal addresses to be
mapped to the same public IP address, which is called multiple-to-one NAT or address multiplexing.
NAPT mapping is based on both the IP address and the port number. With NAPT, packets from multiple
internal hosts are mapped to the same external IP address with different port numbers.
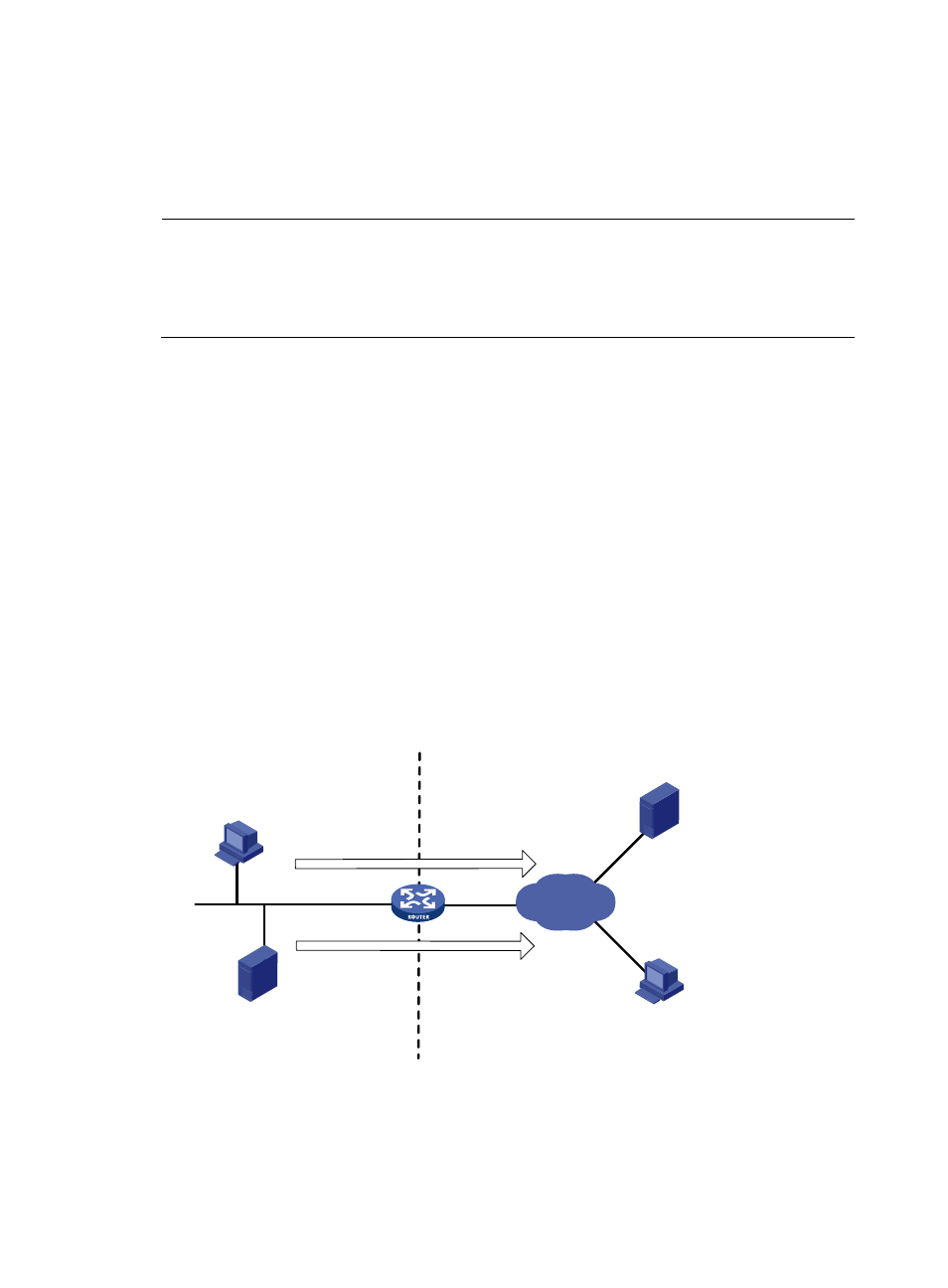
depicts NAPT operation.
Figure 2 Diagram for NAPT operation
As illustrated in
, four IP packets arrive at the NAT gateway. Packets 1 and 2 are from the same
internal address but have different source port numbers. Packets 3 and 4 are from different internal
addresses but have the same source port number. NAPT maps their source IP addresses to the same
external address but with different source port numbers. Therefore, the packets can still be discriminated.
Internet
IP packet 2
Source IP : 192.168.1.3
Source port : 2468
IP packet 2
Source IP : 20.1.1.1
Source port : 2002
192.168.1.1
20.1.1.1
IP packet 3
Source IP : 20.1.1.1
Source port : 2003
IP packet 3
Source IP : 192.168.1.1
Source port : 1111
10.1.1.2
10.1.1.3
Server B
Host
Server A
192.168.1.2
192.168.1.3
Host
IP packet 1
Source IP : 192.168.1.3
Source port : 1537
IP packet 1
Source IP : 20.1.1.1
Source port : 2001
IP packet 4
Source IP : 20.1.1.1
Source port : 2004
IP packet 4
Source IP : 192.168.1.2
Source port : 1111
