Differences between bios and uefi boot modes, Uefi boot options – Dell POWEREDGE M1000E User Manual
Page 6
Page 4
Differences between BIOS and UEFI Boot Modes
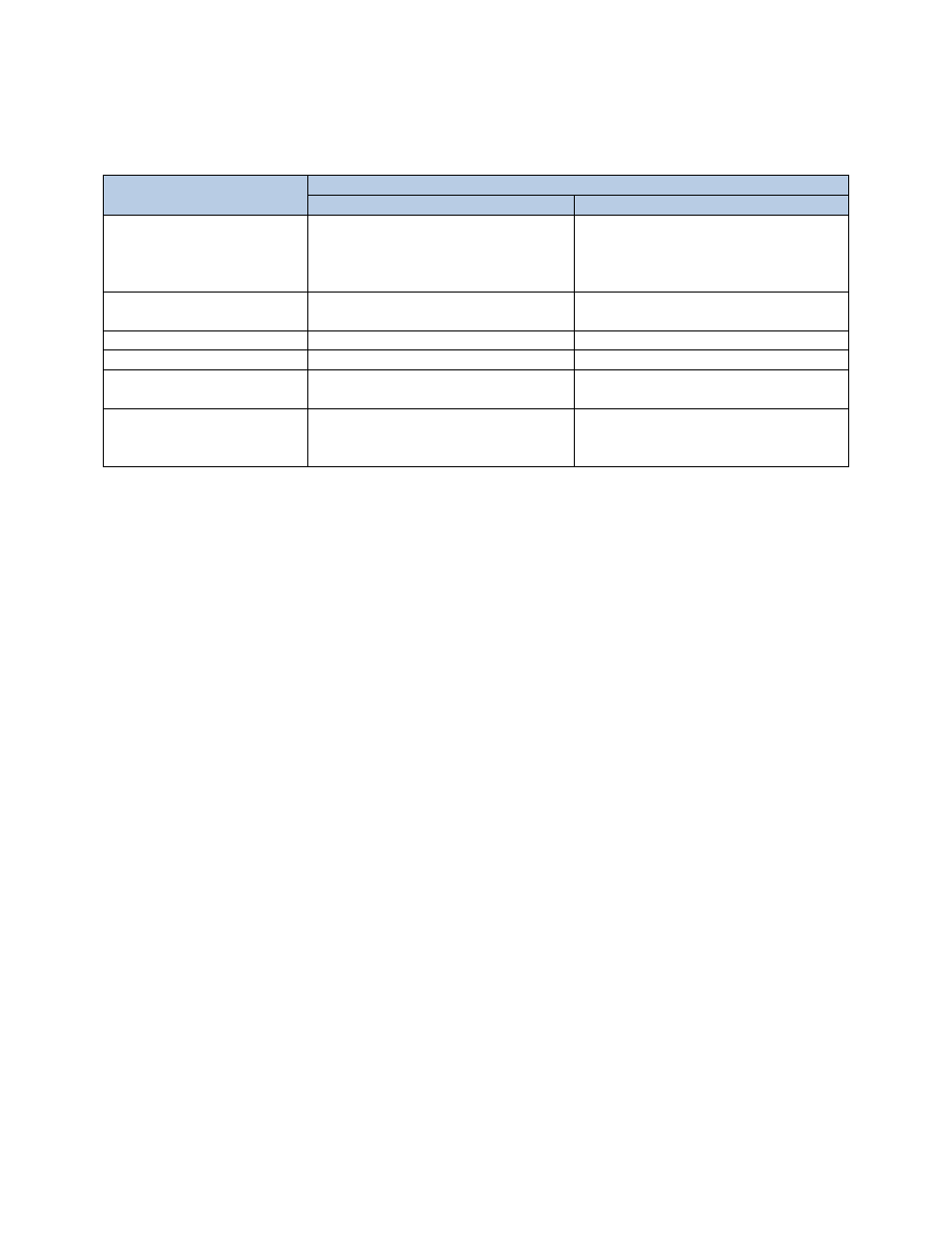
The following table highlights the differences between the boot modes.
Feature
Boot Mode
BIOS
UEFI
Operating System Support
Compatible with operating systems
that do not support UEFI. All the
current and legacy operation systems
can be installed in this boot mode.
Must support UEFI
BIOS POST
Manager Hot Key
Enters BIOS Boot Manager
Enters UEFI Boot Manager
Boot Order Control
Via BIOS Setup Utility
Via UEFI Boot Manager
USB Emulation
Supported via BIOS Setup Utility
Not needed
Default Boot Order
Traditional Dell BIOS default boot
order
None
Boot Options
Legacy BIOS boots to a drive. Support
for multi‐boot drive requires a boot
loader.
In UEFI mode, there is a concept of a
boot file. This allows multiple files to be
added as a boot option on a single drive.
UEFI Boot Options
The way boot options work in UEFI mode differs from that of the legacy BIOS. The UEFI boot option:
• Specifies a file on a drive as a boot target (vs. a drive as in legacy BIOS).
• Is automatically created by the operating system during installation and points to its boot file.
• Provides a predetermined boot path for removable media.
• Can be manually added by the user via the UEFI Boot Manager.
• Points to a specific boot file; hence a system format is not necessary to make a device bootable.
Automatic and Manual Boot Options
In UEFI mode, boot options are automatically added for removable devices. These automatically added boot
options cannot be deleted. Operating System installation automatically adds a boot option that points to the
Operating System Boot loader. Boot options can also be added manually by using the UEFI Boot Manager. Whether
options are added manually or by the operating system, they can be deleted using UEFI Boot Manager.
Multiple boot options per device, or per file, are allowed. You may want to have two boot options for the same
file with different input parameters, such as a debug parameter. When installing a UEFI‐aware operating system,
the installation process will add a corresponding boot option.
Booting to a Removable Media Device
To make a removable device bootable, the UEFI application simply needs to be renamed to BOOTx64.EFI (case
insensitive) and placed in the \EFI\BOOT directory.
When a removable device, such as a USB key, is detected in UEFI Boot Mode, a boot option is automatically added
to point to the following location:
\EFI\BOOT\BOOTx64.EFI
