LaMotte ACID RAIN STUDY OUTFIT ARO User Manual
Page 8
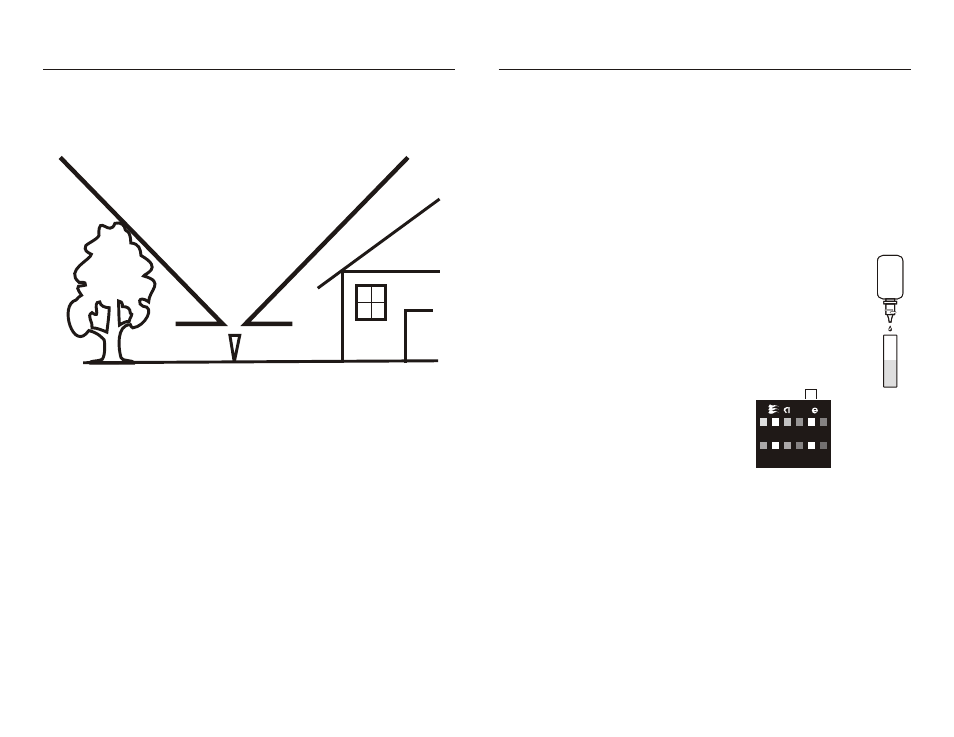
MEA SURING RAIN FALL WITH THE RAIN GAUGE
Place the rain gauge in an open area far enough from buildings, trees, overhead wires
and other obstructions that may cause air turbulence or contamination. Rain falling
on rooftops or trees collects chemicals which will affect the pH. There should be no
obstruction above a 45 degree angle from the top of the rain gauge. In other words,
locate the rain gauge at least 20 feet away from a 20 foot tall obstruction (Fig. 2).
A plastic spike serves as the base for the rain gauge. Select a location for the rain
gauge and push the spike straight into the ground so that the top of the rain gauge is
parallel to the ground. The rain gauge can also be mounted on a post by using the
screws included to fasten the base unit in a vertical position.
Record the amount of rainfall and empty the rain gauge after each rain event before
evaporation occurs. The rain gauge can collect up to 5" of rain. During a very heavy
storm, the rain gauge may be recorded, emptied, and reset. Record the partial
readings and add them to figure the total rainfall for the storm event.
Do not leave the rain gauge outdoors in freezing weather.
8
MEA SURING pH
A pH test indicates whether a substance is acidic, basic, or neutral. Scientists take
pH measurements for water, soil, food, and many other substances. The pH of a
substance can be measured by adding pH indicator solutions to the substance. The
pH indicators are dyes that change color according to the pH of the solution. These
colors are then compared to color standards of a known pH value.
RAIN pH TEST
When a rain storm is expected, carefully clean and thoroughly rinse the rain gauge.
(Dust and other airborne residue inside the rain gauge will affect the pH of the
collected rain.) Rinse the rain gauge and pH kit test tubes with distilled or deionized
water and hang upside-down to dry. Place the rain gauge outdoors in its holder
immediately before the rain begins.
Perform the pH test as soon as possible after the rain has fallen.
PRO CE DURE:
1.
Fill a clean test tube (0230) to the 5 mL line with rain water from
the rain gauge.
2.
Holding the bottle in a vertical position (Fig. 3), add 10 drops of
*Wide Range Indicator (2218). Cap and mix.
3.
Place the test tube in the Wide Range
pH Comparator (2193 or 2196). Match the
color of the sample to the color
standards (Fig. 4). Record the pH value.
4.
If the color observed in your sample is between two colors on the comparator,
the value may be reported to the nearest 0.25 pH unit. If the color produced by
your sample is not in the range of the color standards in the comparator, use the
following chart to estimate the pH of the sample:
pH 7
apple-green
pH 8
green
pH 9
blue-green
pH 10
blue
pH 11
purple
9
L Mott
45°
45°
Fig. 3
Fig. 4
Fig. 2
