Electrical requirements, Minimum air velocities – Greenheck Duct Heaters Series IDHB and IDHC (478052) User Manual
Page 3
Electrical Requirements
Refer to attached wiring diagram and wiring diagram
on inside of cover. Make sure line and control voltage
of system matches that noted on wiring diagram.
Wire in accordance with N.E.C. and any existing
local codes. Check tightness of all factory and field
electrical connections. Make sure fan interlock is
wired in if the Duct Heater does not have an air flow
switch.
Use 90°C (194°F) copper wire.
Control must be wired for N.E.C. Class 1 unless
otherwise specified.
When heater has integral transformer for control
voltage to thermostat, use thermostat with isolating
contacts to prevent interconnection of Class 2
outputs.
Disconnect all electrical power before servicing.
When servicing heater, make sure all components are
repositioned in the proper location and reconnected
per the wiring diagram.
Replacement parts must be identical to the original
components. Contact factory for replacement parts.
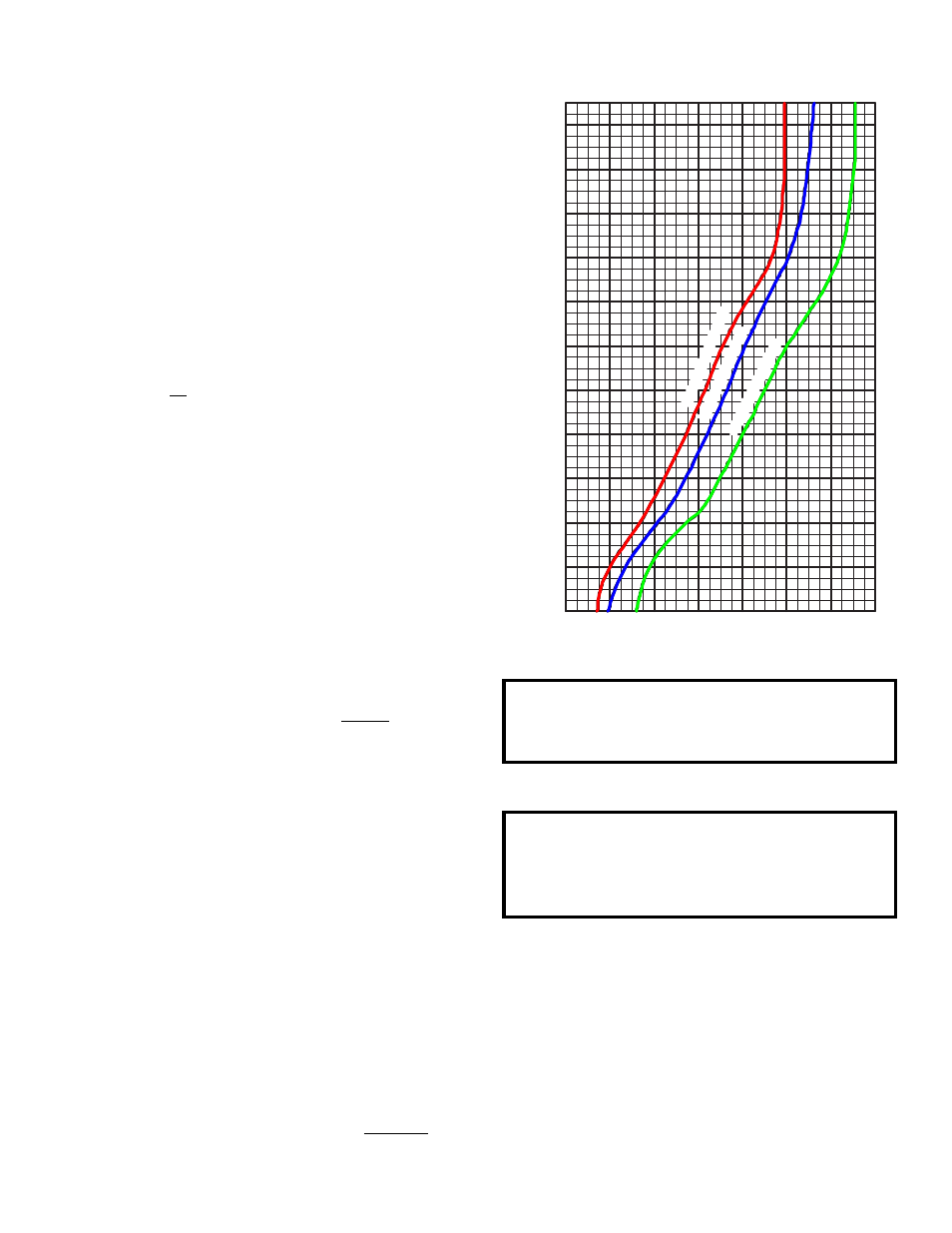
Minimum Air Velocities
The minimum uniform airflow in a duct heater
is directly related to the inlet air temperature.
Consideration must be given to both airflow across
the heater and inlet air temperature, (shown at left).
1. To calculate the watts per sq. ft. of duct
area, divide the total watts required by the
duct area.
EXAMPLE: Duct Size = 2ft. x 3ft.
Total watts = 20,000
W/Sq. Ft. = 20,000 = 3333
6
2. If the air handler equipment is expressed in
F.P.M. then a direct cross reference can be
made by comparing the temperature of the
air (as it enters the Duct Heater) to the KW
rating on the chart of rated velocity.
a. Draw a line horizontally from the Watts/
Sq. Ft. required to the inlet air temperature
being used.
b. From this point of intersection on the Inlet
Air Curve, draw a line down vertically to
establish the air velocity.
c. The velocity should never be lower than
the velocity as determined from the chart.
In cases where this is not true, the velocity
must be increased or the KW required must
be reduced.
3. In cases where the air handling equipment
is expressed in C.F.M., convert to F.P.M. by
dividing the C.F.M. by the duct area.
EXAMPLE: F.P.M. = CFM
Duct
Area
Note: Minimum airflow must be
maintained at any point over the face of
the heater.
Note: Observe at least one complete
heating cycle to insure that cycling of
the safety limit controls does not occur
before leaving the installation.
1,400
4,000
6,000
8,000
10,000
12,000
14,000
16,000
18,000
20,000
W
ATTS PER SQUARE FOOT
, DUCT
AREA
22,000
Minimum Air Velocity (fpm)
2,000
1,200
1,000
800
600
400
200
BELOW 78°F INLET
AIR
78° T
O 90°F INLET
AIR
91° T
O 1
10°F INLET
AIR
Minimum Air Velocities
3
