Sensor uncertainty – Bird Technologies 5015 Series-Manual User Manual
Page 18
6
Example - If a sensor has a specified accuracy
of 5% of reading + 1.0 uW, then for a 10 mW
signal the uncertainty is ± 0.501 mW. For a 1
mW signal the measurement uncertainty is
± 0.051 mW.
Sensor Uncertainty
While this value is a good estimate, the sensor is actu-
ally more accurate. The sensor’s accuracy also depends
on the temperature, and the power and frequency of
the source; Table 1 lists some examples of uncertainty
factors. If an uncertainty is given as a power, divide
this value by the measured RF power and convert to a
percentage. For example, an uncertainty of ± 0.25 µW
with a RF power of 10 µW is a 2.5% uncertainty.
Table 2 lists external factors, such as using attenua-
tors or using a cable to connect the TPS to the trans-
mitter, which could affect the measurement
uncertainty.
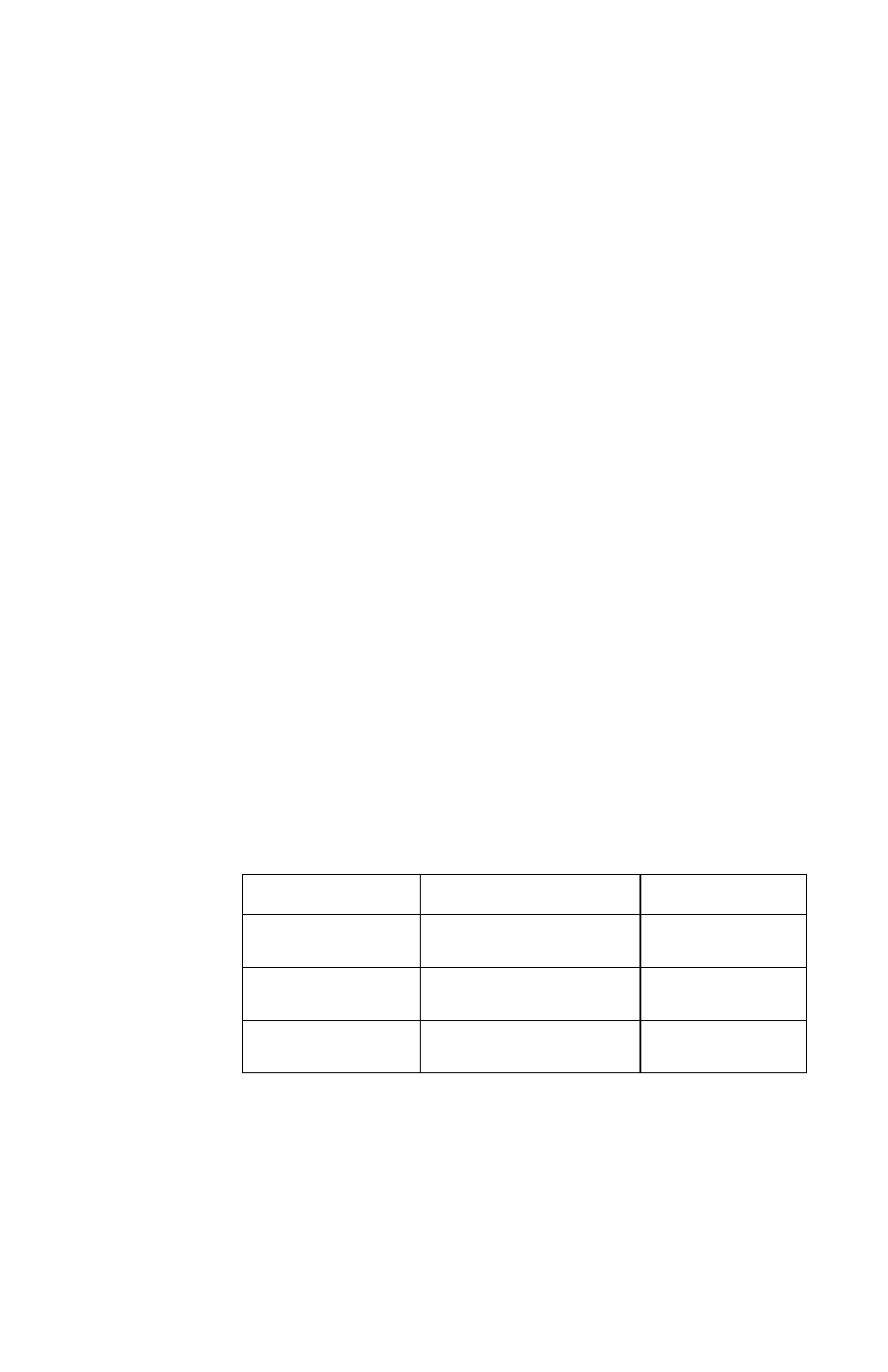
Table 1 - Example Uncertainty Factors
Error Source
Conditions
Uncertainty
Calibration
Uncertainty
± 1.13%
Frequency
Response
40 MHz to 4 GHz
± 3.42%
Temperature
Linearity
–10 to +50 °C
± 3.43%
