Synchronized operations, Figure 11 – Measurement Computing USB-1208FS-Plus-OEM User Manual
Page 17
USB-1208FS-Plus-OEM User's Guide
Functional Details
17
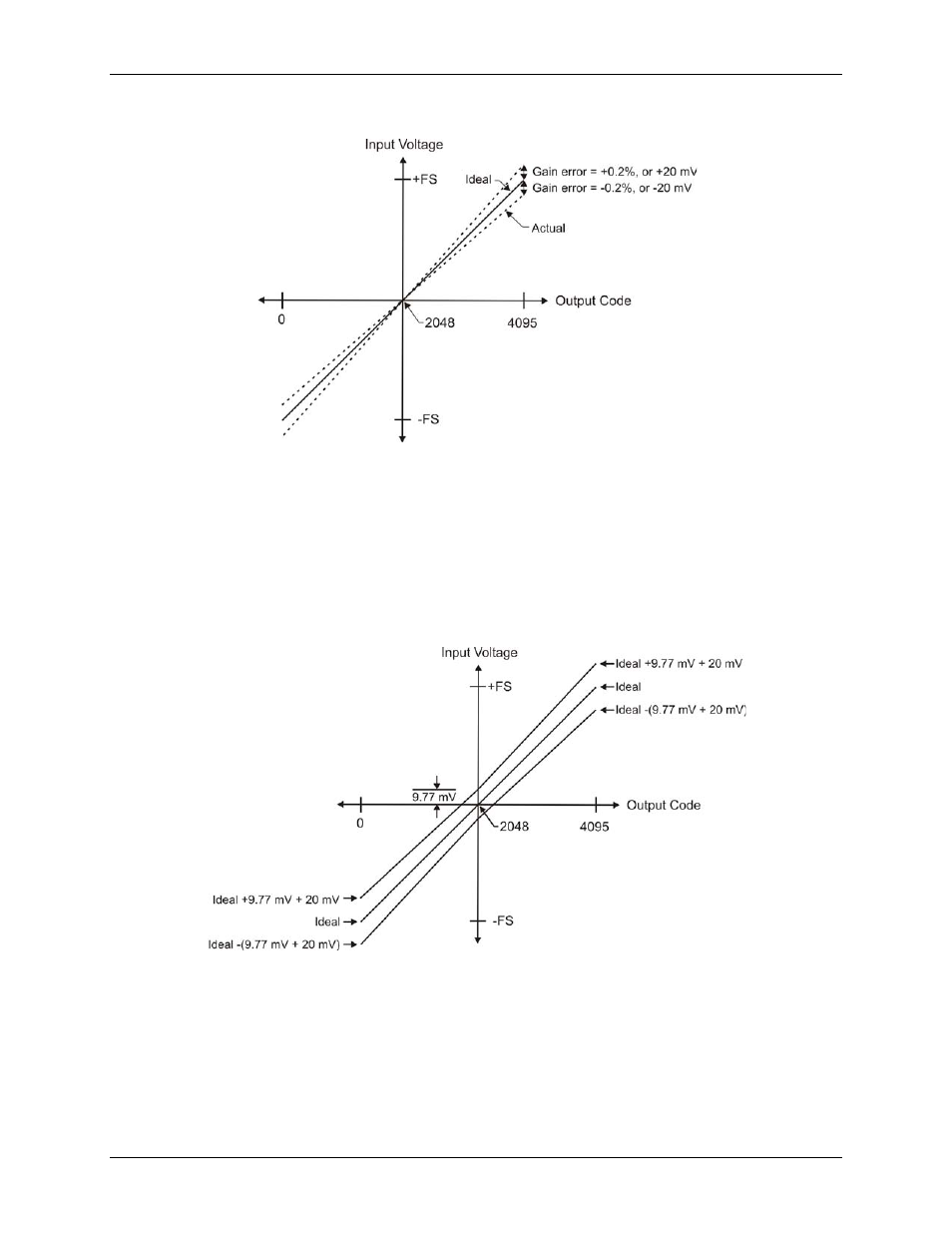
The accuracy plots in Figure 11 are drawn for clarity and are not drawn to scale.
Figure 11. ADC Transfer function with gain error
For example, the USB-1208FS-Plus-OEM exhibits a typical calibrated gain error of ±0.2% on all ranges. For
the ±10 V range, this would yield 10 V × ±0.002 = ±20 mV. This means that at full scale, and neglecting the
effect of offset, the measurement would be within 20 mV of the actual value. Note that gain error is expressed
as a ratio. Values near ±FS are more affected from an absolute voltage standpoint than are values near mid-
scale, which see little or no voltage error.
Combining these two error sources in Figure 12, we have a plot of the error band for the ±10 V range. This is a
graphical version of the typical accuracy specification of the product.
The accuracy plots in Figure 12 are drawn for clarity and are not drawn to scale.
Figure 12. Error band plot
Synchronized operations
You can connect the SYNC pin of two devices together in a master/slave configuration and acquire data from
the analog inputs of both devices using one clock.
When the SYNC pin is configured as an output, the internal A/D pacer clock signal is sent to the header
connector. Output the clock signal to the SYNC pin of a second device that is configured for A/D pacer input.
