7 virtex 4 fx fpga, 1 fpga configuration, 2 fpga configuration via jtag – Sundance SMT362 User Manual
Page 10: Virtex 4 fx fpga
4.2.7 Virtex 4 FX FPGA
This device,
, is responsible for the provision of the two SHBs, 6 Com-Ports,
and the RSLs. On power-up, this device is un-configured (SRAM based FPGA technology).
During the DSP boot process, the FPGA is configured for normal operation.
4.2.7.1 FPGA
Configuration
Before any functions of the FPGA can be used it must be configured. This is a
process undertaken by DSP A during its boot procedure. The FPGA is configured via
the slave serial mode with the DSP presenting the serial data on EMIF data bit 8.
First, the PROG pin must be asserted low, then high. The FPGA’s PROG pin is
connected directly to DSPA’s general purpose i/o pin 2 (GPIO).
Then data must be read from the flash (During the normal boot process, the
configuration data is read from flash. If the FPGA needs to be reconfigured during
application execution, then the configuration data maybe read from any source.) and
written to the FPGA.
This procedure is completely automatic during the module’s boot process.
Removing jumper JP2 will hold the FPGA in an unconfigured state. This could be
useful if an erroneous bit stream has been loaded into flash (EMIF data bus
corruption etc), which could result in the module not being accessible even using
Code Composer (JTAG).
4.2.7.2 FPGA Configuration via JTAG
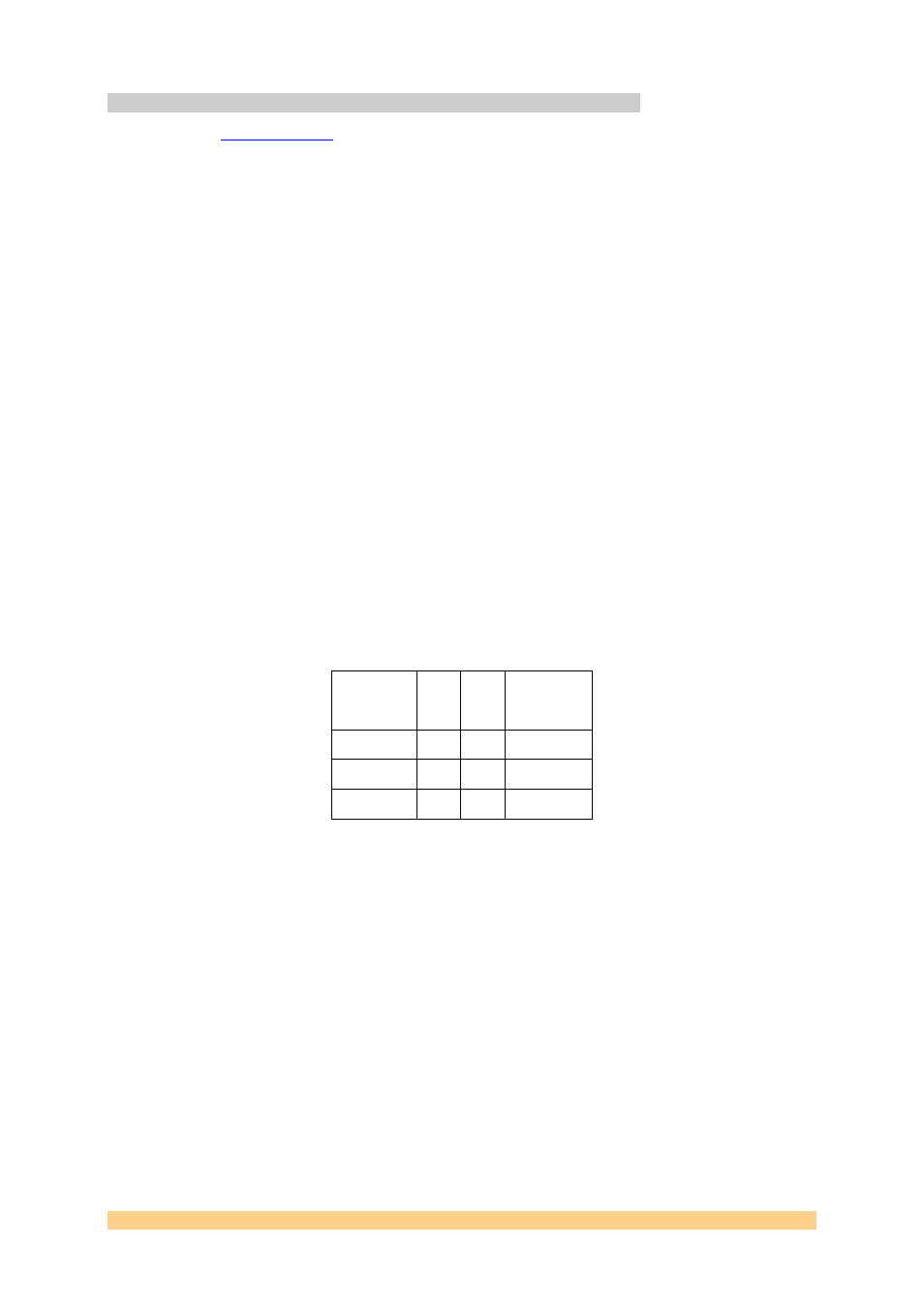
The FPGA may also be configured using a Xilinx JTAG programming system
connected to header JP1. The pin-out of this header is given here;
Signal Pin
Pin
Signal
Power 1 4 TMS
Ground 2 5 TDI
TCK 3 6 TDO
User Manual SMT362
Page 10 of 30
Last Edited: 29/04/2009 08:56
