About your raid configuration, Raid level 0 configuration – Dell XPS 720 H2C (Mid 2007) User Manual
Page 29
Setting Up and Using Your Computer
29
About Your RAID Configuration
NOTICE:
In order to use the migrating option to convert a RAID configuration without losing data, your hard drive
must initially be set up as a single drive RAID 0 array before the operating system is loaded onto the drive (see
"Using the NVIDIA MediaShield ROM Utility" on page 33 for instructions).
This section provides an overview of the RAID configuration you may have selected when you purchased
your computer. There are several RAID configurations available in the computer industry for different
types of uses. Your computer supports RAID level 0, RAID level 1, RAID level 5 (customer-installed), or
RAID level 0+1 (customer-installed). A RAID level 0 configuration is recommended for high-
performance programs, while RAID level 1 is recommended for users that desire a high level of data
integrity.
NOTE:
RAID levels do not represent a hierarchy. A RAID level 1 configuration is not inherently better or worse than
a RAID level 0 configuration.
The drives in a RAID configuration should be the same size in order to ensure that the larger drive does
not contain unallocated (and therefore unusable) space.
RAID level 0 and RAID level 1 require a minimum of two drives. RAID level 5 requires a minimum of
three drives. RAID level 0+1 requires a minimum of four drives.
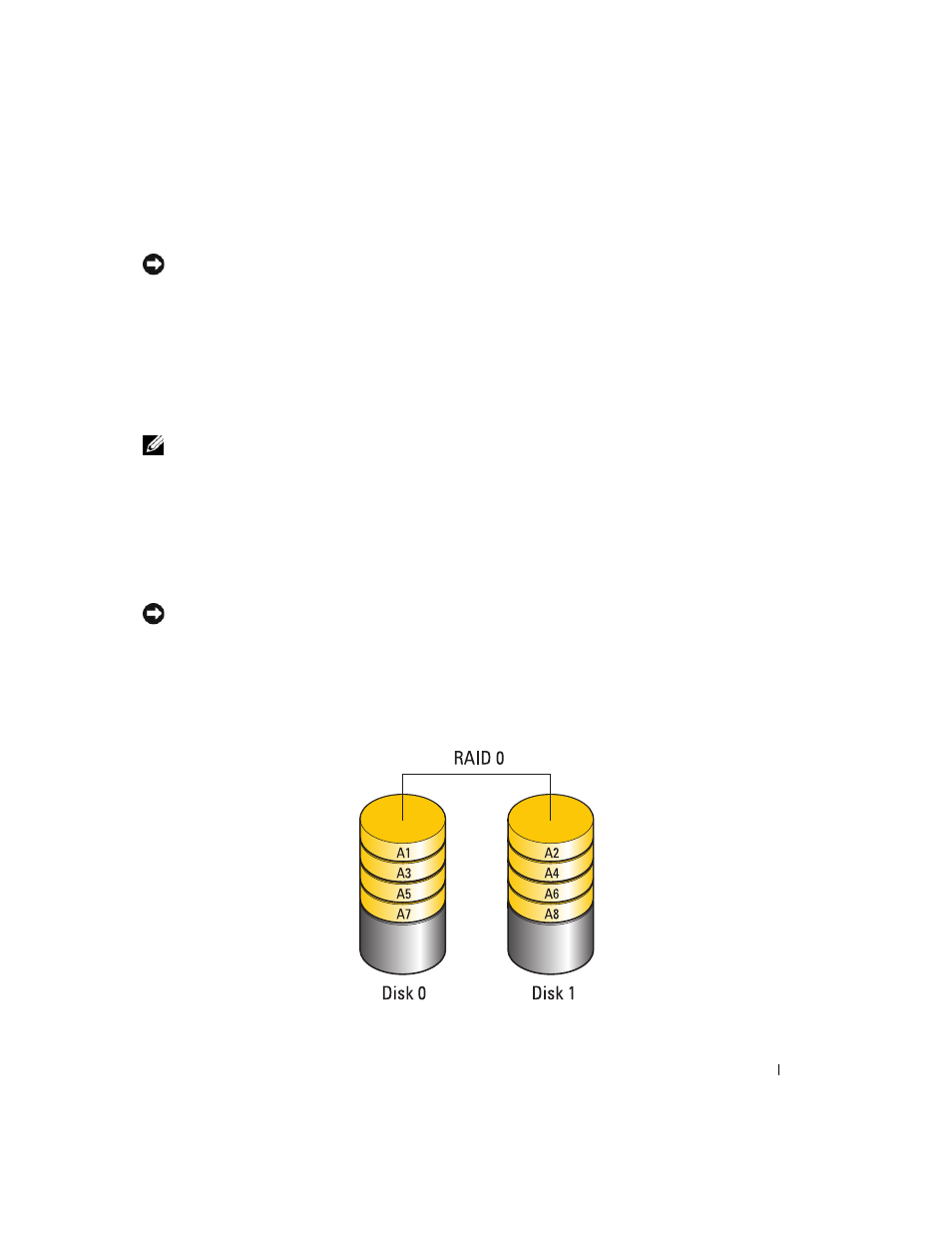
RAID Level 0 Configuration
NOTICE:
Because a RAID level 0 configuration provides no data redundancy, a failure of one drive results in the
loss of all data. To protect your data when using a RAID level 0 configuration, perform regular backups.
RAID level 0 uses a storage technique known as "data striping" to provide a high data access rate. Data
striping is a method of writing consecutive segments, or stripes, of data sequentially across the physical
drive(s) to create a large virtual drive. Data striping allows one of the drives to read data while the other
drive is searching for and reading the next block.
