Hanna Instruments HI 3896 User Manual
Page 4
4
The physical structure of the soil depends on the dimension of the particles of its make up
(Tab. 1). In addition, the particles also differ based on their shape and volumic mass (mass
per unit of volume)
DIAMETER OF THE PARTICLES (mm)
CLASSIFICATION
> 2
stony texture
2 - 0.2
coarse sand
0.2 - 0.02
fine sand
0.02 - 0.002
silt
< 0.002
clay
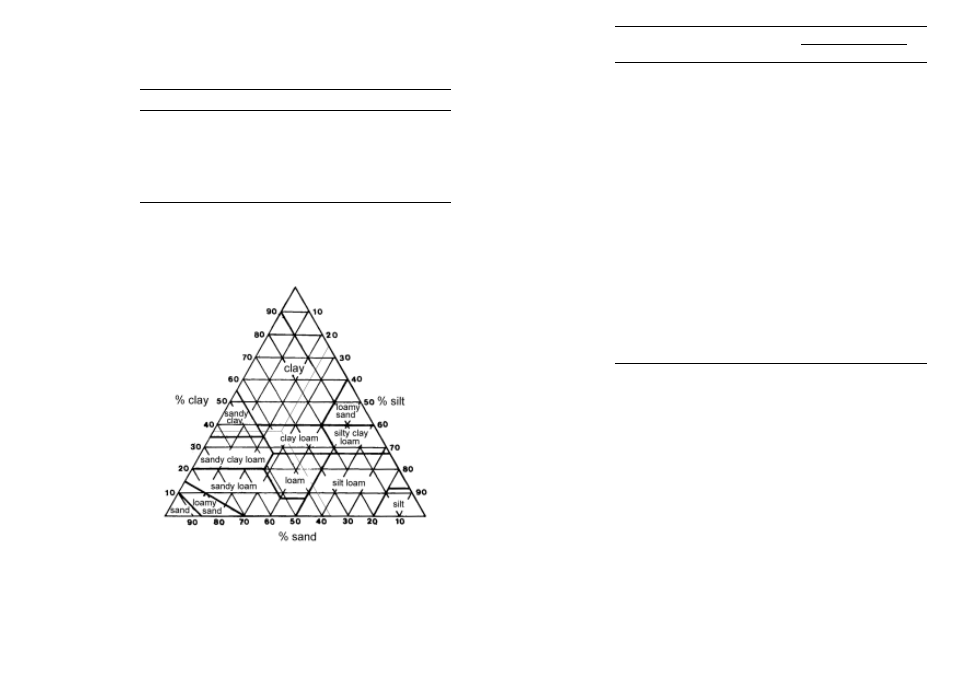
Soil is divided into many classes of texture, according to the percentage of the basic
particles (clay, sand and silt). If, for example, we have a soil with 37% clay, 38% sand
and 25% silt, the soil is classified as “clay loam” (Fig. 2).
PHYSICAL STRUCTURE
Tab. 1. Particles
classification according to
“International Society of
Soil Science” (ISSS)
Fig. 2. Types of soil in
relation to the texture
Among different types of soil, the loam soil is considered as being suitable for crop
growth. However, other types of soil, with a rational management, can also provide
positive results.
The soil texture is the cause of important aspects such as porosity, tenacity, adhesivity
and plasticity.
13
Apple
very low
150
120
230
low
130
90
150
medium
110
70
120
medium-high
90
50
90
high
80
40
60
very high
70
20
40
Grape
very low
150
90
230
low
120
70
180
medium
100
60
150
medium-high
90
40
120
high
80
30
90
very high
70
20
60
Peach
very low
200
120
230
low
160
90
150
medium
140
70
120
medium-high
120
50
90
high
100
40
60
very high
80
20
40
Pear
very low
150
120
230
low
130
90
150
medium
110
70
120
medium-high
90
50
90
high
80
40
60
very high
70
20
40
The soil analysis is very useful, in order to plan fertilization and to know the residues of
fertilizers in relation to the crop, tillage and climate. An analysis can highlight shortages
and help the understanding of the causes of an abnormal growth.
Testing the soil during the crop cycle and comparing the results with the plant growth can
be an useful experiment for the next cultivation.
1) Extracting Soil Sample
– With a large field, take 1 or 2 samples per 1000 m2 (0.25 acre) of homogeneous
areas.
– Even for smaller areas, 2 samples are recommended (the more the samples, the
better the end-results, because the sample is more representative)
– For a small garden or plot, 1 sample is sufficient
2) Avoid extracting samples from soil presenting obvious anomalies
3) Sample quantity:
Take the same quantity of soil for each sample. For example, use bags with similar
dimensions (1 bag per sample)
CROP
SOIL CONTENT
ADVISED DOSES (kg/ha)
N
P
2
O
5
K
2
O
Tab. 7.
SOIL ANALYSIS
Sampling
(data ESAV)
