Humus – LaMotte STH Series User Manual
Page 12
Humus
Humus consists of the complex remains of fresh plant and animal
residue after extensive chemical and biological breakdown.
Humus accounts for 60% to 70% of the total organic carbon in
soils. It can modify the physical properties of a soil, strongly
affecting its chemical and biological properties.
Procedure:
1. Use the plastic soil measure (0819) to add two level measures
of soil to a soil extraction tube (0704).
2. Use the Demineralizer Bottle (1155) to fill the tube to the 14
mL mark with demineralized water. Cap and shake to mix.
3. Use a 0.5 g spoon (0698) to add two level measures of
*Humus Screening Reagent Powder (5119). If necessary, add
more demineralized water to return the level of the liquid to
the 14 mL mark. Cap and shake vigorously for one minute.
4. Add 15 drops of Soil Flocculating Reagent (5643). Cap and
mix gently. Allow to settle for several minutes.
5. Use a piece of filter paper (0465) and a plastic funnel (0459)
to filter the mixture into a second extraction tube. (Fold filter
paper in half and then in half again to form a cone which is
fitted into the funnel.)
6. Compare the clear filtrate in the second extraction tube with
the Humus Color Chart (1384).
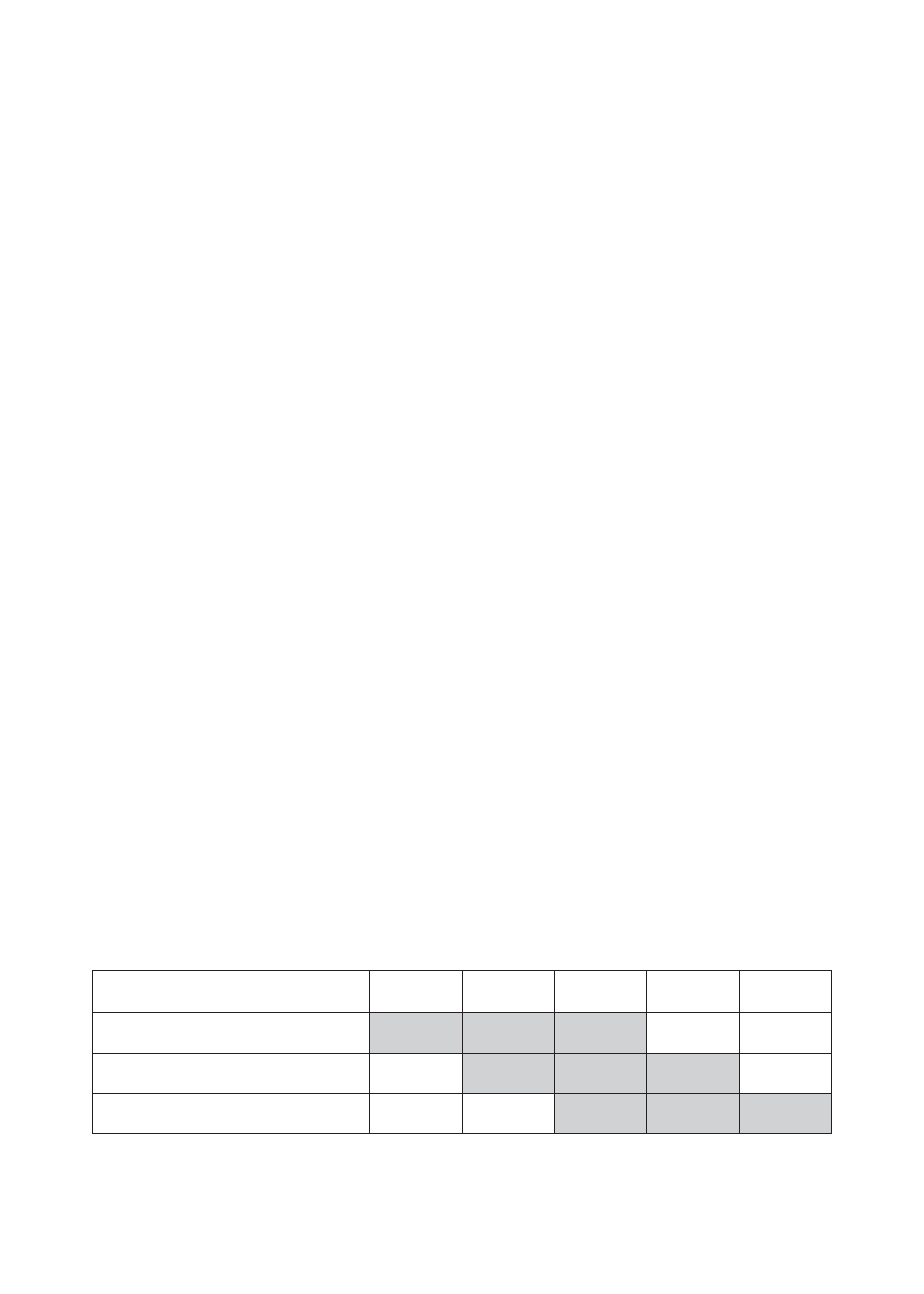
Interpretation
The Humus color comparator is labeled with values of 1, 2, 3, 4,
and 5. The results are interpreted as follows:
Humus or Organic Matter in Soil
Humus Reading
1
2
3
4
5
Agricultural Soils
Low
Medium
High
Garden Greenhouse Soils
Low
Medium
High
Organic Soils
Low
Medium
High
10
