Estimating performance factors – ProgressiveRC 4S Gold FMA Cellpro User Manual
Page 8
8
Estimating performance factors
If you don’t have a way to directly measure your propulsion system’s electrical parameters, the
Cellpro 4s Charger enables you to estimate them using before- and after-flight measurements.
1. Collect data
a. Charge pack.
b. When charging is finished, record Fuel % and total pack voltage (i.e. sum of cell volt-
ages).
c. Fly plane (or test on the ground). Record flight time in minutes.
d. Connect pack to charger. Record Fuel % and total pack voltage.
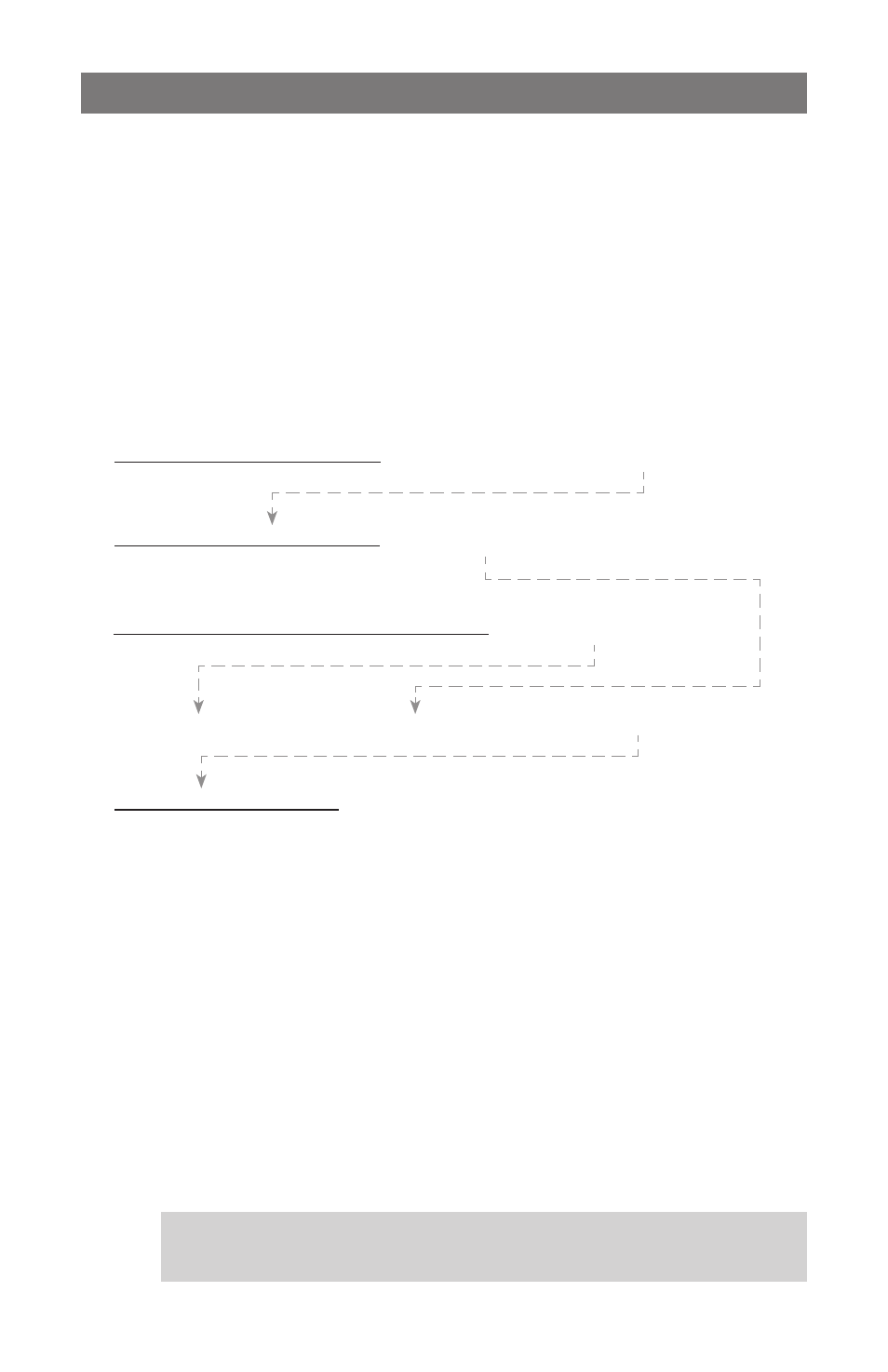
2. Calculate performance factors
(Fuel % before flight) – (Fuel % after flight)
100
x (Pack capacity, Ah) =
Capacity consumed during flight, Ah
(Capacity consumed during flight, Ah) x 60
(Flight time, minutes)
=
Average current during flight, A
(Pack voltage before flight, V) + (Pack voltage after flight, V)
2
=
Average voltage during flight, V
(Average voltage during flight, A) x (Average current during flight, V) =
Average power during flight, Watts
The “LiPo Performance Estimator” spreadsheet, which simplifies these calculations, can be
downloaded from www.fmadirect.com/tech_data/techdocs/.
3. Evaluate results
n
Average current during flight gives you a rough idea whether system components—ESC,
motor, connectors and wiring—are operating within their current ratings. Keep in mind that
peak current during flight may greatly exceed the average current you calculated.
n
Watts per pound is an approximate indicator of aircraft performance (other factors influenc-
ing performance include lift, drag and motor type). Here are some guidelines:
25 to 30 watts per pound: level flight.
40 to 50 watts per pound: take off from smooth surface, climb.
50 to 75 watts per pound: take off from grass, sport aerobatics.
75 to 125 watts per pound: pattern aerobatics.
Over 125 watts per pound: 3D.
Tip: For more direct electrical measurements, consider these FMA products:
n
60A Current Shunt (Model DVM-SHUNT-60)
n
Digital Multimeter (Model DVM-VC890D)
(Average power during flight, Watts)
(Model weight, pounds)
=
Watts per pound
