Dv-29 micron gauge hook-up – Just Better Deep Vacuum Principles and Applications User Manual
Page 3
Flare
Fitting
45°
Positive
Stop
Specially
Designed
Groove
Locks
O-Ring In
Place
1
2
ing and testing hoses are designed for pressure. Even
with the advanced technology of today's hoses, perme-
ation through the hose compound still exists. When
checking pressure rise, the atmosphere will permeate to
the lower pressure in the hoses and the micron reading
will slowly rise.
Another source of leakage is the gasket seal in
valve and hose
couplers. This seal is
designed for charging
and will not give a
perfect seal required
in deep vacuum
service. An O-ring
seal coupler, such as
that made by J/B,
forms around irregu-
larities in the flare
fitting. When the
coupler is screwed
down, we get a metal
to metal seat and the
o-ring lays around
the lip of the flare to give a positive seal.
Connecting Lines
We have now covered the simplest hookup to this
point; gauge
manifold with
two 1/4" I.D.
connecting
lines to the
system and a
3/8" connection
to the pump via
line or fittings.
Much has been
said and
written regard-
ing line size,
which would
lead us to
believe the
bigger line we connect, the faster job we’ll do. This
would be true except for the compressor’s service
valves 3/16" orifice. Therefore, we only need to keep the
connecting lines’ I.D. larger than 3/16" This is one of the
limiting time factors in evacuation.
Evacuation should always be done from both the
low and high sides of the system. This could save as
much as 3/4 of the time when evacuating from only one
side. Short connecting lines will save some time;
however, not nearly what some maintain. In relation to
the lengths of tubing in the system, we add very little
restriction via connecting lines.
Before You Start
It is a good idea to attach the micron gauge to the
vacuum pump to make sure the pump pulls down to at
least 50 microns. If it doesn't, your pump is contami-
nated and the oil should be changed. Do not shut-off the
blank-off valve on the pump and expect the gauge to
hold a vacuum as the gauge will fall back to atmo-
sphere. The reason for this is that the sensor is too
close to the pump and the gauge's sensor doesn't have
time to equalize.
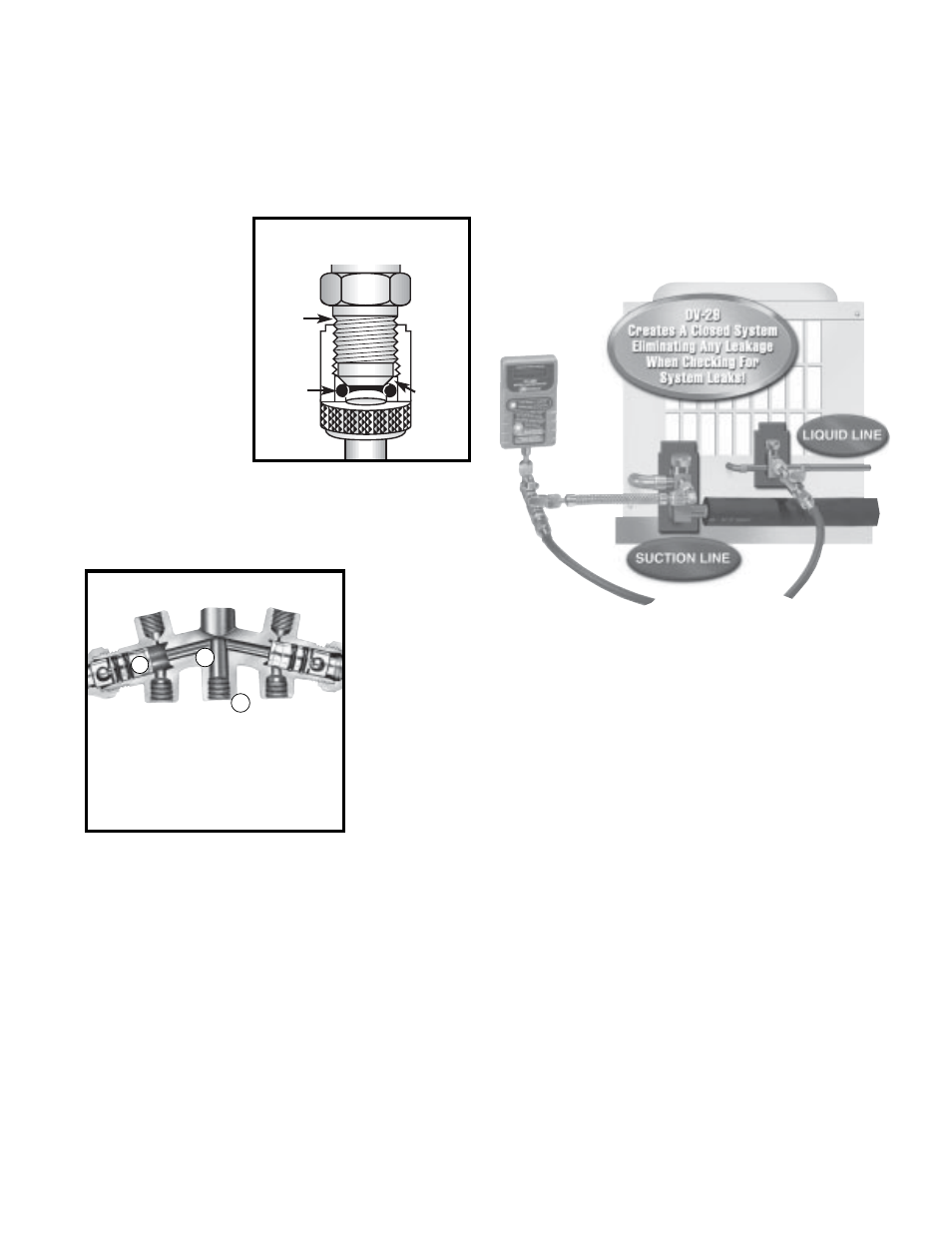
Most Leak-Proof Micron Gauge Hook-up
The most leak-proof setup is by using the DV-29.
This unit creates a closed system eliminating any
leakage under deep vacuum.
J/B Piston Type Manifolds
Deep Vacuum
O-Ring Coupler Cut-Away
1. Stem seats retract completely
from flow path.
2. Double size flow path through-
out length of center port.
3. Convert to 3/8" port with 3/8mf x
1/8mp
3
The DV-29 test unit (see illustration) eliminates
other problems when attaching the micron gauge into
the system. If the micron gauge is attached directly to
the vacuum pump or with 3' dedicated hose, we will get
a lower reading as the gauge is sensing what the pump
is doing and not what the pump is doing to the system.
General Micron Gauge Hook-up
When designing your hook-up system, choose from
the following hoses, valve and coupler designed for
leak-proof service in a deep vacuum environment.
1. D10436 or D10427 1/4" Metal Hose and D10636 or
D10660 3/8" Metal Hose with o-ring couplers. Your
hook-up through manifold, pump and if desired, to the
micron gauge.
2. A34000 Quick Coupler Tee w/o-ring seal. Since the
most accurate reading is obtained at the
compressor's high or low side, use to tee-off the
gauge.
3. D10162 ball valve with O-ring quick coupler to valve
off gauge before charging. Depending on the gauge,
it should be remembered that the electronic gauge's
sensors will not take pressure beyond 1 to 100
pounds. Depending on hook-up, use with metal hose
or A34000 coupler.
1. Works with all micron gauges
2. No additional equipment needed
3. Leak-proof components
DV-29 Micron Gauge Hook-Up
Hoses to Manifold
