Air for combustion and ventilation – Desa VUL18 User Manual
Page 7
www.desatech.com
119426-01A
7
AIR FOR COMbUSTION
AND VENTILATION
Continued
Space:
Includes the room in which you will install
fireplace plus any adjoining rooms with doorless pas-
sageways or ventilation grills between the rooms.
1. Determine the volume of the space (length x
width x height).
Length x Width x Height =__________cu. ft.
(volume of space)
Example:
Space size 20 ft. (length) x 16 ft.
(width) x 8 ft. (ceiling height) = 2560 cu. ft.
(volume of space)
If additional ventilation to adjoining room is
supplied with grills or openings, add the volume
of these rooms to the total volume of the space.
2. Multiply the space volume by 20 to determine
the maximum Btu/Hr the space can support.
__________ (volume of space) x 20 = (Maxi-
mum Btu/Hr the space can support)
Example:
2560 cu. ft. (volume of space) x 20 =
51,200 (maximum Btu/Hr the space can support)
3. Add the Btu/Hr of all fuel burning appliances in
the space.
Vent-free fireplace
___________ Btu/Hr
Gas water heater*
___________ Btu/Hr
Gas furnace
___________ Btu/Hr
Vented gas heater
___________ Btu/Hr
Gas fireplace logs
___________ Btu/Hr
Other gas appliances* + __________ Btu/Hr
Total
= __________ Btu/Hr
* Do not include direct-vent gas appliances. Di-
rect-vent draws combustion air from the outdoors
and vents to the outdoors.
Example:
Gas water heater
___________ Btu/Hr
Vent-free fireplace
+ __________ Btu/Hr
Total
= __________ Btu/Hr
4. Compare the maximum Btu/Hr the space can
support with the actual amount of Btu/Hr used.
__________ Btu/Hr (maximum the space can support)
__________Btu/Hr (actual amount of Btu/Hr used)
Example:
51,200 Btu/Hr (maximum the space
can support)
73,000 Btu/Hr (actual amount of
Btu/Hr used)
The space in the above example is a confined space
because the actual Btu/Hr used is more than the maxi-
mum Btu/Hr the space can support. You must provide
additional fresh air. Your options are as follows:
A. Rework worksheet, adding the space of an adjoin-
ing room. If the extra space provides an unconfined
space, remove door to adjoining room or add
ventilation grills between rooms. See Ventilation
Air From Inside Building.
B. Vent room directly to the outdoors. See Ventila-
tion Air From Outdoors, page 8.
C. Install a lower Btu/Hr fireplace, if lower Btu/Hr
size makes room unconfined.
If the actual Btu/Hr used is less than the maximum
Btu/Hr the space can support, the space is an un-
confined space. You will need no additional fresh
air ventilation.
WARNING: If the area in
which the heater may be oper-
ated is smaller than that defined
as an unconfined space or if the
building is of unusually tight
construction, provide adequate
combustion and ventilation air
by one of the methods described
in the National Fuel Gas Code,
ANSI Z223.1/NFPA 54 Section 5.3
or applicable local codes.
