Modbus, Basic principles, Bus topology – BECKHOFF BK7300 User Manual
Page 19
MODBUS
BK7300
15
MODBUS
Basic Principles
The MODBUS is a master-slave bus system in which only one device (the
master) actively starts a transaction (queries). The passive device (the
slave) then sends an answer (response) if the telegram was directly
addressed to it and provided that it has no errors.
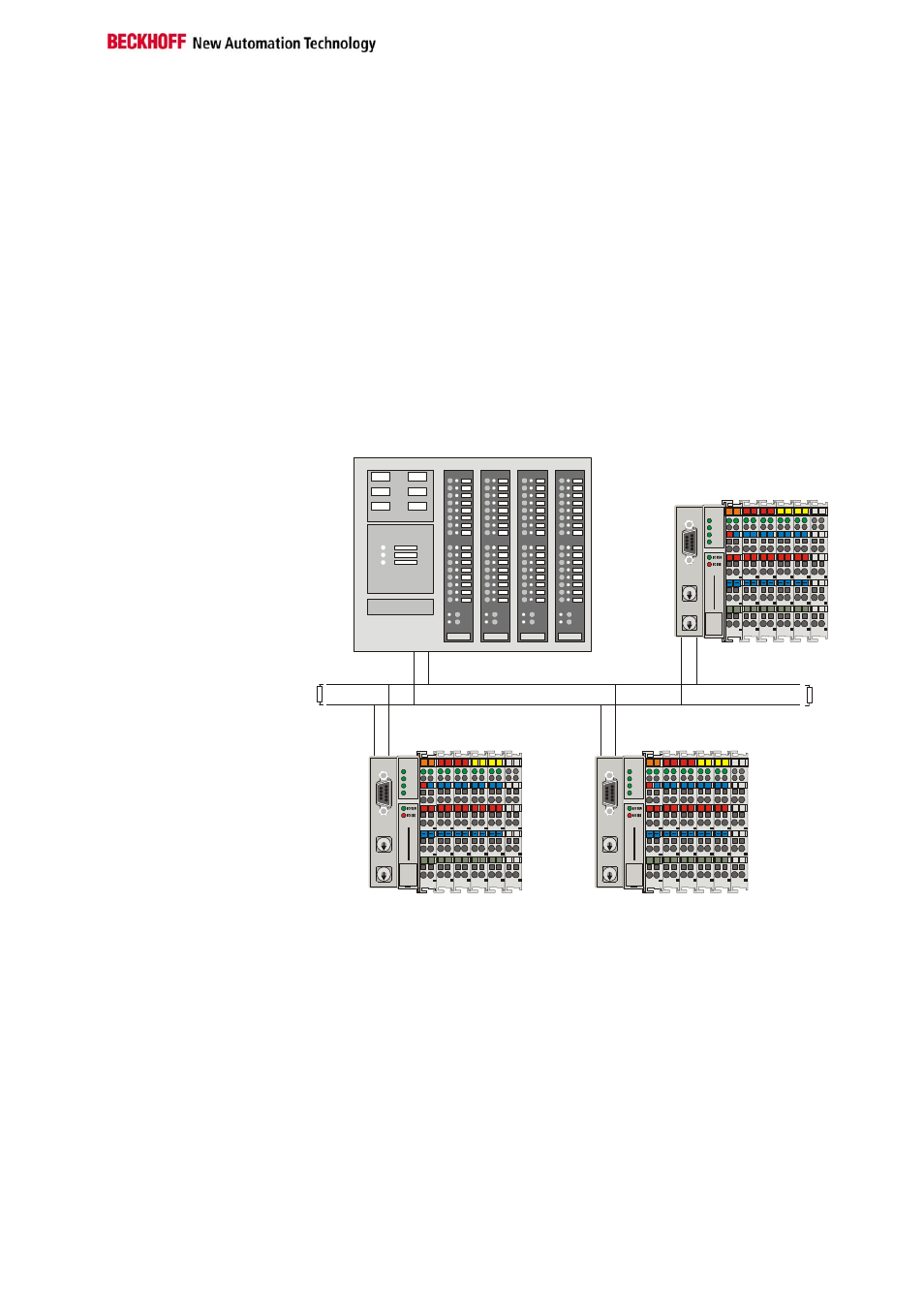
Bus Topology
Physically, the BK7300 uses RS485 transmission. This means that a two-
wire cable is needed for the data transmission. The topology is linear. At
the beginning and end of the lines the bus requires termination resistors.
The structure of the Modbus network is similar to that of PROFIBUS.
02
02
01
01
+
+
+
+
PE
PE
PE
PE
RUN
RX
TX
MODBUS
BE
C
K
HOFF
24V
0V
0
9
8
7
6 5 4
3
2
1
0
9
8
7
6 5 4
3
2
1
BK
73
00
02
01
02
01
+ +
PE PE
02
01
+ +
PE PE
02
01
+ +
PE PE
02
02
01
01
+
+
+
+
PE
PE
PE
PE
RUN
RX
TX
MODBUS
BE
CK
HOFF
24V
0V
0
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
9
8
7 6 5 4
3
2
1
BK
7
300
02
01
02
01
+ +
PE PE
02
01
+ +
PE PE
02
01
+ +
PE PE
02
02
01
01
+
+
+
+
PE
PE
PE
PE
RUN
RX
TX
MODBUS
BE
CK
HOFF
24V
0V
0
9
8
7
6 5 4
3
2
1
0
9
8
7 6 5 4
3
2
1
BK
7
300
02
01
02
01
+ +
PE PE
02
01
+ +
PE PE
02
01
+ +
PE PE
Broadcast function
The Beckhoff bus couplers support the broadcast function. For this
purpose the slave address in the telegram must be set to "00". Slaves do
not answer a broadcast. Not all functions are supported.
Functions that support a broadcast:
• 5
Force
single
coil
• 6
Preset single register
• 15
Force multiple coils
• 16
Preset multiple register
PIN assignment
The BK7300 uses RS485 for the data transmission. A screened two-wire
cable is sufficient. The connection to the coupler is a 9-pin sub-D socket.
The data line is connected to PIN 3 and PIN 8.
