Dell PowerVault MD1120 User Manual
Page 27
A REFERENCE GUIDE FOR OPTIMIZING DELL™ POWERVAULT™ MD1XXX FAMILY SAS SOLUTION
VER A02
PAGE 27
6/16/2008
7. Storage Applications and Components
Identify customer usage model and needs
In order to select the correct storage solution, it is important to understand the application and user
requirements. A good starting point is to use the following basic storage profiling considerations.
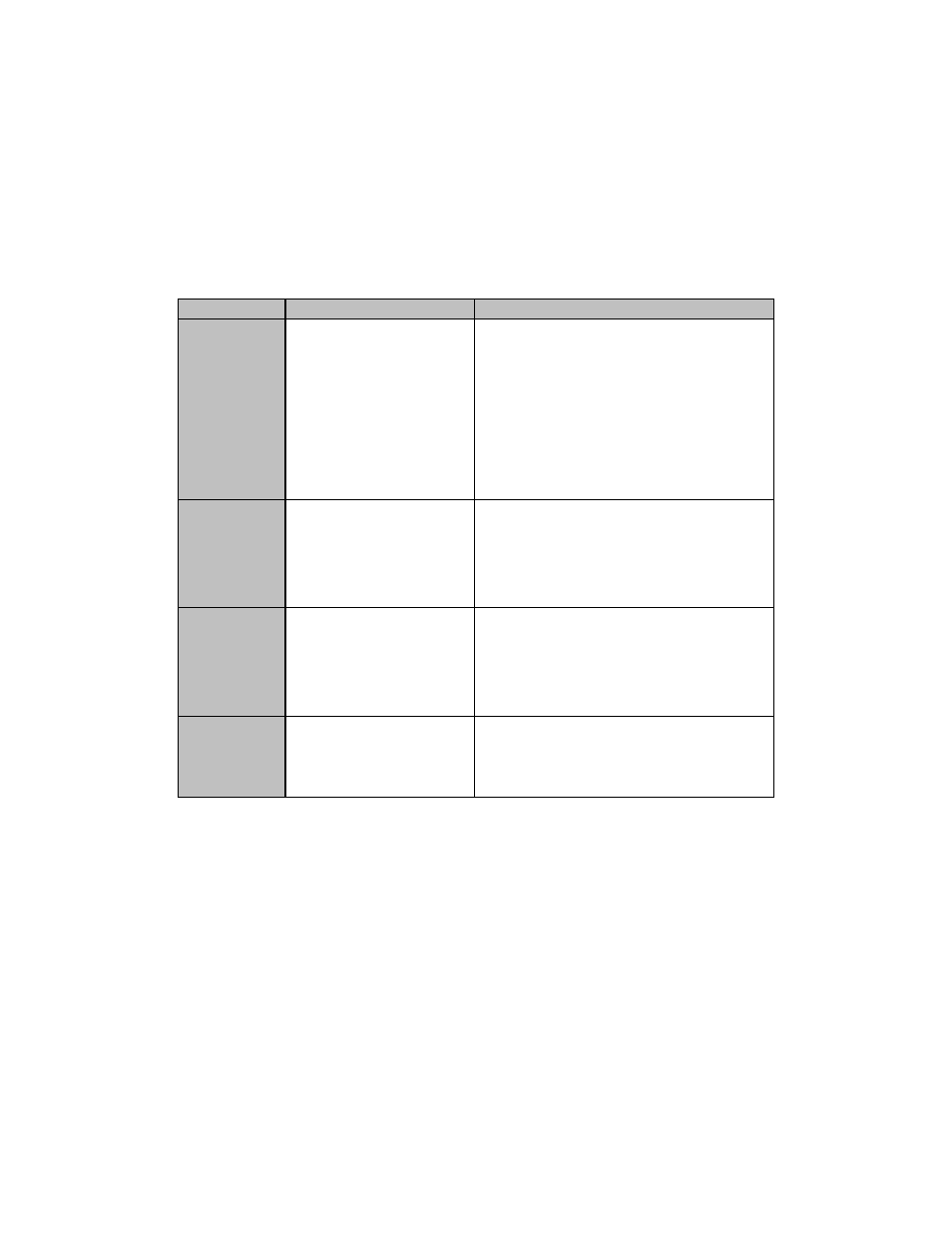
Table 5: Storage Profiling Considerations
Characteristic Values
Description
Performance
• Throughput (MB per
sec.)
• I/O per Second (IOps)
• I/O size (KB/MB)
• I/O Profile (read/write
and random/sequential
access mix)
• Latency
Performance is the overall ability of the
solution to read and write data to the disk.
The performance requirements are usually
determined by the type of application that is
used. Different applications have different
performance requirements. For example, a
database or e-mail server has mostly
random disk access operations while a
streaming media server would have mostly
sequential disk access.
Storage
Capacity
Needs
Gigabytes (GB)
Terabytes (TB)
Storage capacity is the amount of storage
space required by the application and user
data. For example, e-mail storage for 100
users would require much less storage
capacity than an e-mail store for 1000
users.
Storage
Growth Rate
Percent increase per year
Storage growth is the expected increase in
the amount of the capacity that will be
required as the usage increases. This can
be estimated by forecasting the number of
users or clients expected to access the
application in the future.
Criticality
Low, Medium, High, Very
High
Criticality defines the impact to business
needs if the storage is offline. This
characteristic is important for choosing the
right RAID level.
Picking a solution based on the application profile
One of the most important factors to consider when selecting a storage solution is the type of
application that will be utilizing the storage solution. This defines the overall purpose of the
server/storage solution and will determine what RAID configuration will be optimal for the
application. Table 6 outlines the recommended RAID solution based on the usage of the server.
General RAID Configuration Guidelines
RAID 0
RAID 0 is generally not a recommended solution due to lack of data redundancy and protection.
However, it may be utilized in situations where this is not required and maximum storage capacity
and performance are essential.