VENTILATION AIR
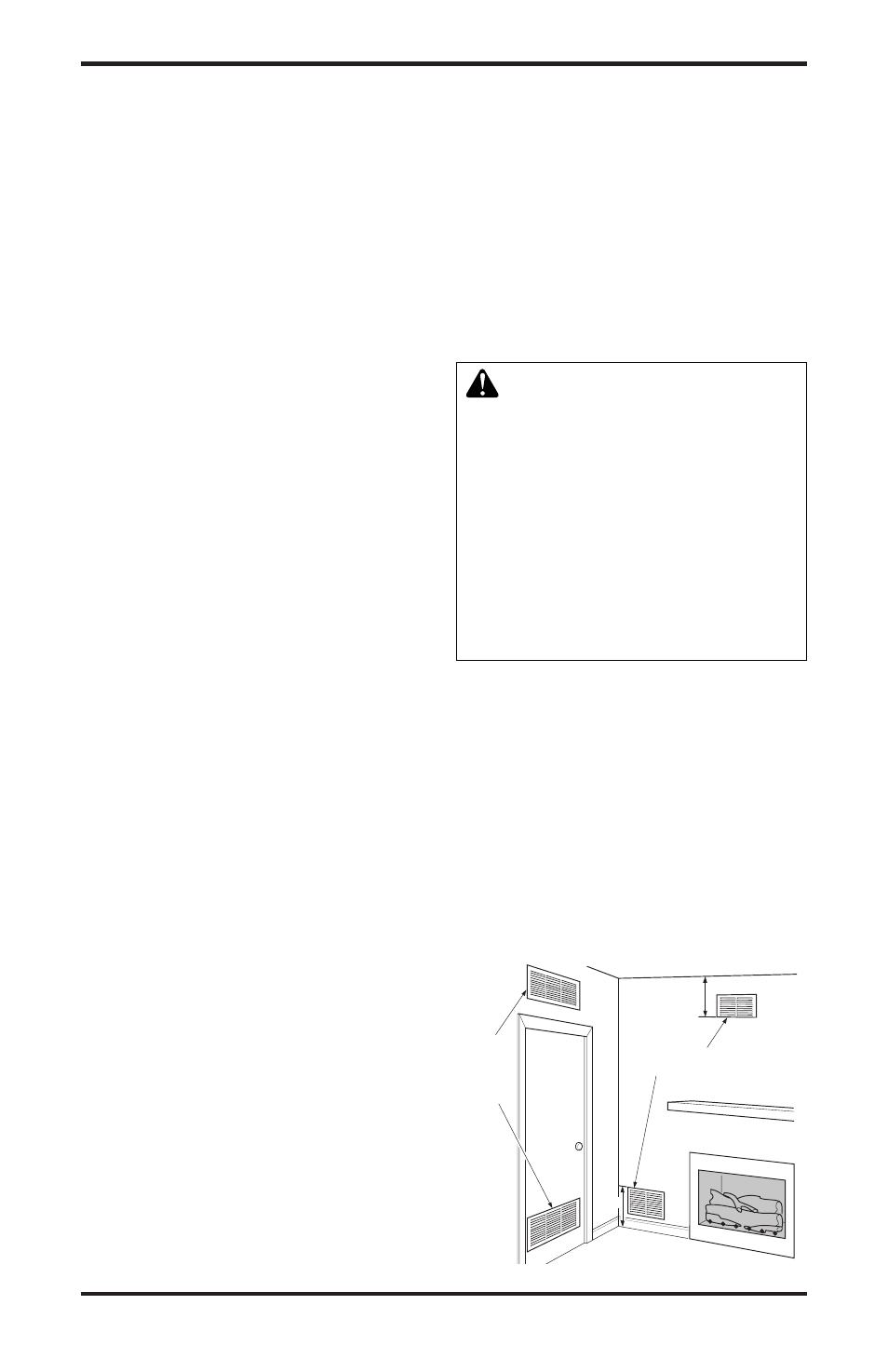
Ventilation Air From Inside Building
This fresh air would come from an adjoining un-
confined space. When ventilating to an adjoining
unconfined space, you must provide two perma-
nent openings: one within 12" of the ceiling and
one within 12" of the floor on the wall connecting
the two spaces (see options 1 and 2, Figure 2). You
can also remove door into adjoining room (see
option 3, Figure 2). Follow the National Fuel Gas
Code, ANSI Z223.1/NFPA 54, Section 5.3, Air for
Combustion and Ventilation for required size of
ventilation grills or ducts.
40,000
33,000
73,000
Figure 2 - Ventilation Air from Inside Building
Or
Remove
Door into
Adjoining
Room,
Option
3
Ventilation Grills
Into Adjoining Room,
Option 2
Ventilation
Grills Into
Adjoining
Room,
Option 1
12"
12"
