Conditioning guidelines, Exercise intensity, Fat burning – Sears 631.29739 User Manual
Page 14: Aerobic exercise, High performance athletic conditioning, Workout guidelines, Conditioning guidelines warning
Attention! The text in this document has been recognized automatically. To view the original document, you can use the "Original mode".
CONDITIONING GUIDELINES
WARNING
I Before beginning
this or any exercise program, consult your
physician. This is especially important for in
dividuals over the age of 35 or individuals
with pre-existing health problems.
The following guidelines will help you to plan your ex
ercise program. Remember—these are general guide
lines only. For more detailed exercise information, ob
tain a reputable book or consult your physician.
EXERCISE INTENSITY
Whether your goal is to burn fat or to strengthen your
cardiovascular system, the key to achieving the desired
results is to exercise with the proper intensity. The
proper intensity level can be found by using your heart
rate as a guide. The chart below shows recommended
heart rates for fat burning and aerobic exercise.
HEART RATE TRAINING ZONE
MIN BPM *
ÍMSE
Max Bum
(
20
125
145
( 30
(
40
120
138
115
130
165
)
D
155
145
CW
110
125
140
З6Ф~
105
118
130
Œ
S5
no
125
)
(
80
90
103
115
To find the proper heart rate for you, first find your age
on the left side of the chart (ages are rounded off to
the nearest ten years). Next, find the three numbers to
the right of your age. The three numbers are your
“training zone.” The lower two numbers are recom
mended heart rates for fat burning; the higher number
is the recommended heart rate for aerobic exercise.
Fat Burning
To burn fat effectively, you must exercise at a relatively
low intensity level for a sustained period of time. During
the first few minutes of exercise, your body uses easily
accessible carbohydrate calories for energy. Only after
the first few minutes does your body begin to use
stored fat calories for energy. If your goal is to burn fat,
adjust the speed and incline of the treadmill until your
heart rate is near one of the lower two numbers in your
training zone. It may also be helpful to set the speed
control on the console to FAT BURN to help you main
tain the proper intensity level. (See page 9.)
Aerobic Exercise
If your goal is to strengthen your cardiovascular sys
tem, your exercise must be “aerobic.” Aerobic exercise
is activity that requires large amounts of oxygen for
prolonged periods of time. This increases the demand
on the heart to pump blood to the muscles, and on the
lungs to oxygenate the blood. For aerobic exercise,
adjust the speed and incline of the treadmill until your
heart rate is near the higher number in your training
zone. It may also be helpful to set the speed control on
the console to AEROBIC to help you maintain the
proper intensity level. (See page 9.)
High Performance Athletic Conditioning
If your goal is high performance athletic conditioning,
set the speed control on the console to PERFOR
MANCE to help you maintain the proper intensity level.
(See page 9.) Note: During the first few weeks of your
exercise program, keep your heart rate near the low
end of your training zone.
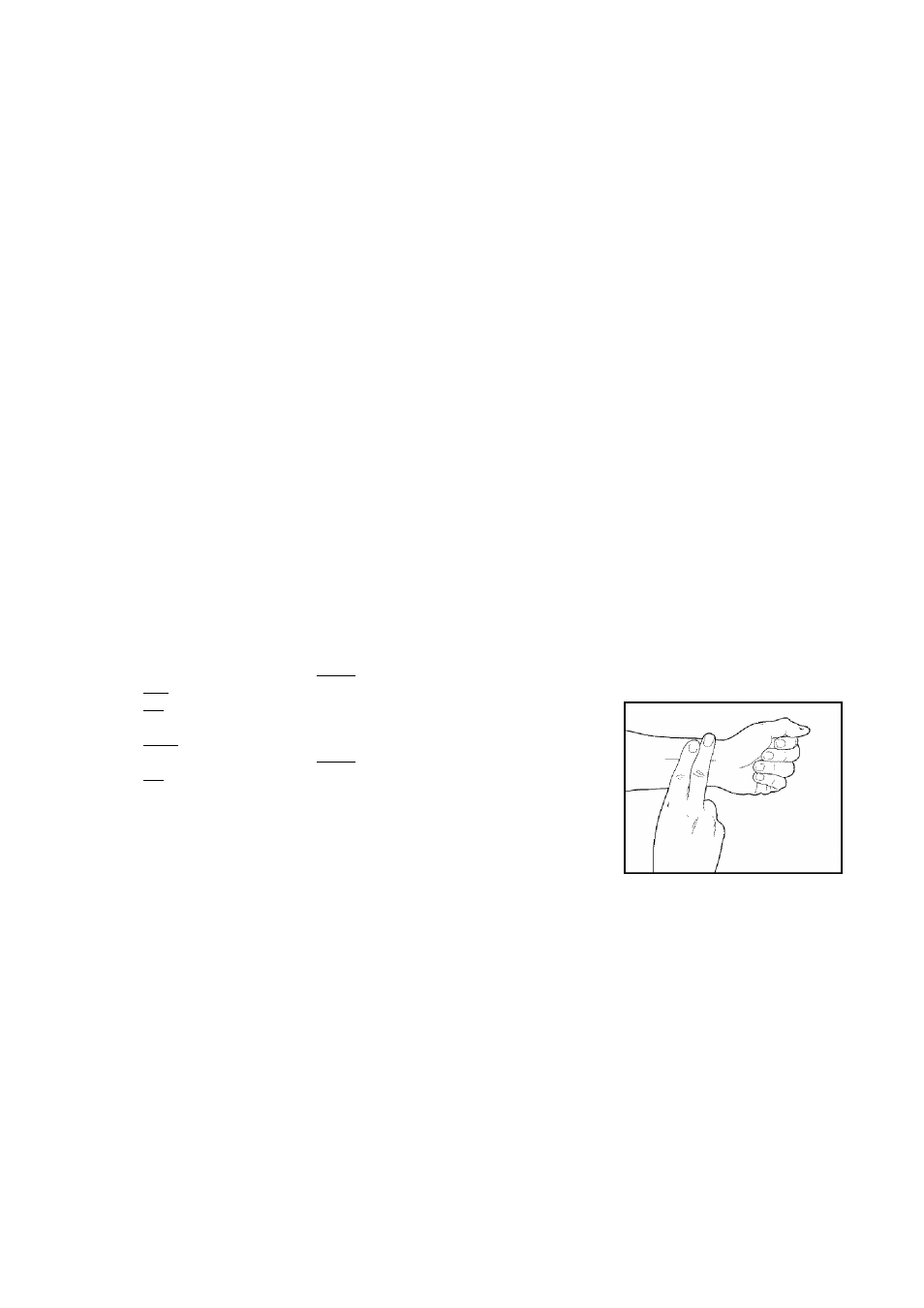
HOW TO MEA
SURE YOUR
HEART RATE
To measure your
heart rate, stop
exercising and
place two fingers
on your wrist as
shown. Take a
six-second heart
beat count, and
multiply the result by ten to find your heart rate. (A six-
second count is used because your heart rate drops
quickly when you stop exercising.) If your heart rate is
too high or too low, adjust the speed or incline of the
treadmill accordingly.
WORKOUT GUIDELINES
Each workout should include the following three parts:
Warming Up
Start each workout with 5 to 10 minutes of stretching
and light exercise. A proper warm-up increases your
body temperature, heart rate, and circulation in prepa
ration for exercise.
14
