Operating instructions glossary – Elenco Logic Probe Kit User Manual
Page 11
-10-
Alternating Current (AC)
Non-polarized power that is
constantly changing back and
forth between positive and
negative.
Anode
The positive terminal of a diode
or other polarized component.
Capacitor
Electrical
component
for
accumulating energy.
Cathode
The negative terminal of a
diode or other polarized
component.
CMOS
(Complimentary Metal Oxide
Semiconductor) A
type
of
transistor circuit which uses P-
and N-type field-effect transistors.
Current
The flow of electrons.
Diode
An electronic component that
changes alternating current to
direct current.
Direct Current (DC)
Voltage that has polarity.
Frequency
The number of cycles per
second produced.
Impedance
In circuit, the opposition that
circuit elements present to
alternating current.
Input Impedance
The impedance seen by source
when a device or circuit is
connected across the source.
Integrated Circuit (IC)
Any of a huge number of
semiconductor packages that
contain entire elements.
Inverter
The circuit where the output state
is the opposite of the input state.
Light Emitting Diode (LED)
A semiconductor device that
glows when power is applied to
its electrodes.
Logic Probe
An electronic test device that
detects the status of a signal.
Oscillator
A device that moves back and
forth between two boundaries.
PC Board
Printed Circuit Board.
Power Supply
An electronic circuit that
produces the necessary power
for another circuit or device.
Pulse
A sudden change from one
level to another, followed after
a time by a sudden change
back to the original level.
Resistor
An electronic component that
obstructs (resists) the flow of
electricity.
Speaker
Component
that
converts
electrical energy into sound
energy.
Troubleshoot
To find and fix the problem with
something.
TTL (Transistor-Transistor Logic) A type of integrated circuit logic
that uses bipolar junction
transistors.
Voltage
The electromotive force that
“pushes” electrons through
conductive materials.
Zener
A type of diode that acts as a
voltage regulator by restricting
the flow of voltage above its
rating.
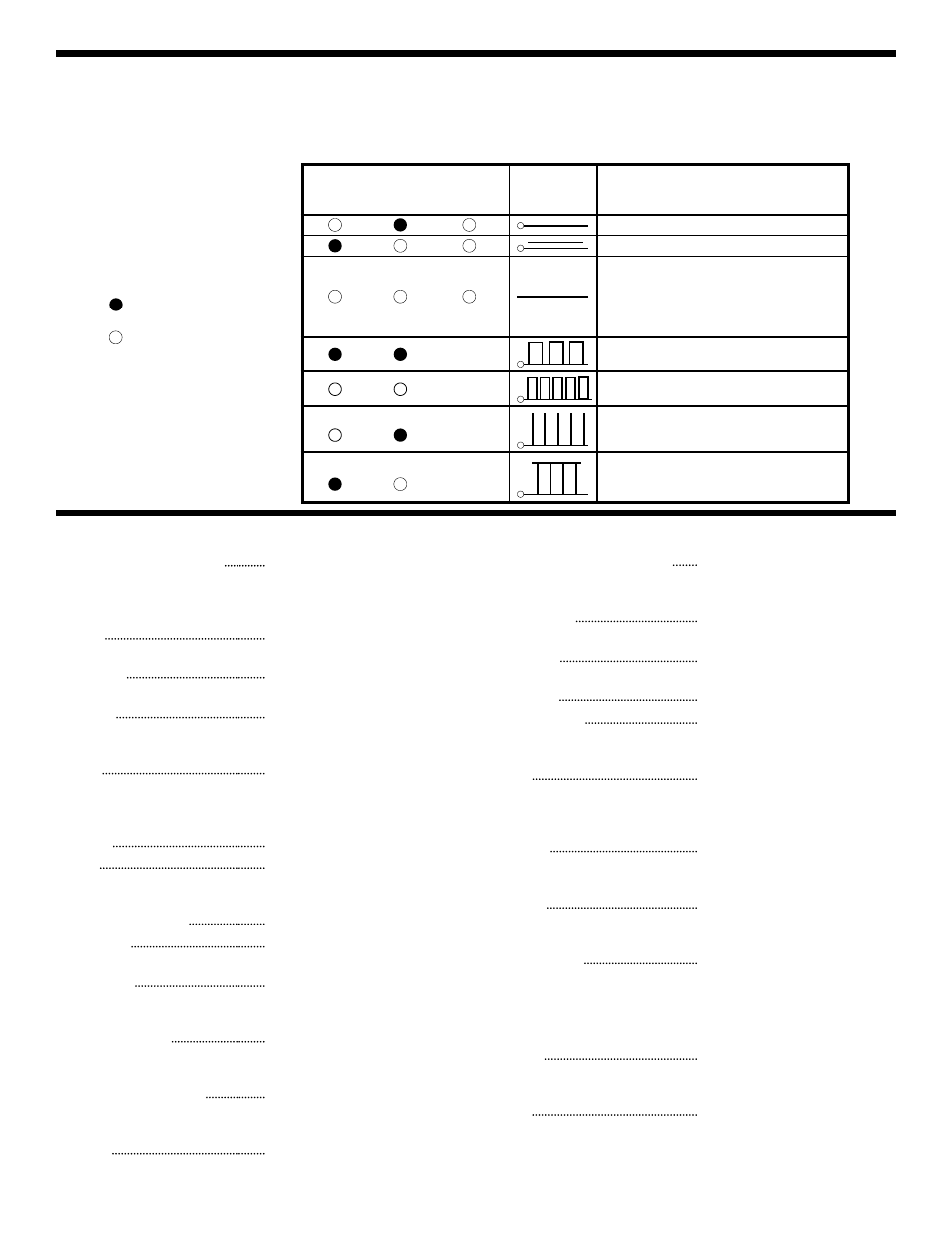
LED STATES
INPUT
HIGH
LO
PULSE
SIGNAL
Logic “0” no pulse activity.
Logic “1” no pulse activity.
All LEDs off
1. Test point is an open circuit.
2. Out of tolerance signal.
3. Probe not connected to power.
4. Node or circuit not powered.
*
Equal brightness of the HI and LO LED indicates
approximately a 50% duty cycle square wave.
*
High frequency square wave greater than
approximately 3MHz.
*
Logic “0” with positive pulses present. Low duty
cycle since HI LED is not on. If duty cycle were
increased, the HI LED would start to turn on.
*
Logic “1” with negative pulses present. High duty
cycle since LO LED is not on. If duty cycle were
reduced, the LO LED would start to turn on.
Interpreting
the LEDs
LED On
LED Off
LED Blinking
*
To operate the logic probe, connect the two alligator clips to the circuit DC
power supply, red clip to the positive voltage, black to ground. BE SURE
THE CIRCUIT SUPPLY IS UNDER 35V OR DAMAGE MAY OCCUR TO
THE PROBE. Set the logic family switch to TTL or CMOS. Touch the
probe tip to the circuit node to be analyzed. The LED display on the probe
body will light to indicate the condition of the node. Refer to the chart
below to interpret the LED readings. To prevent power supply spikes,
connect the leads as close to the node to be tested as possible.
OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS
GLOSSARY
