Ncast n-way reference manual – NCast N-Way Server User Manual
Page 29
NCast N-Way Reference Manual
packet with the source address of the originating machine and the TTL value will be set to 1. The media decoding
processes in the Telepresenter (or PCs connected to the local LAN) will receive this packet and determine what
appropriate processing steps are needed.
If the N-Way Client option “Send Local Only” is off, then RTP packets from the LAN with the correct multicast
group address (a “join” is active) will be forwarded as well. This allows media streams from other Telepresenters
on the same LAN to use the tunnel established by this N-Way Client.
If the N-Way Client option “Receive Local Only” is off, then IGMP requests from other Telepresenters on the LAN
will be forwarded to the server. This allows the N-Way Client tunnel to be used to receive multicast traffic on
behalf of other machines on the LAN.
6.2.N-W
AY
C
ONNECTIVITY
- S
ENDING
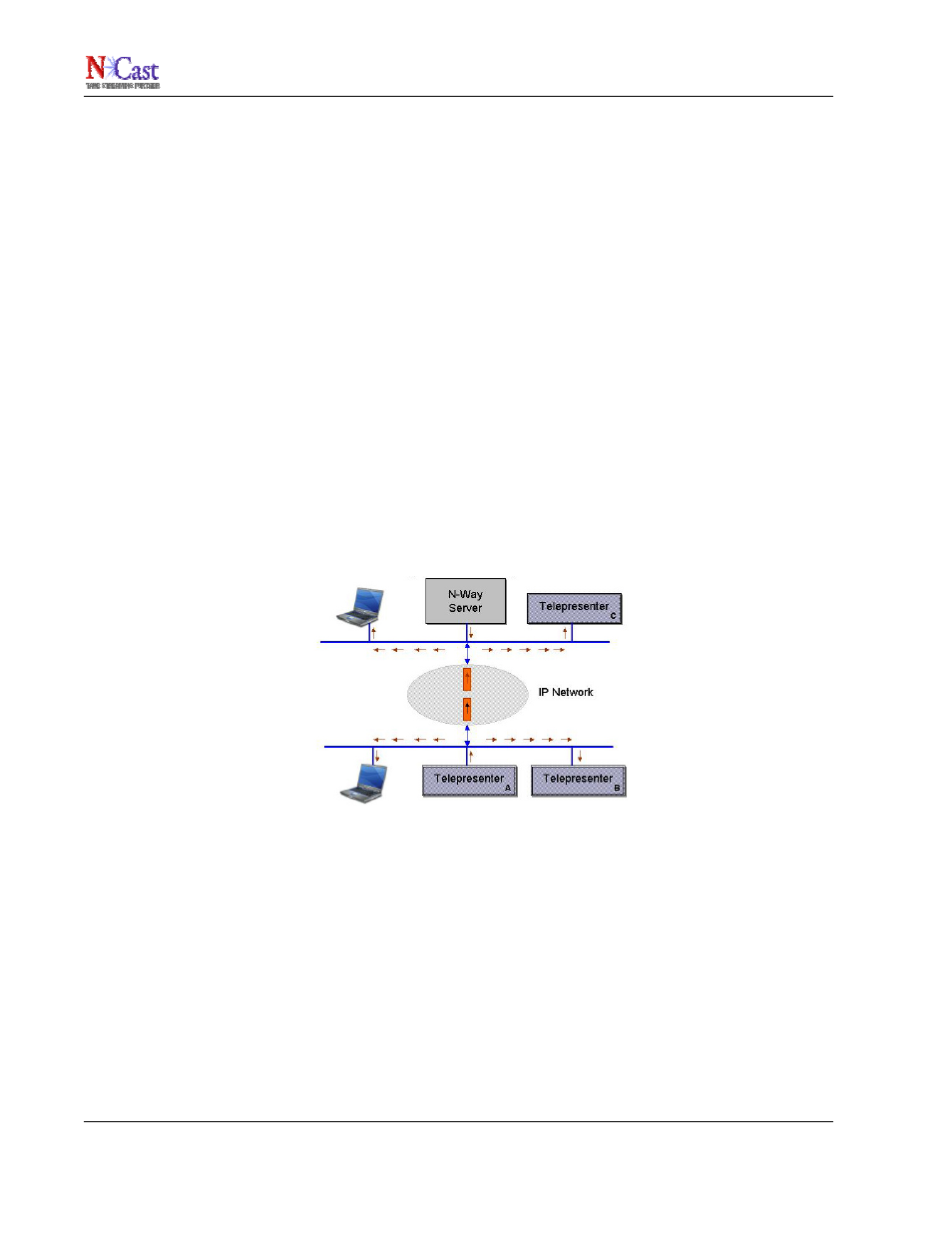
In the diagram below Telepresenter “A” is set to broadcast graphics and audio on some multicast group address.
Telepresenter B and the PC on that LAN will receive these broadcasts directly through multicast packets placed
on the LAN by Telepresenter “A”. If the N-Way Client is enabled, this multicast traffic is encapsulated and sent to
the server as a unicast stream. When the N-Way Server receives these encapsulated messages it processes
each packet in two ways. First, it un-encapsulates the packet and places it on the server’s local LAN as a
multicast packet from Telepresenter A (source address of “A”) with a TTL (time-to-live) value of 1. It also checks
to see what other N-Way connections are active, and if one of them has requested multicast traffic with this
packet’s multicast address, it forward this multicast packet through the tunnel to the requesting Telepresenter.
So Telepresenter “C” receives a copy of the multicast traffic from the server, as does any PC attached to the LAN.
Remote Telepresenters connected to the server will also get the traffic if they previously requested it.
6.3.N-W
AY
C
ONNECTIVITY
- R
ECEIVING
In the case where Telepresenter “A” wants to receive traffic from a particular multicast group, it uses the N-Way
Client to forward an IGMP request for that group to the server, which then makes its own request for any multicast
traffic on that group. If there is multicast traffic on the LAN for the group (shown in the diagram as originating from
Telepresenter “C”) then the server picks it up and forwards it as encapsulated packets through the unicast tunnel
to the N-Way Client on Telepresenter “A” which will unpack the RTP messages and place them as multicast
traffic on the LAN of Telepresenter “A” (the TTL is set to 1 and the source address is from Telepresenter “C”).
With this arrangement, all machines on the LAN may receive the multicast traffic from Telepresenter “C”.
NCast Corporation
Revision 1.3
Page 29
